Los inmunoensayos son técnicas basadas en placas que pueden detectar y cuantificar muchos tipos de moléculas a través de reacciones anticuerpo-antígeno. Un inmunoensayo generalmente involucra un analito, un anticuerpo específico y marcadores. La clasificación de los inmunoensayos se basa en el tipo de marcador utilizado, que incluye enzimas (ELISA, por sus siglas en inglés), moléculas/trazadores emisores de luz (e.g., inmunoensayos de quimioluminiscencia y fluorescencia) e isótopos radiactivos (radioinmunoensayos). Estos inmunoensayos especializados son relativamente sensibles, específicos, económicos y rápidos, y se usan ampliamente en un entorno clínico. Los inmunoensayos se utilizan en el diagnóstico de enfermedades infecciosas, la identificación de marcadores tumorales, las pruebas de alergia y el control de los niveles de medicamentos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria inmunoensayos son técnicas de ensayo basadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum placas diseñadas para detectar y cuantificar péptidos, proteínas, anticuerpos y hormonas. El elemento más crucial de la estrategia de detección es una reacción antígeno-anticuerpo altamente específica.
El tipo de marcador define el inmunoensayo que se está realizando:
Hay 4 tipos principales de ELISA ELISA An immunoassay utilizing an antibody labeled with an enzyme marker such as horseradish peroxidase. While either the enzyme or the antibody is bound to an immunosorbent substrate, they both retain their biologic activity; the change in enzyme activity as a result of the enzyme-antibody-antigen reaction is proportional to the concentration of the antigen and can be measured spectrophotometrically or with the naked eye. Many variations of the method have been developed. St. Louis Encephalitis Virus, que son variaciones del proceso general de inmunoensayo:
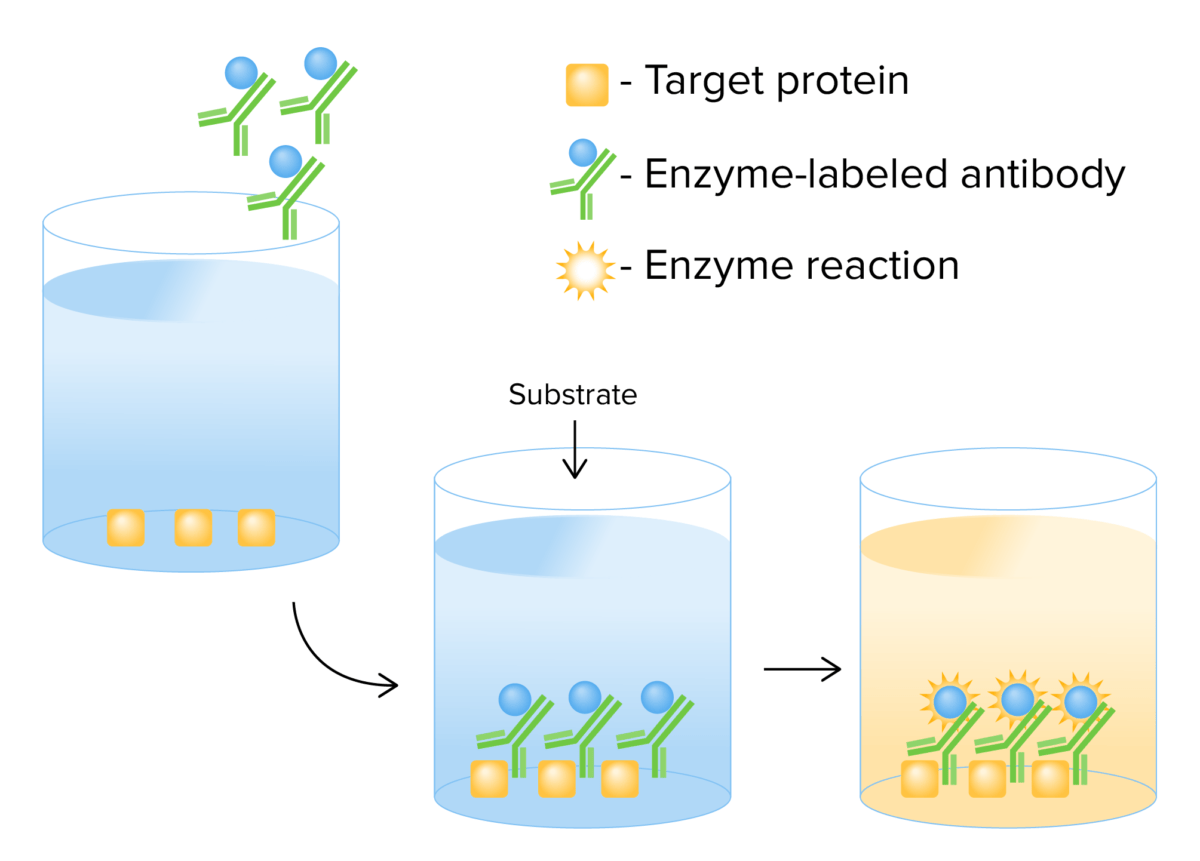
Mecanismo de ELISA directo: Se agrega un antígeno objetivo a una placa junto con anticuerpos marcados con enzimas específicos para ese antígeno. Después de la incubación, el exceso de anticuerpos no unidos se elimina mediante lavado y se agrega un sustrato. En presencia del marcador enzimático, se produce una reacción que da como resultado un cambio de color.
Imagen por Lecturio.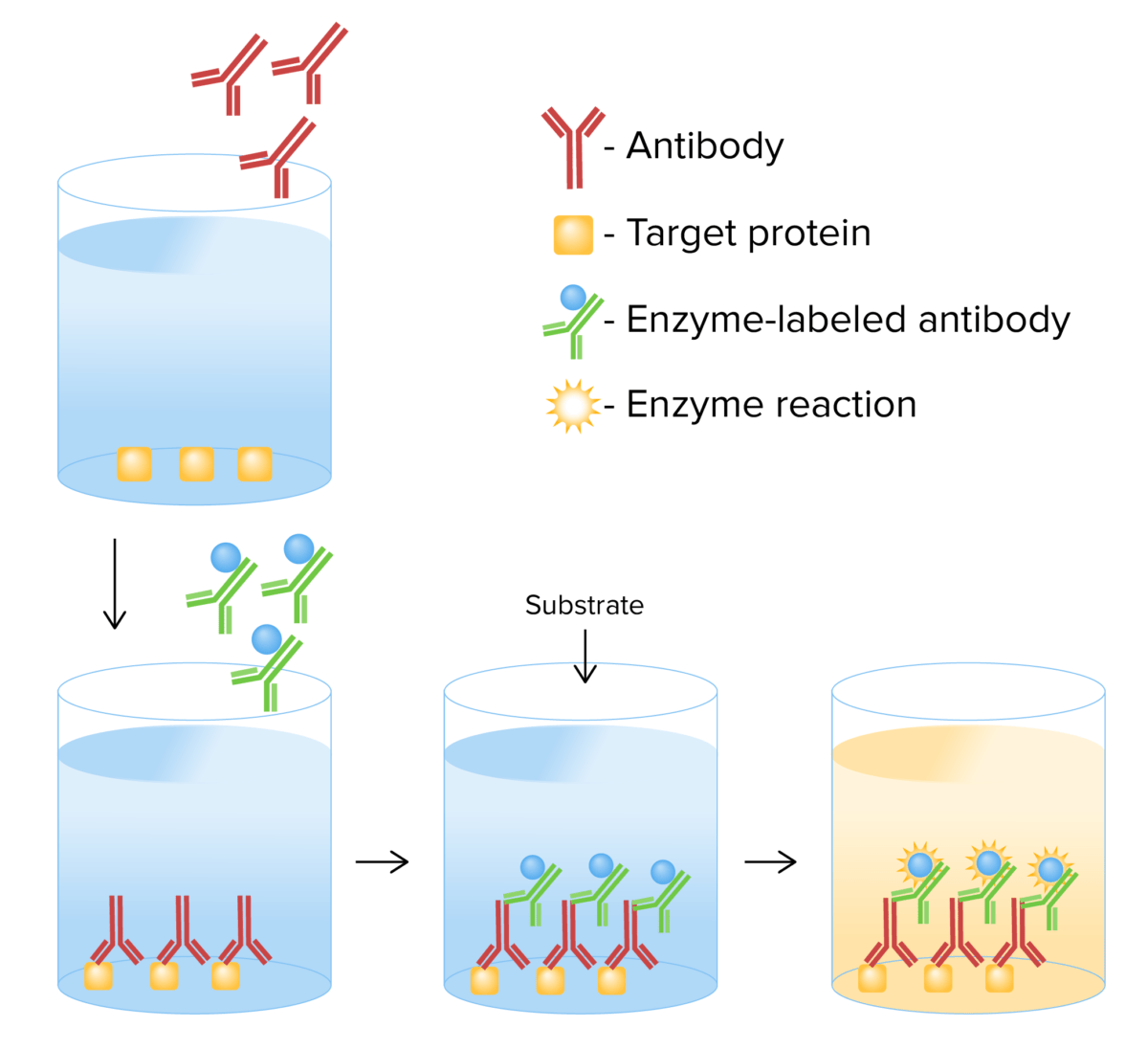
Mecanismo de ELISA indirecto: Se agrega un antígeno diana a una placa recubierta con anticuerpos primarios. Después de la incubación se forma un complejo antígeno-anticuerpo. El exceso de anticuerpo se elimina mediante lavado y se agregan anticuerpos secundarios marcados con enzimas, que se unen al complejo anticuerpo-antígeno. El exceso de anticuerpos se elimina por lavado y se añade el sustrato. La presencia del marcador enzimático da como resultado un cambio de color.
Imagen por Lecturio.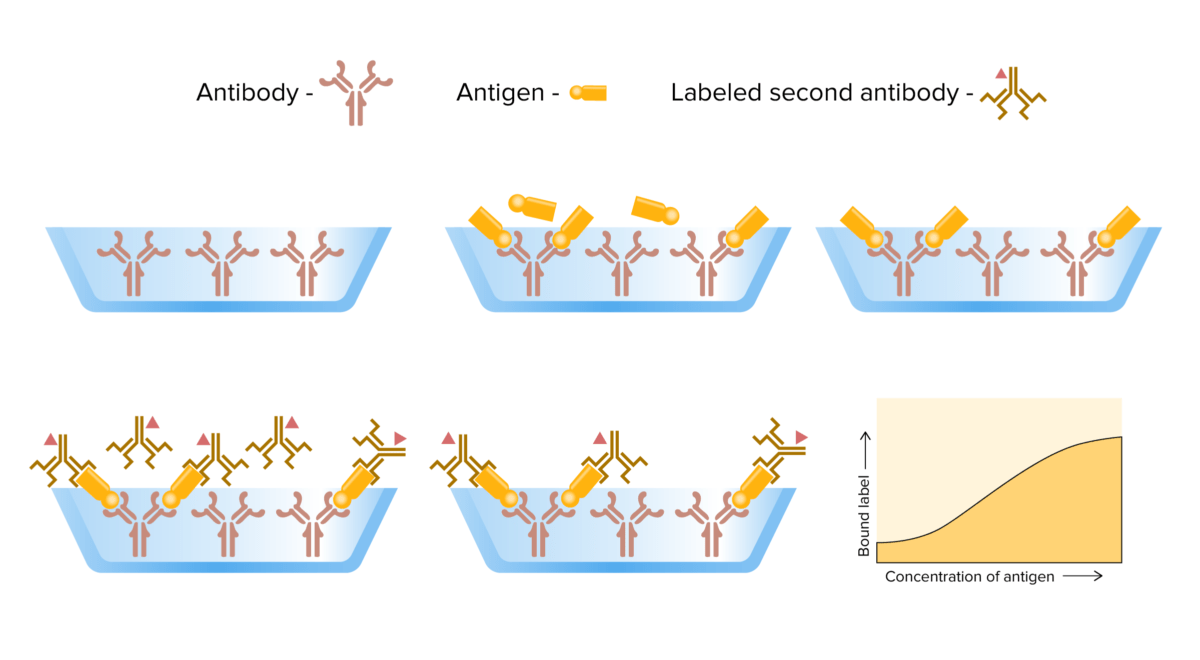
Mecanismo de inmunoensayo sándwich:
De izquierda a derecha: el antígeno del analito se agrega a una placa recubierta de anticuerpos. Los antígenos no unidos se eliminan mediante lavado y se agregan anticuerpos secundarios marcados con enzimas, que se unen a los antígenos. El exceso de anticuerpos marcados no unidos se elimina mediante lavado. Se añade el sustrato y se detecta/mide el cambio de color resultante.
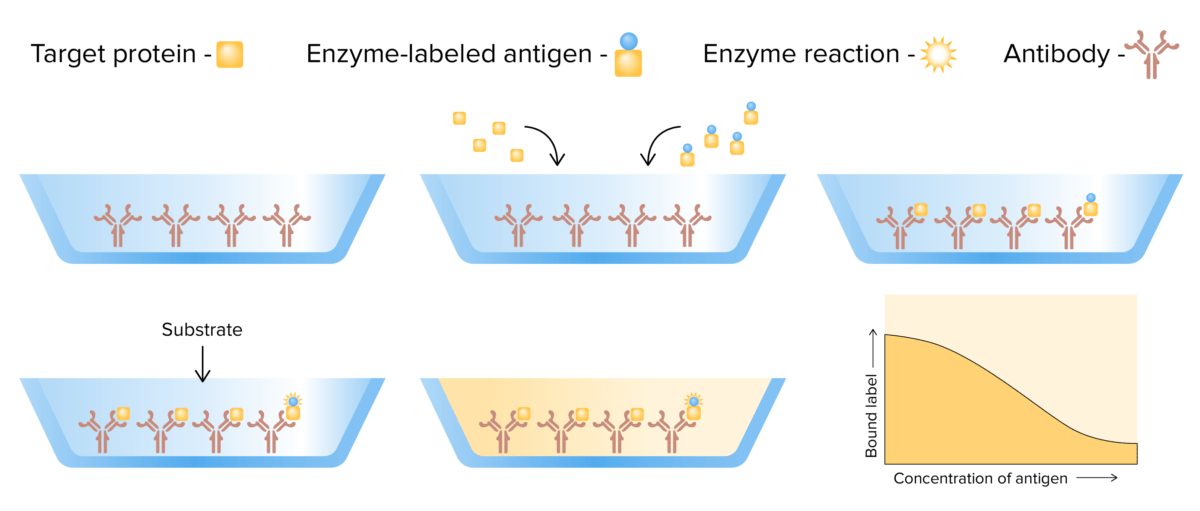
Mecanismo de ELISA competitivo:
De izquierda a derecha: se agregan un antígeno objetivo y un antígeno marcado con enzima a una placa recubierta de anticuerpos. Los antígenos compiten por unirse a los anticuerpos. A continuación, se añade un sustrato y se detecta/mide el cambio de color subsiguiente. A diferencia de otras formas de inmunoensayos, menos cambio de color indica una mayor concentración del antígeno objetivo (ya que no contiene el marcador enzimático).
Los LOS Neisseria inmunoensayos tienen una amplia gama de aplicaciones clínicas. Los LOS Neisseria ejemplos enumerados a continuación no son todos ellos.
Los LOS Neisseria inmunoensayos se pueden utilizar para identificar directamente microorganismos (basados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum antígenos o toxinas) o evaluar indirectamente los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos contra el agente infeccioso. Algunos ejemplos son:
Pueden utilizarse inmunoensayos para detectar marcadores tumorales. Ejemplos incluyen:
Los LOS Neisseria inmunoensayos se pueden utilizar para detectar anticuerpos IgE IgE An immunoglobulin associated with mast cells. Overexpression has been associated with allergic hypersensitivity. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions contra alérgenos específicos:
La monitorización de medicamentos terapéuticos es una aplicación importante de los LOS Neisseria inmunoensayos. Los LOS Neisseria ejemplos incluyen el control de los LOS Neisseria niveles de medicamentos de:
Las pruebas de laboratorio adicionales donde se pueden utilizar inmunoensayos incluyen:
Las ventajas dependen del tipo de inmunoensayo utilizado; sin embargo, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, son: