La hiperpotasemia se define como una concentración sérica de potasio (K+) > 5,2 mEq/L. Los LOS Neisseria mecanismos homeostáticos mantienen la concentración sérica de K+ entre 3,5 y 5,2 mEq/L, a pesar de la marcada variación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la ingesta dietética. La hiperpotasemia puede deberse a una variedad de causas, que incluyen cambios transcelulares, destrucción de tejidos, excreción renal inadecuada y medicamentos. La hiperpotasemia leve suele ser asintomática; sin embargo, las elevaciones agudas o la hiperpotasemia grave pueden provocar arritmias cardíacas potencialmente mortales. El tratamiento se guía por la gravedad e incluye medidas para estabilizar el potencial de la membrana miocárdica, desplazar el K+ al AL Amyloidosis espacio intracelular transitoriamente, eliminar el K+ del cuerpo y tratar las condiciones predisponentes subyacentes.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El K+ es el principal catión intracelular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todas las células y se distribuye de manera desigual entre el líquido intracelular (98%) y el líquido extracelular (2%).
Una dieta occidental normal contiene aproximadamente 70–150 mmol de K+ por día. Es poco probable que esta dieta conduzca al AL Amyloidosis desarrollo de hiperpotasemia solo por el aumento de la ingesta, debido a los LOS Neisseria siguientes mecanismos:
Las etiologías de la hiperpotasemia se pueden agrupar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 5 categorías: cambios transcelulares, destrucción de tejidos, excreción renal inadecuada, inducida por medicamentos y pseudohiperpotasemia.

Desplazamiento transcelular de K+:
Desplazamiento extracelular de K+:
1. La acidosis (aumento de H+) provoca el bloqueo del intercambiador Na+/H+, lo que provoca una disminución del Na+ intracelular, bloqueando a su vez la Na+/K+ ATPasa. Por otro lado, la acidosis activa el intercambiador H+/K+. Ambos provocan un aumento del K+ extracelular.
2. El aumento de la osmolaridad en el espacio extracelular (hiperglucemia, contraste intravenoso, manitol) desplaza el agua fuera de la célula, disminuyendo la concentración de K+. El aumento del gradiente provoca la difusión del K+ al exterior.
Desplazamiento intracelular de K+:
1. La alcalosis (disminución del H+) provoca la activación del intercambiador Na+/H+, lo que provoca un aumento del Na+ intracelular, activando a su vez la Na+/K+ ATPasa. Por otro lado, la alcalosis bloquea el intercambiador H+/K+. Ambos provocan una disminución del K+ extracelular.
2. La insulina y los agonistas β2 adrenérgicos activan la Na+/K+ ATPasa, disminuyendo la concentración plasmática de K+.
Insuficiencia renal:
Depleción de volumen:
Hipoaldosteronismo funcional:
Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos son una causa muy común de hiperpotasemia y la provocan una variedad de los LOS Neisseria mecanismos mencionados anteriormente. Una parte clave del diagnóstico de hiperpotasemia es revisar todos los LOS Neisseria fármacos y medicamentos recientes que ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia recibido un paciente.
| Clases de medicamentos (ejemplos) | Mecanismo |
|---|---|
| IECA (e.g., lisinopril Lisinopril One of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), orally active, that has been used in the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors, captopril Captopril A potent and specific inhibitor of peptidyl-dipeptidase a. It blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a vasoconstrictor and important regulator of arterial blood pressure. Captopril acts to suppress the renin-angiotensin system and inhibits pressure responses to exogenous angiotensin. Hypertension Drugs) | Inhiben la formación de angiotensina II → disminuyen la secreción de aldosterona → disminuyen la secreción renal de K+ |
| ARA (e.g., losartán, valsartán) | Bloquean el receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de angiotensina → ↓ secreción de aldosterona → ↓ secreción renal de K+ |
| Inhibidores directos de la renina (e.g., aliskiren Aliskiren Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors) | Impiden que la renina convierta el angiotensinógeno en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum angiotensina l → disminuyen la secreción de aldosterona → ↓ excreción renal de K+ |
| Diuréticos ahorradores de K+ (e.g., amilorida, triamtereno, espironolactona) | Bloquean el canal de sodio epitelial ( ENaC ENaC Sodium channels found on salt-reabsorbing epithelial cells that line the distal nephron; the distal colon; salivary ducts; sweat glands; and the lung. They are amiloride-sensitive and play a critical role in the control of sodium balance, blood volume, and blood pressure. Liddle Syndrome, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) (amilorida, triamtereno) o el receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de aldosterona (espironolactona, eplerenona) → ↓ excreción renal de K+ |
| Glucósidos cardíacos (digoxina) | Inhiben la bomba Na+/K+ ATPasa → se mueve menos K+ a las células |
| AINE (e.g., ibuprofeno) | Disminuyen renina y aldosterona → ↓ secreción renal de K+ |
| Inhibidores de la calcineurina (e.g., ciclosporina, tacrolimus Tacrolimus A macrolide isolated from the culture broth of a strain of streptomyces tsukubaensis that has strong immunosuppressive activity in vivo and prevents the activation of T-lymphocytes in response to antigenic or mitogenic stimulation in vitro. Immunosuppressants) | Multifactorial/comprendido de forma incompleta: ↓ liberación de aldosterona, ↓ sensibilidad a la aldosterona, inhibición de la bomba Na+/K+ ATPasa, bloqueo del canal ENaC ENaC Sodium channels found on salt-reabsorbing epithelial cells that line the distal nephron; the distal colon; salivary ducts; sweat glands; and the lung. They are amiloride-sensitive and play a critical role in the control of sodium balance, blood volume, and blood pressure. Liddle Syndrome |
| Succinilcolina | Provoca fuga extracelular de K+ a través de canales activados por receptores de acetilcolina |
| Antimicrobianos (e.g., trimetoprima, pentamidina) | Bloquean el canal ENaC ENaC Sodium channels found on salt-reabsorbing epithelial cells that line the distal nephron; the distal colon; salivary ducts; sweat glands; and the lung. They are amiloride-sensitive and play a critical role in the control of sodium balance, blood volume, and blood pressure. Liddle Syndrome |
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas más graves de la hiperpotasemia son la alteración de la conducción eléctrica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el corazón. Es más probable que los LOS Neisseria síntomas cardíacos ocurran con el aumento de la gravedad y la agudeza de la hiperpotasemia; sin embargo, incluso la hiperpotasemia relativamente grave puede ser asintomática. Se pueden observar síntomas musculares, y estos incluyen debilidad y parálisis.
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas cardíacos son los LOS Neisseria síntomas más importantes de la hiperpotasemia, ya que pueden ser rápidamente fatales.
Algunos pacientes no tendrán cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ni arritmias, incluso con hiperpotasemia grave.
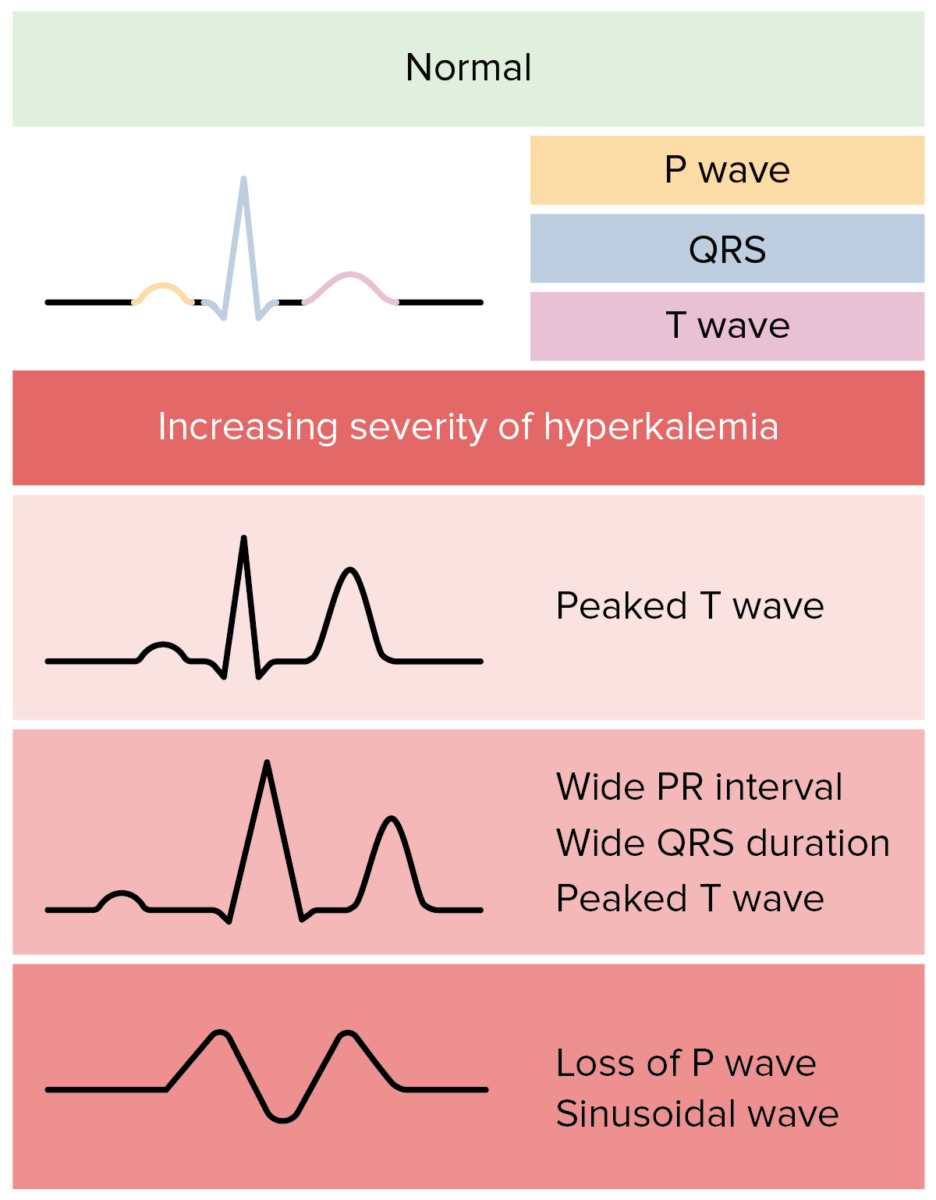
Cambios en el ECG en la hiperpotasemia:
En realidad, los cambios del ECG en la hiperpotasemia son más variables y menos predecibles.
El tratamiento de la hiperpotasemia a menudo tiene prioridad sobre el diagnóstico debido a la posibilidad de arritmias potencialmente mortales y se guía por la determinación del nivel de urgencia necesario para el tratamiento. Por lo general, la etiología de la hiperpotasemia no es difícil de determinar y no se ve VE Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing impedida por tratarla primero.
| Meta | Intervención | Propiedades/indicación |
|---|---|---|
| Estabilizar el miocardio | Calcio intravenoso |
|
| Ingresar el K+ a la célula | Insulina |
|
| Bicarbonato de sodio (NaHCO3) |
|
|
| Agonista β2 |
|
|
| Aumentar la excreción de K+ del cuerpo | A través de la orina |
|
| A través del tracto gastrointestinal | Resinas de intercambio catiónico: unen K+ a cambio de Na+ o Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ | |
| Diálisis |
|