La evaluación enfocada con ultrasonido para traumatismos es un protocolo de examen de ultrasonido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el punto de atención para las cavidades abdominal y torácica que se realiza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sala de emergencias como parte de la evaluación secundaria en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el soporte vital avanzado para traumatismos. El objetivo principal del examen FAST es identificar líquido intraperitoneal Intraperitoneal Peritoneum: Anatomy libre (sangre) y derrame pericárdico por traumatismo. Como el FAST requiere solo una máquina de ultrasonido a la cabecera del paciente y un ultrasonografista experimentado, está ampliamente disponible, es más rápida y menos invasiva que otras modalidades de imagenología. La evaluación enfocada con ultrasonido para traumatismos ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia reemplazado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran medida al AL Amyloidosis lavado peritoneal diagnóstico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La evaluación enfocada con ultrasonido para traumatismos (FAST, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es un protocolo de examen de ultrasonido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el punto de atención de las cavidades abdominal y torácica realizado con el objetivo de identificar líquido intraperitoneal Intraperitoneal Peritoneum: Anatomy libre y/o derrame pericárdico.
| Ventajas | Desventajas |
|---|---|
|
|
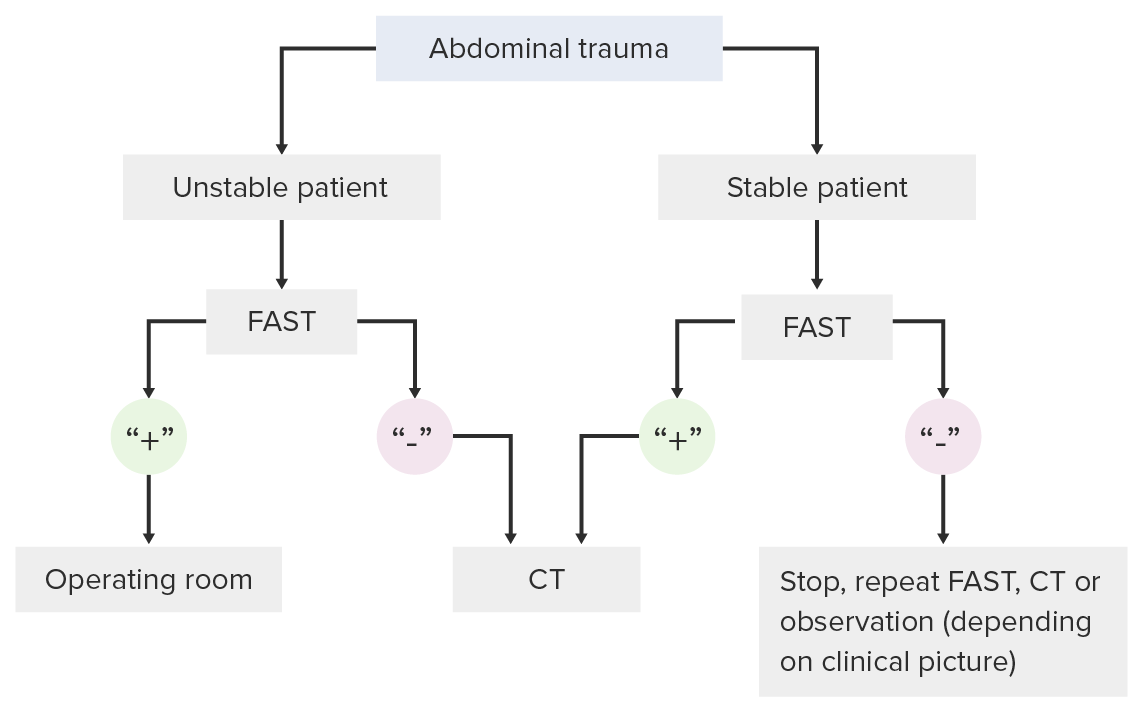
Algoritmo de toma de decisiones para el uso del examen FAST en el entorno de un traumatismo
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Conceptos básicos de imagenología del ultrasonido
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Máquina de ultrasonido
Imagen: “Aloka SSD 3500 ultrasound machine” por Kitmondo Marketplace. Licencia: CC BY 2.0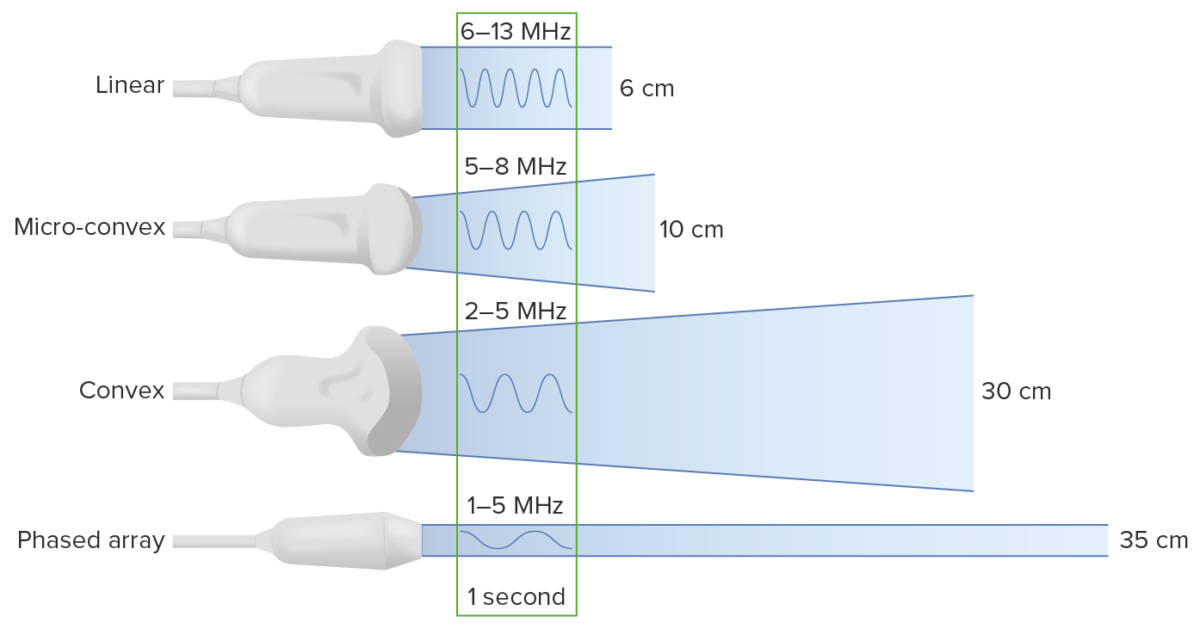
Tipos de transductores:
Obsérvese que la disminución de la frecuencia aumenta la profundidad a la que viajan las ondas de ultrasonido. Sin embargo, esto viene a costa de la resolución de la imagen.
Seleccionar la sonda:
Localización:
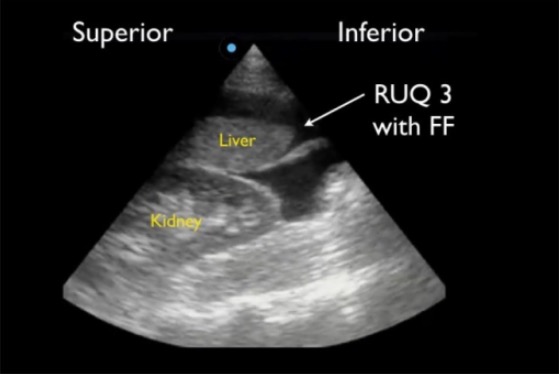
Ventana del cuadrante superior derecho (RUQ, por sus siglas en inglés) en un FAST positivo que muestra un canal paracólico superior alrededor del borde hepático caudal (RUQ3), la región más sensible para detectar líquido libre (FF, por sus siglas en inglés).
Imagen: “Positive right upper quadrant (RUQ) FAST view” por Viveta Lobo, MD et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0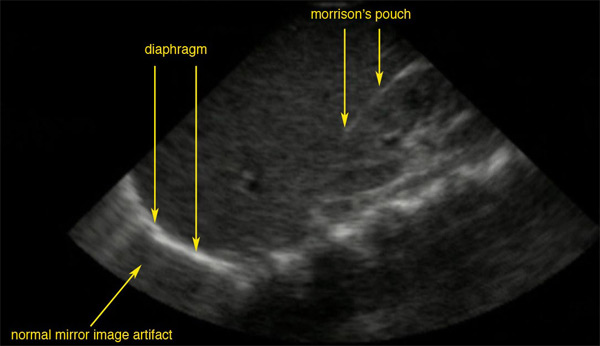
Ventana ultrasonográfica normal del espacio de Morrison:
La línea brillante es la cápsula del riñón; no hay líquido presente y por lo tanto no hay espacio visible.
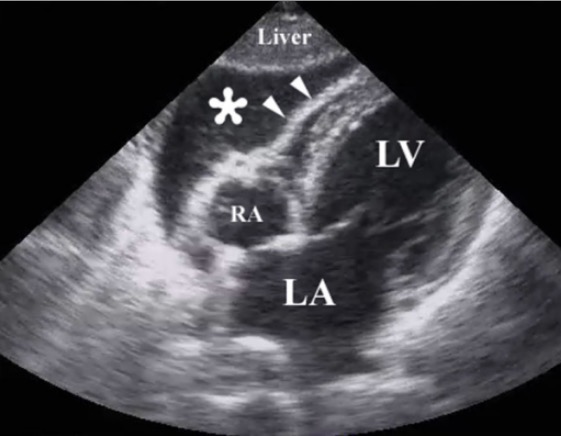
Imagen de ultrasonido de reanimación tras un traumatismo torácico penetrante que ilustra la presencia de un taponamiento pericárdico por hemopericardio (*):
Las puntas de flecha ilustran la pared del ventrículo derecho.
RA: aurícula derecha (por sus siglas en inglés)
LA: aurícula izquierda (por sus siglas en inglés)
LV: ventrículo izquierdo (por sus siglas en inglés)
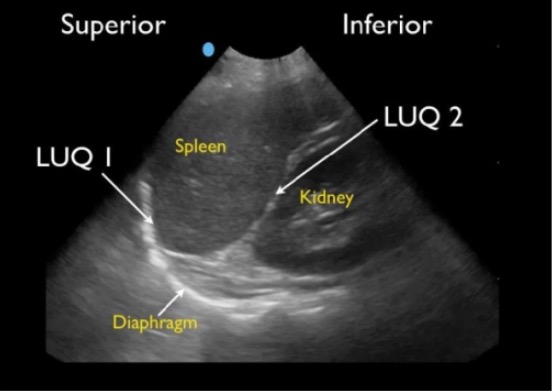
Ventana esplenorrenal normal:
Ventana del cuadrante superior izquierdo (LUQ, por sus siglas en inglés) en un FAST normal que muestra el espacio esplenodiafragmático (LUQ1) y el espacio esplenorrenal (LUQ2)
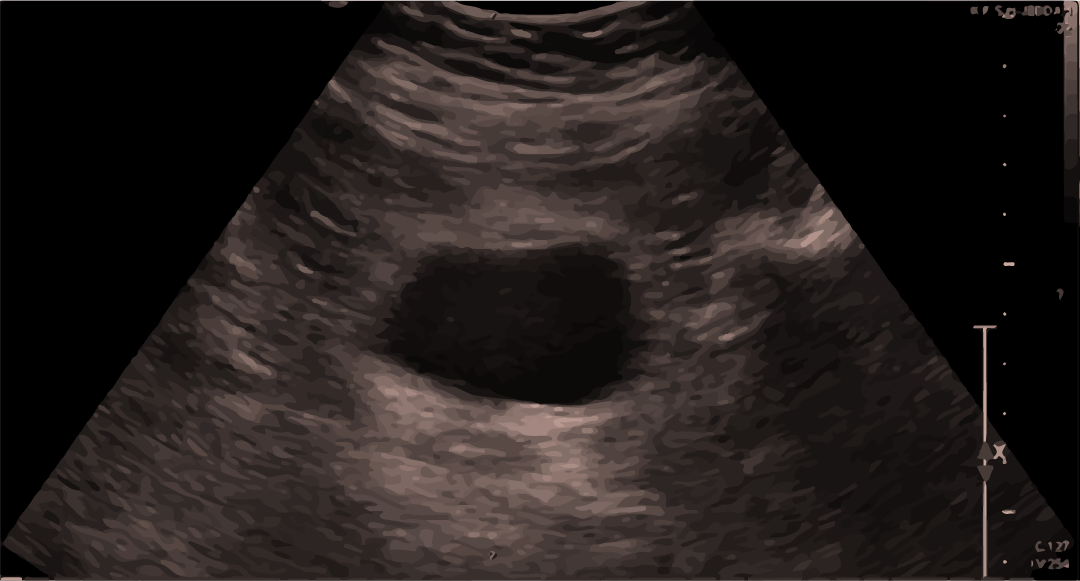
Ultrasonido normal de la vejiga:
Se puede observar sangre/líquido por encima o por debajo de la vejiga.