Las inmunoglobulinas ( Ig Ig X-linked Agammaglobulinemia), también conocidas como anticuerpos, son moléculas de glicoproteínas producidas por las células plasmáticas que actúan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las respuestas inmunitarias al AL Amyloidosis reconocer y unirse a antígenos específicos. Los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos se someten a procesos que mejoran la afinidad por el antígeno y proporcionan una defensa adecuada mediante el cambio de clase. Las diversas clases de Ig Ig X-linked Agammaglobulinemia son IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (la más abundante), IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, IgE IgE An immunoglobulin associated with mast cells. Overexpression has been associated with allergic hypersensitivity. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, IgD IgD An immunoglobulin which accounts for less than 1% of plasma immunoglobulin. It is found on the membrane of many circulating B lymphocytes. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions e IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, que difieren en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sus características biológicas, estructura, especificidad por su objetivo y distribución. Las funciones generales incluyen opsonización, neutralización de la infectividad de los LOS Neisseria patógenos, citotoxicidad y activación del complemento. Las clases específicas tienen mecanismos defensivos únicos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
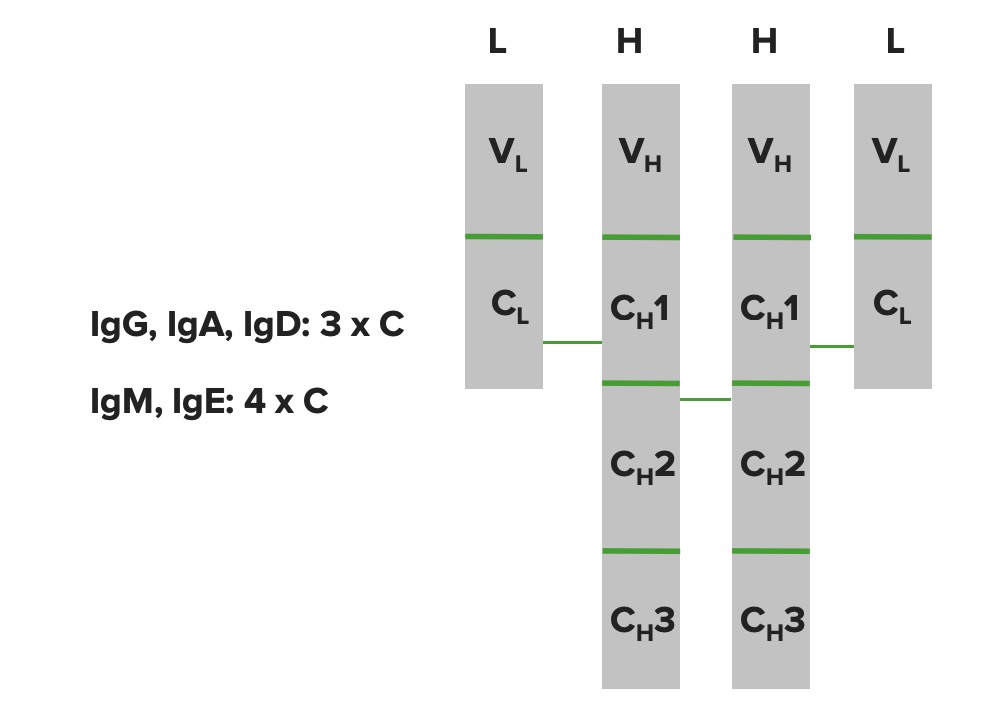
Dominios de una inmunoglobulina:
Las cadenas pesadas y las cadenas ligeras se pliegan en estructuras en forma de dominios. La cadena ligera tiene 1 dominio variable y 1 dominio constante. La cadena pesada tiene 1 dominio variable, pero tiene diferentes dominios constantes dependiendo de la molécula de Ig (IgG, IgA e IgD tienen 3 dominios constantes, mientras que IgM e IgE tienen 4 dominios constantes).
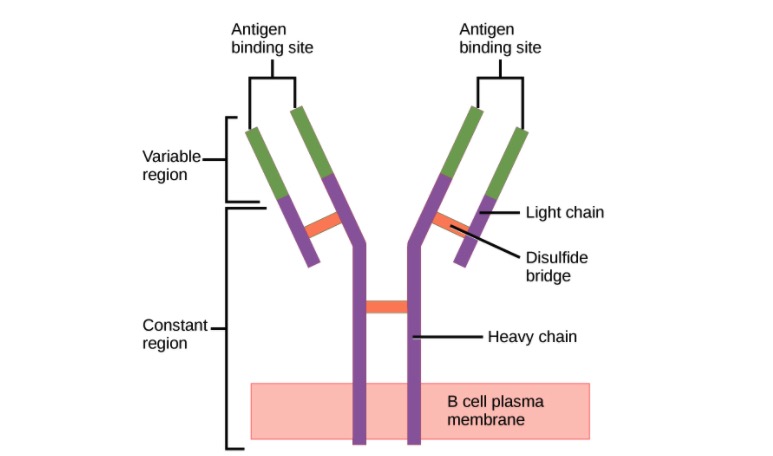
Estructura del anticuerpo (regiones):
El anticuerpo tiene una región variable única (formada por cadenas pesadas y ligeras) capaz de unirse a un antígeno diferente y una región constante (formada por cadenas pesadas).
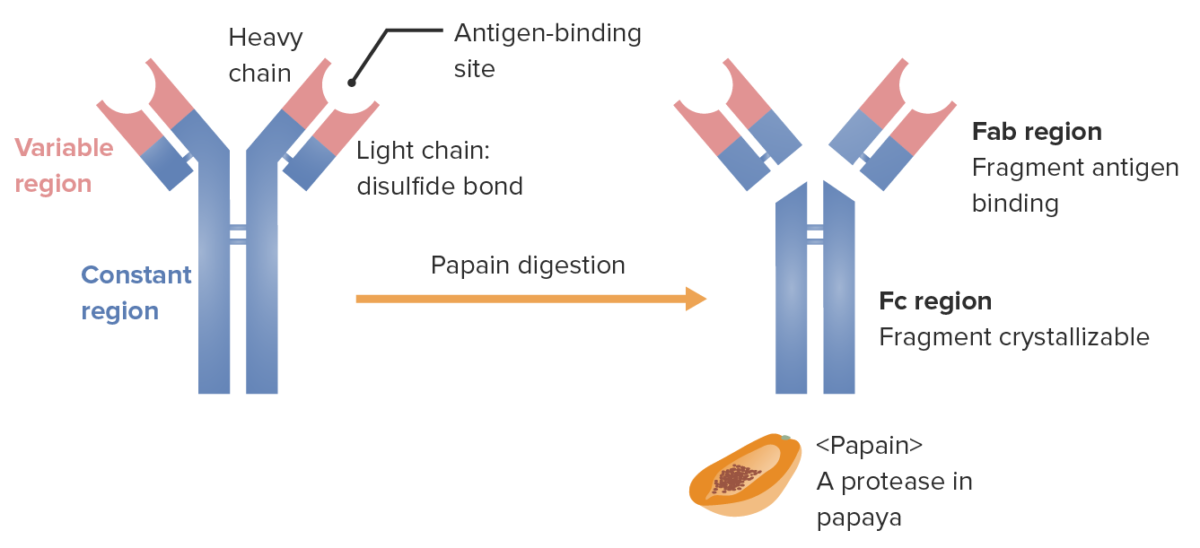
Fragmentos de la Ig (determinados por el lugar donde la enzima papaína divide la Ig):
Fab (fragmento de unión al antígeno) contiene las regiones variables (rojo) y partes de la región constante (azul) de las cadenas pesada y ligera. Fc (fragmento cristalizable) contiene la parte restante (cola) del anticuerpo (región constante de la cadena pesada únicamente).
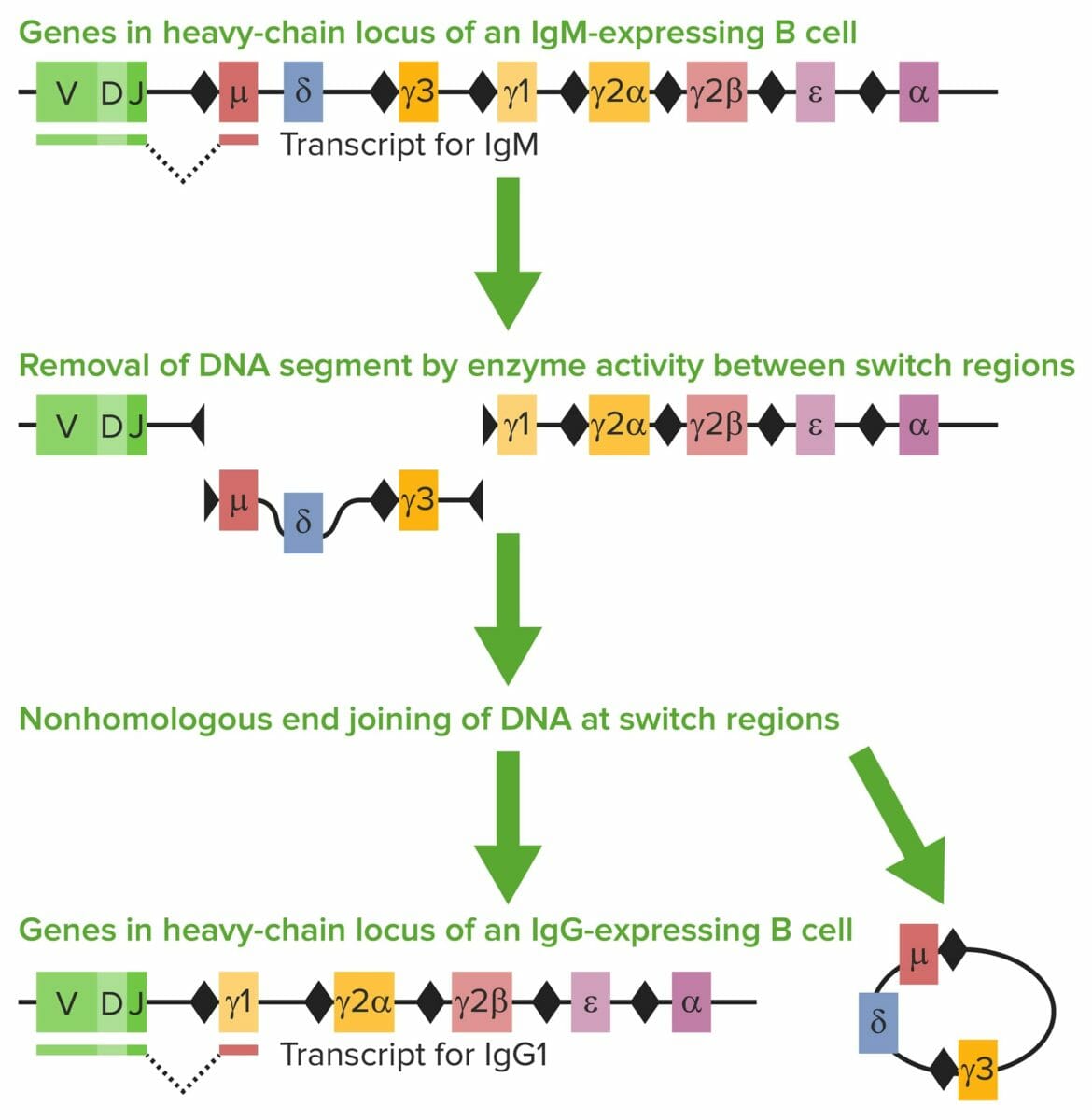
Recombinación de cambio de clase:
La cadena pesada tiene diferentes segmentos génicos: región variable (V), región de diversidad (D), región de acoplamiento (J) y región constante (C).
La región C de la cadena pesada determina la clase/isotipo de Ig. Cuando se encuentran antígenos, los linfocitos B maduros IgM-positivos se someten a recombinación de cambio de clase. Se escinden los exones que codifican el segmento del gen codificante constante (Cμ) de la IgH. Están presentes áreas repetitivas de ADN llamadas regiones de cambio (rombos negros).
Las regiones de cambio guían enzimas (e.g., desaminasa de citidina inducida por activación) en cuanto a dónde crear rupturas de doble cadena de ADN y dónde se une el segmento VDJ y la nueva región constante mediante una enzima reparadora. El Cμ se reemplaza con un nuevo segmento de gen constante (e.g., Cγ, Cε o Cα). En la imagen, Cγ1 se une al segmento VDJ, creando IgG1.
Los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos que se crean tienen propiedades importantes (diversidad y especificidad) que son esenciales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la respuesta inmune.
Los LOS Neisseria mecanismos únicos que crean diversidad de anticuerpos incluyen:
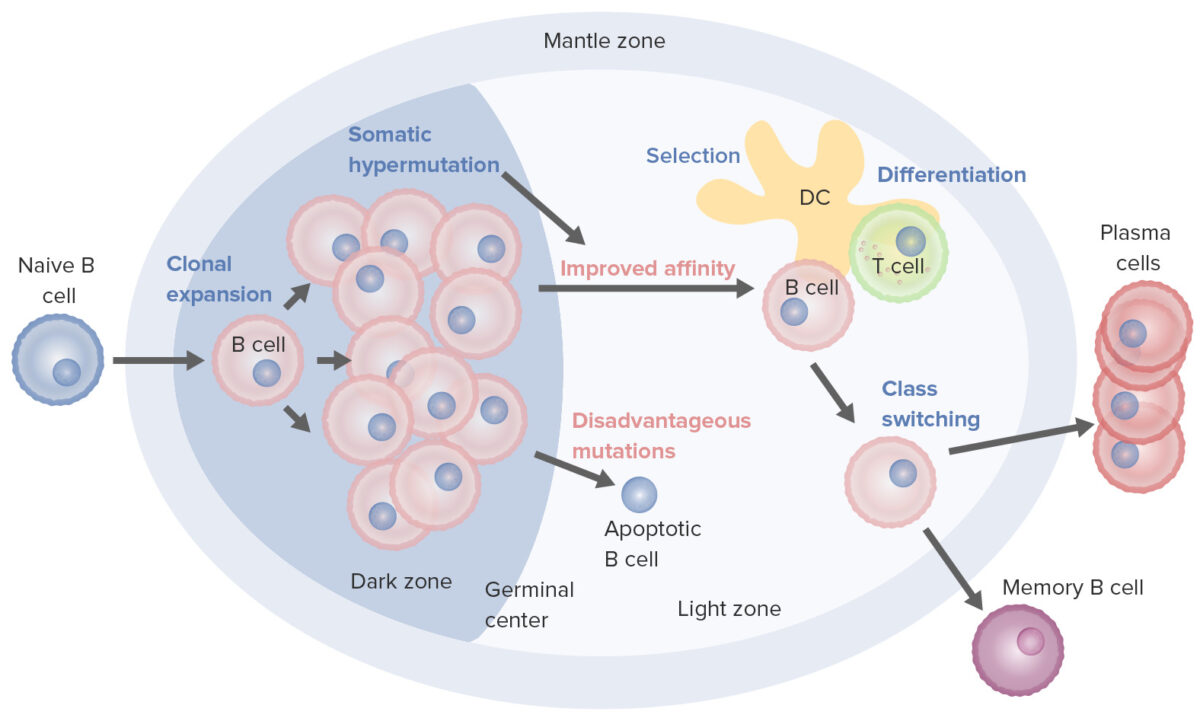
Procesos de activación y maduración de los linfocitos B que tienen lugar en el centro germinal:
Al activarse, el linfocito B se mueve desde la zona del manto y entra al centro germinal. Tiene lugar la proliferación de linfocitos B (expansión clonal) y la afinidad del anticuerpo por el antígeno aumenta a través del proceso de hipermutación somática. Los ciclos repetidos de proliferación e hipermutación afinan el receptor de linfocito B. Sin embargo, no todos los linfocitos B continúan diferenciándose, especialmente si la afinidad es débil. La apoptosis ocurre si la unión antígeno-anticuerpo no está optimizada. Los linfocitos B con fuerte afinidad sobreviven (selección), con la ayuda de las señales de supervivencia de las células dendríticas foliculares y los linfocitos T. Estos linfocitos B seleccionados pasan al cambio de clase y la diferenciación en células plasmáticas o células de memoria.
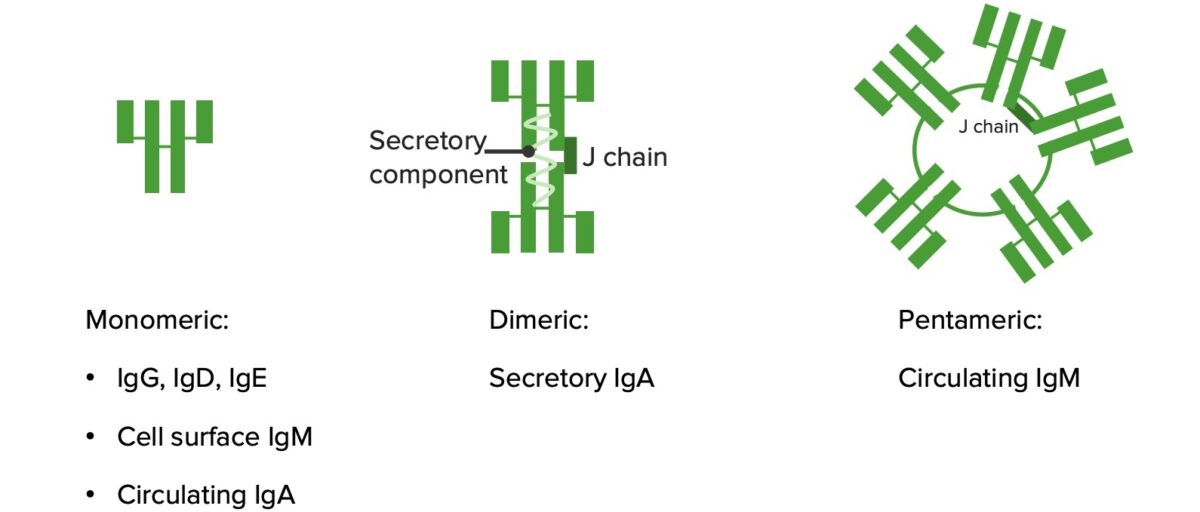
Monómeros y polímeros:
IgG, IgD e IgE son monómeros (estructura ilustrada en la imagen de la izquierda). IgA se convierte en un dímero en las secreciones mucosas. IgM forma un pentámero.
Imagen por Lecturio.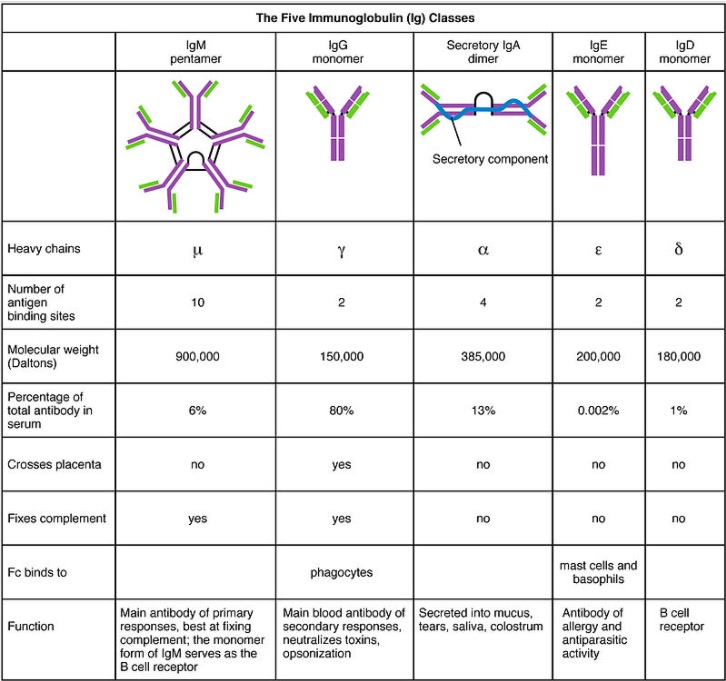
Las 5 clases de Ig, sus estructuras y sus características
Imagen: “Five immunoglobulin classes” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0