La leucemia de células pilosas es una leucemia crónica y rara de las células B caracterizada por la acumulación de pequeños linfocitos B maduros que tienen “proyecciones similares a pelos” visibles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el microscopio. Las células anormales se acumulan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre periférica, médula ósea (causando fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans) y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pulpa roja del bazo, lo que provoca citopenias, como anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, trombocitopenia, neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia y monocitopenia. La leucemia de células pilosas generalmente afecta a hombres de mediana edad y se presenta con debilidad, fatiga, infecciones oportunistas y esplenomegalia (que a menudo es severa). La leucemia de células pilosas se diagnostica mediante la identificación de células pilosas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un frotis de sangre periférica, citopenias características en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hemograma con diferencial, biopsia de médula ósea e inmunofenotipicación. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum observación para pacientes asintomáticos y análogos de purina para pacientes sintomáticos. Tanto la enfermedad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sí como sus tratamientos pueden causar inmunosupresión, por lo que también es importante la prevención y el tratamiento oportuno de las infecciones.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La leucemia de células pilosas es una leucemia crónica de células B rara caracterizada por la acumulación de pequeños linfocitos B maduros que tienen proyecciones similares a pelos visibles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el microscopio.
La leucemia de células pilosas es una neoplasia maligna clonal de células B. Se desconoce la etiología exacta, pero varias exposiciones ambientales parecen aumentar el riesgo de desarrollar leucemia de células pilosas.
El problema subyacente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la leucemia de células pilosas es que la médula ósea produce demasiados linfocitos B, que desplazan a los LOS Neisseria otros tipos de células sanguíneas. Estas células B anormales no pueden proteger al AL Amyloidosis cuerpo de los LOS Neisseria invasores infecciosos de la misma manera que lo hacen las células B normales.
La patogenia no se conoce por completo, pero la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos parecen surgir de células B de memoria activadas tardíamente, que adquieren una mutación activadora del gen BRAF V600E.
El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la identificación de células pilosas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un frotis de sangre periférica, inmunohistoquímica y/o citometría de flujo y, potencialmente, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una biopsia de médula ósea.
Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos de laboratorio pueden incluir:
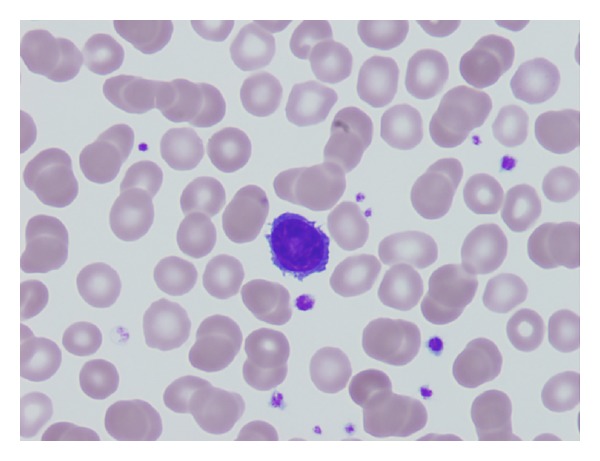
Frotis de sangre periférica que muestra una célula pilosa
Imagen: “Primary hairy cell leukemia/lymphoma of the breast: a case report and review of the literature” por Pilichowska M, Shariftabrizi A, Mukand-Cerro I, Miller K. Licencia: CC BY 3.0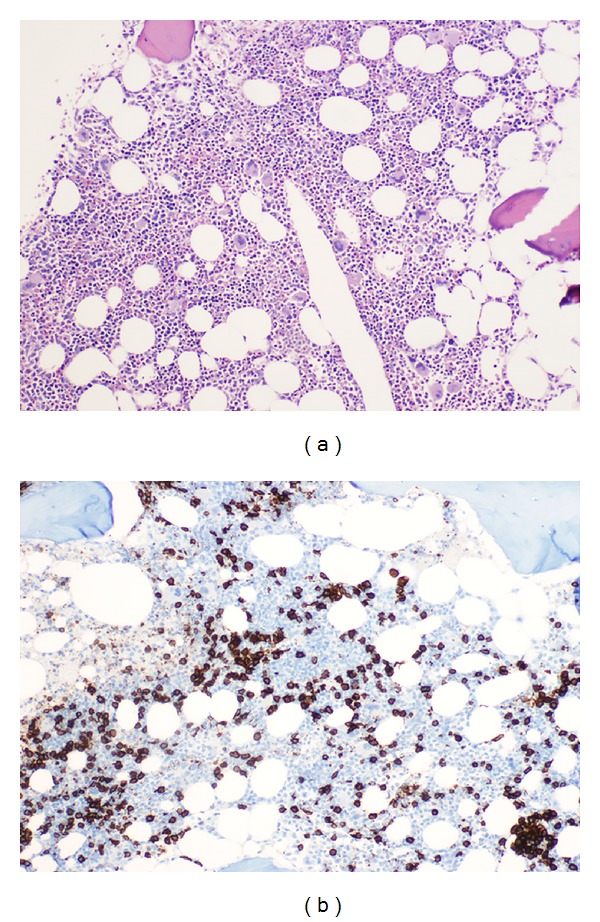
Biopsia de médula ósea:
(a): Infiltrado difuso bastante discreto de linfocitos maduros pequeños (hematoxilina y eosina, ×200).
(b): Tinción de inmunohistoquímica para CD20 que revela la naturaleza de células B del infiltrado (inmunoperoxidasa, ×200).
Los LOS Neisseria pacientes asintomáticos deben ser observados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum lugar de tratados.
El tratamiento está indicado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las siguientes situaciones clínicas: