La hipernatremia es una concentración sérica elevada de sodio > 145 mmol/L. El sodio sérico es el mayor contribuyente a la osmolalidad del plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products, que está muy estrictamente controlada por el hipotálamo a través del mecanismo de la sed y la liberación de la hormona antidiurética (ADH, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). La hipernatremia se produce por la falta de acceso al AL Amyloidosis agua o por una ingesta excesiva de sodio. El volumen total de agua perdido (por lo general a través de las vías gastrointestinal o renal) se recupera a través de la ingesta oral normal. Por lo tanto, si un paciente tiene acceso al AL Amyloidosis agua y un mecanismo de sed intacto, muchas etiologías de la hipernatremia pueden permanecer ocultas. La etiología de la hipernatremia a menudo se determina fácilmente mediante los LOS Neisseria antecedentes clínicos. El tratamiento es principalmente un reemplazo del déficit de agua libre por vía intravenosa u oral.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La regulación del agua está controlada por la interacción entre los LOS Neisseria osmorreceptores en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hipotálamo y la respuesta a la ADH en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria riñones, lo que da como resultado un control muy estricto del sodio sérico y la osmolalidad plasmática.
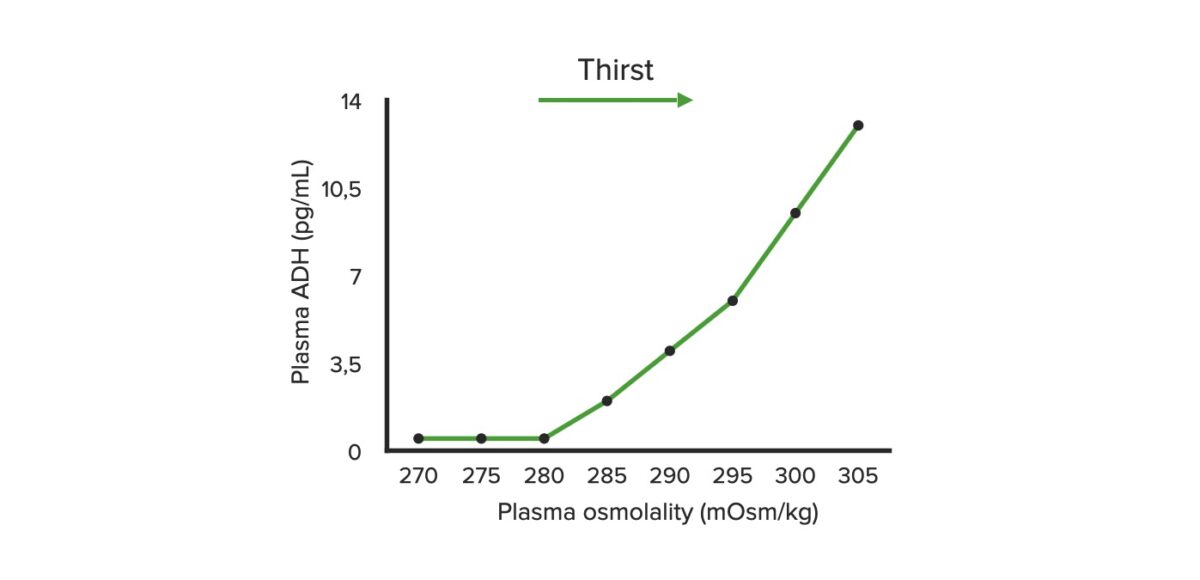
Osmolalidad plasmática y hormona antidiurética (ADH): gráfico que ilustra la relación entre la osmolalidad plasmática y la liberación de ADH
Imagen por Lecturio.Las etiologías de la hipernatremia se clasifican según el estado del volumen.
El principal hallazgo clínico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la hipernatremia es la sed. Si el paciente no puede ingerir suficiente agua para evitar que su sodio sérico aumente significativamente, también pueden ocurrir deshidratación y hallazgos neurológicos. La gravedad de los LOS Neisseria hallazgos neurológicos depende del tiempo de instauración y la magnitud de la hipernatremia.
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos, la etiología de la hipernatremia será clara y el tratamiento puede iniciarse sin más pruebas. Si el diagnóstico no está claro, los LOS Neisseria siguientes pasos pueden ser útiles:
La hipernatremia se trata reemplazando el déficit de agua libre administrando una solución hipotónica (i.e., dextrosa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum agua al AL Amyloidosis 5% intravenosa). El tratamiento es generalmente empírico con monitoreo frecuente del sodio sérico y ajuste de la tasa de administración de líquidos.
Consideraciones sobre el estado del volumen:
Hipernatremia aguda:
Hipernatremia crónica:
Un aumento agudo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la tonicidad da como resultado un movimiento abrupto de líquido fuera del cerebro. Un aumento lento de la tonicidad permite que el cerebro se adapte y minimice el efecto de los LOS Neisseria cambios de líquidos. Una corrección demasiado rápida de la hipernatremia podría resultar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un movimiento abrupto de líquido hacia el cerebro y causar edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema cerebral.