La gastritis Gastritis Gastritis refers to inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Gastritis may occur suddenly (acute gastritis) or slowly over time (chronic gastritis). Gastritis may be asymptomatic or with symptoms, including burning abdominal pain (which either worsens or improves with eating), dyspepsia, nausea, and vomiting. Gastritis es la inflamación de la mucosa gástrica y puede clasificarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función del tiempo de evolución (aguda o crónica), las características histológicas y la etiología. Las causas predominantes son la infección por Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter y el consumo de aspirina y AINES. La gastritis Gastritis Gastritis refers to inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Gastritis may occur suddenly (acute gastritis) or slowly over time (chronic gastritis). Gastritis may be asymptomatic or with symptoms, including burning abdominal pain (which either worsens or improves with eating), dyspepsia, nausea, and vomiting. Gastritis crónica (metaplásica) puede deberse a causas autoinmunes o ambientales y es un factor de riesgo de cáncer gástrico. Las personas con gastritis Gastritis Gastritis refers to inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Gastritis may occur suddenly (acute gastritis) or slowly over time (chronic gastritis). Gastritis may be asymptomatic or with symptoms, including burning abdominal pain (which either worsens or improves with eating), dyspepsia, nausea, and vomiting. Gastritis pueden ser asintomáticas o presentar dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, dispepsia y náuseas. El tratamiento de la gastritis Gastritis Gastritis refers to inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Gastritis may occur suddenly (acute gastritis) or slowly over time (chronic gastritis). Gastritis may be asymptomatic or with symptoms, including burning abdominal pain (which either worsens or improves with eating), dyspepsia, nausea, and vomiting. Gastritis aguda y crónica debida a la infección por H. pylori H. pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum suprimir la acidez y administrar antibióticos. Otras causas se tratan evitando los LOS Neisseria agentes causantes y sustituyendo las deficiencias asociadas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La gastritis Gastritis Gastritis refers to inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Gastritis may occur suddenly (acute gastritis) or slowly over time (chronic gastritis). Gastritis may be asymptomatic or with symptoms, including burning abdominal pain (which either worsens or improves with eating), dyspepsia, nausea, and vomiting. Gastritis es la inflamación de la mucosa gástrica asociada a una lesión de la mucosa.
La gastritis Gastritis Gastritis refers to inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Gastritis may occur suddenly (acute gastritis) or slowly over time (chronic gastritis). Gastritis may be asymptomatic or with symptoms, including burning abdominal pain (which either worsens or improves with eating), dyspepsia, nausea, and vomiting. Gastritis suele deberse a una infección o a un proceso inmunitario.
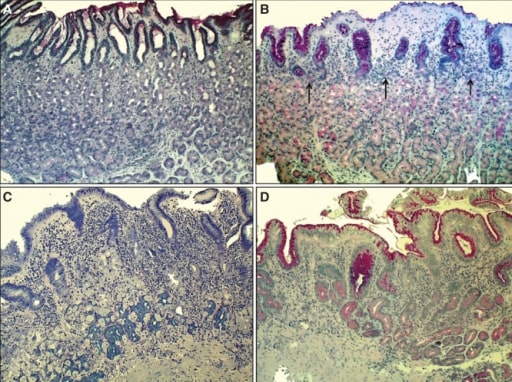
Gastritis crónica por H. pylori:
A: Mucosa normal del cuerpo estomacal
B: Gastritis no atrófica: se observa una leve inflamación mononuclear en la capa superior de la mucosa (gastritis superficial indicada por flechas). La capa glandular está todavía intacta.
C: Gastritis atrófica moderada: se produce una intensa inflamación mononuclear crónica en las capas inferiores, acompañada de atrofia de las glándulas oxínticas (lo que indica estómago con hipoclorhidria). La secreción de ácido se ve afectada por la pérdida de células parietales (en las glándulas oxínticas).
D: Gastritis atrófica severa, que muestra una leve inflamación, pero hay pérdida de glándulas oxínticas.
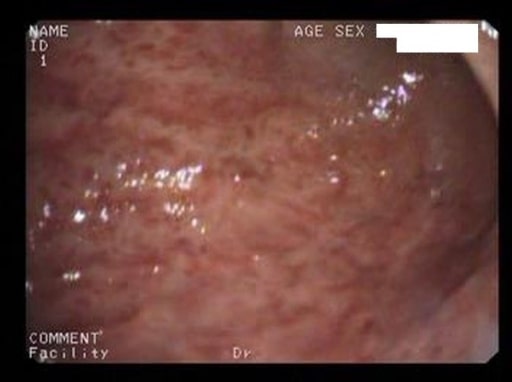
Cambios en la gastritis erosiva aguda (vista endoscópica) en un paciente que ha recibido un tratamiento prolongado con AINE COX-2
Imagen: “Acute erosive gastritis” por Department of Medical Sciences II, Medical Rehabilitation, University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova, Romania. Licencia: CC BY 2.0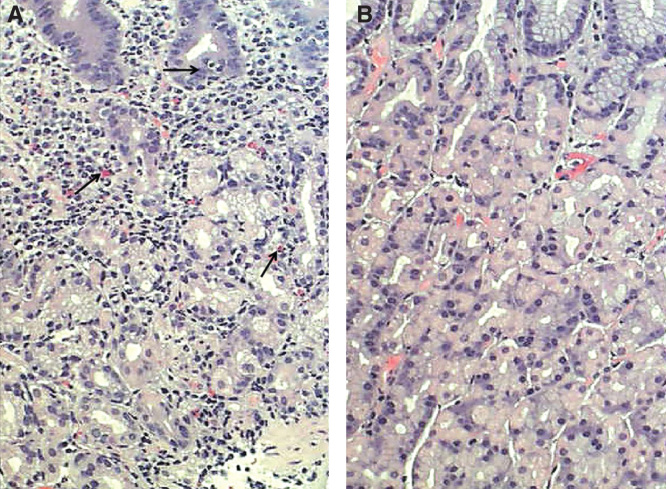
Gastritis crónica. A: inflamación de la mucosa con muchas células mononucleares (flechas); B: mucosa normal.
Imagen: “Corpus mucosa” por Informa Healthcare. Licencia: CC BY 4.0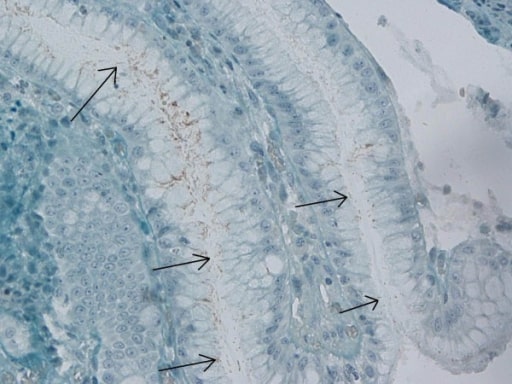
Tinción inmunohistoquímica para H. pylori en el antro gástrico
Imagen: “Immunohistochemical H. pylori” por Department of Gastroenterology, Bakirkoy Dr Sadi Konuk Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 2.0