Las lesiones epiteliales benignas de la mama se agrupan histológicamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum no proliferativas, proliferativas sin atipia e hiperplasia atípica. Las clasificaciones se basan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el riesgo de cáncer posterior en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cualquiera de las mamas. El tipo no proliferativo no conlleva ningún riesgo, mientras que el fibroadenoma Fibroadenoma Fibroadenomas are the most common benign tumor of the female breast and the most common breast tumor in adolescent and young women. The tumors are well-circumscribed, mobile, and unencapsulated, with a rubbery or firm consistency. Fibroadenoma, el tumor Tumor Inflammation benigno más común, es una lesión mamaria proliferativa (i.e., puede presentar un ligero aumento del riesgo de malignidad si es complejo). Dado que la hiperplasia atípica comparte algunas características con el carcinoma de mama in situ, el potencial de cáncer futuro es mayor. El tratamiento va VA Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing desde la monitorización frecuente hasta la escisión quirúrgica, dependiendo de ciertos factores, incluido el riesgo inherente al AL Amyloidosis diagnóstico patológico. Otros trastornos mamarios sin posibilidad de malignidad se asocian a una infección subyacente o a una enfermedad sistémica, por lo que el tratamiento es diferente. Las enfermedades mamarias benignas son frecuentes, pero se presentan de forma diversa. Es importante distinguirlas para determinar la probabilidad de cáncer y el mejor tratamiento.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las lesiones no proliferativas de la mama son afecciones que generalmente no se asocian con un mayor riesgo de cáncer de mama.
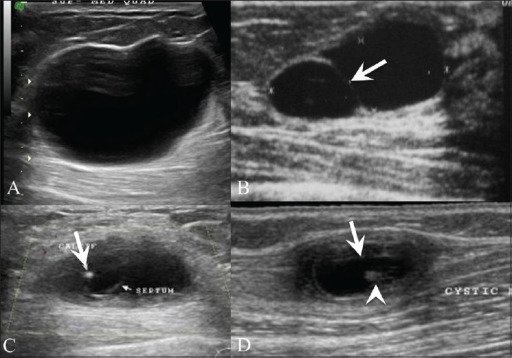
Ultrasonido de mama que muestra un quiste simple (A) que se presenta como una lesión anecoica con realce posterior y un quiste (B) con un tabique (flecha). Ultrasonido de mama (C) en una mujer de 26 años con un bulto palpable indoloro en la mama izquierda muestra un quiste complejo con un foco ecogénico localizado excéntricamente (flecha) que representa el escólex de un granuloma de cisticerco. La paciente también tenía una inflamación similar en la parte superior del brazo derecho, se tomó un ultrasonido (D) que reveló un quiste (flecha) con un escólex ecogénico (cabeza de flecha) en su interior.
Imagen: “Breast USG” por Advanced Radiology Centre, Mumbai, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las lesiones proliferativas sin atipia de la mama, el desarrollo de cáncer de mama es 1,5–2 veces el riesgo de la población general.
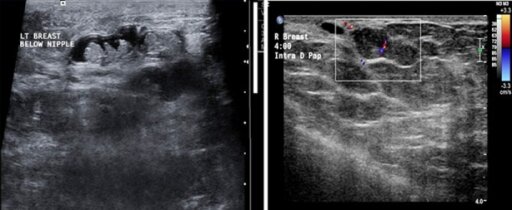
A: Múltiples papilomas intraductales dentro del mismo ducto dilatado.
B: Un papiloma que surge de la pared ductal, casi llenando el lumen del mismo. Se observa un pedúnculo vascular.
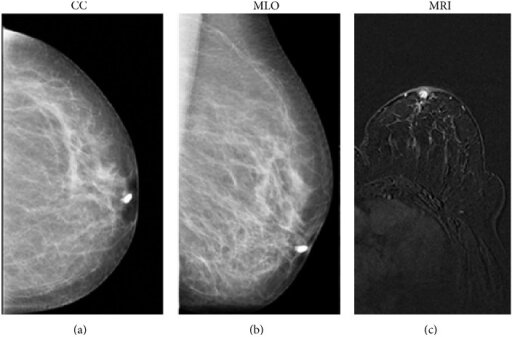
Imágenes mamográficas craneocaudal (a) y mediolateral oblicua (b) que muestran que el llenado se detiene a pocos milímetros del pezón del ducto canulado; el hallazgo imagenológico es sugestivo de papiloma.
Una resonancia magnética (RM) (flash 3D ponderado en T1 adquirido en el plano axial) muestra un realce intraductal de la masa en la zona retroareolar (c) con márgenes redondos y nítidos, indicativo de una proliferación benigna del epitelio ductal (papiloma). La histología confirmó posteriormente el diagnóstico de papiloma.
Imagen: “Galactography” por Department of Radiological Sciences, Sapienza University of Rome, Umberto I Hospital, Viale Regina Elena 324, 00161 Rome, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 3.0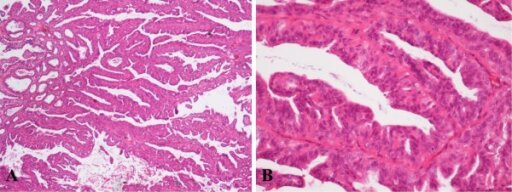
Aspecto histológico del papiloma intraductal de la mama izquierda en campo de baja potencia, ×40 (A). Patrón bicelular revestido por células cuboidales luminales y una capa externa diferenciada de células mioepiteliales a mayor aumento, ×200 (B). Imagen: “Histological appearance of IDP” por Institute for Oncology and Radiology of Serbia, 14 Pasterova, Belgrade 11000, Serbia. Licencia: CC BY 2.0
Papilomas intraductales
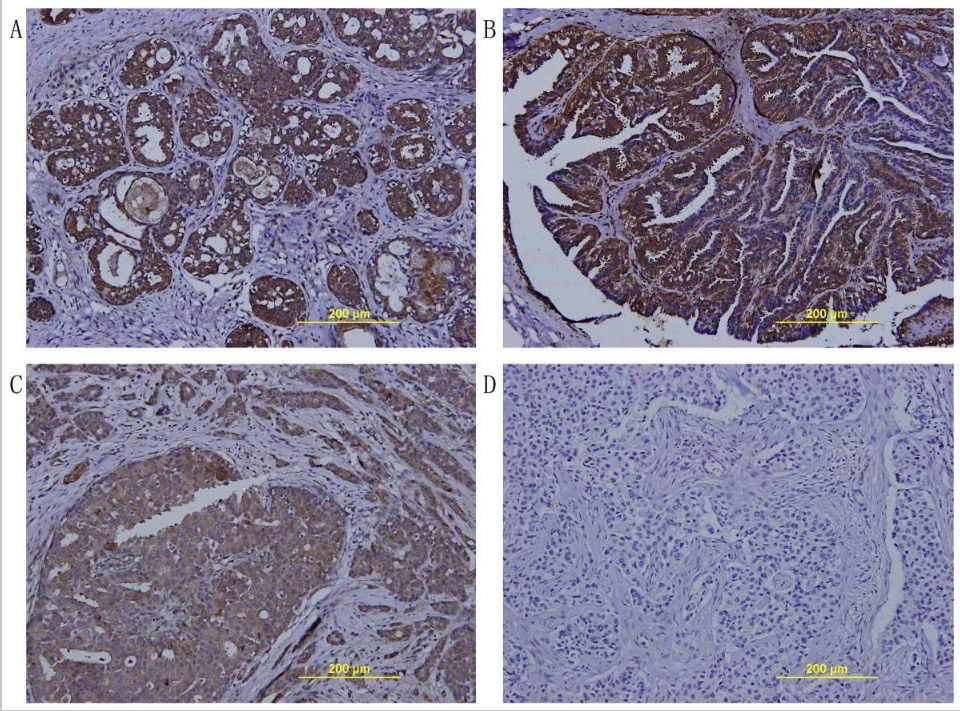
Examen microscópico del fibroadenoma intraductal o tumor filoides intraductal de la mama
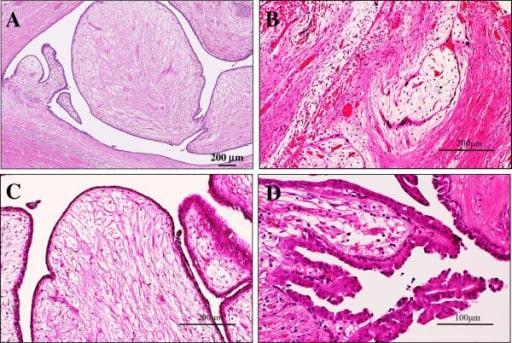
(A) La vista de baja potencia mostró que sus partes polipoides estaban compuestas por procesos en forma de hoja con un estroma hipocelular y mixoide prominente, que sobresalía en los espacios quísticos, lo que recuerda al fibroadenoma de tipo intracanalicular o a las características del tumor filoides benigno (tinciones de hematoxilina y eosina). Barra = 200 μm.
(B) En algunas zonas, había focos de la típica variante intracanalicular del fibroadenoma, en la que los lúmenes ductales estaban comprimidos por el estroma mixoide proliferante (tinciones de hematoxilina y eosina). Barra = 200 μm.
(C) En la vista de alta potencia, esas células estromales no mostraron ninguna atipia significativa, pero los componentes epiteliales hiperplásicos que las cubrían también tenían un aspecto anodino en 2 capas celulares. Se observaron muy raramente figuras mitóticas (tinciones de hematoxilina y eosina). Barra = 200 μm.
(D) En otros, raramente se observaron pequeños focos de papiloma intraductal benigno con delicados pedúnculos fibrovasculares característicos (tinciones de hematoxilina y eosina). Barra = 100 μm.
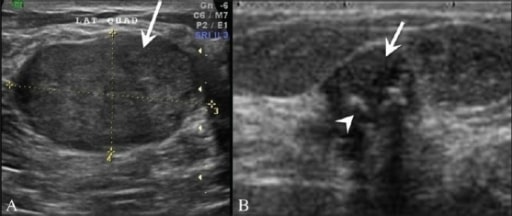
A: Ultrasonido mamario de una paciente de 25 años que muestra una lesión homogénea, hipoecoica y suavemente lobulada (flecha), sugestiva de un fibroadenoma.
B: Ultrasonido que muestra un fibroadenoma degenerado (flecha) con calcificaciones gruesas (cabeza de flecha) y sombra posterior de los focos calcificados.
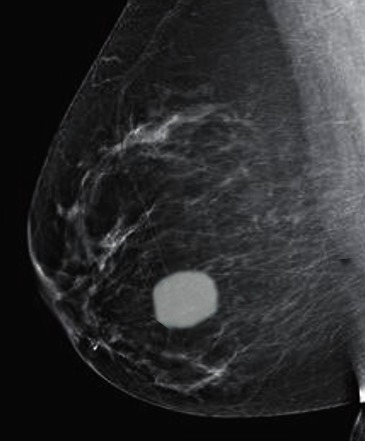
Fibroadenoma en una mamografía
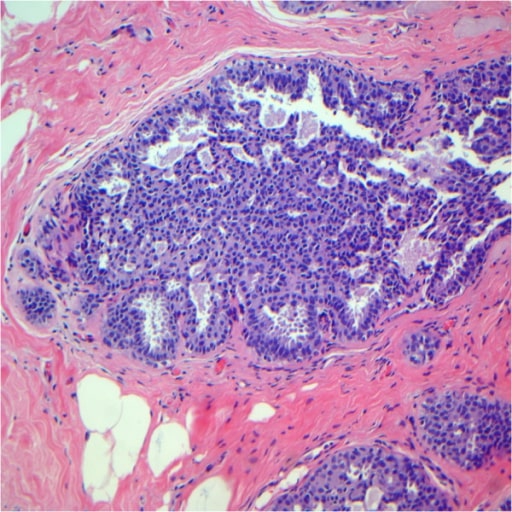
Hiperplasia ductal usual tras la revisión. Obsérvese que las células epiteliales muestran una orientación desordenada y la presencia de lúmenes secundarios en forma de hendidura localizados periféricamente.
Imagen: “Usual ductal hyperplasia” por Breast Pathology Laboratory, School of Medicine, Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG), Av, Professor Alfredo Balena, 190, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais 30130-100, Brazil. Licencia: CC BY 2.0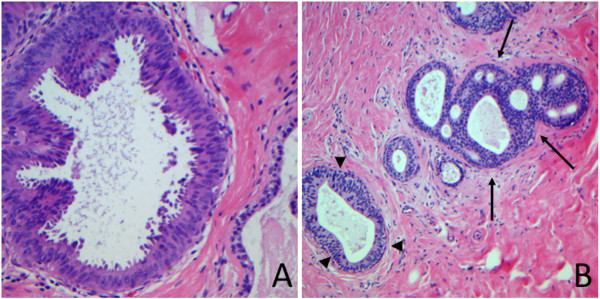
Hiperplasia ductal atípica (flechas)
Imagen: “Atypical ductal hyperplasia” por Breast Pathology Laboratory, School of Medicine, Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG), Av, Professor Alfredo Balena, 190, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais 30130-100, Brazil. Licencia: CC BY 2.0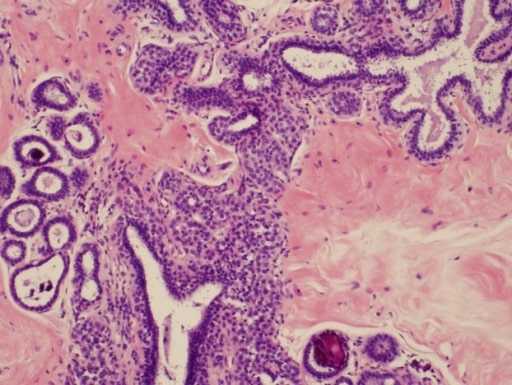
Microfotografía de hiperplasia lobulillar atípica asociada a cambios de células columnares y a microcalcificaciones incidentales y focalizadas
Imagen: “Atypical lobular hyperplasia” por Department of Pathology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. Licencia: CC BY 3.0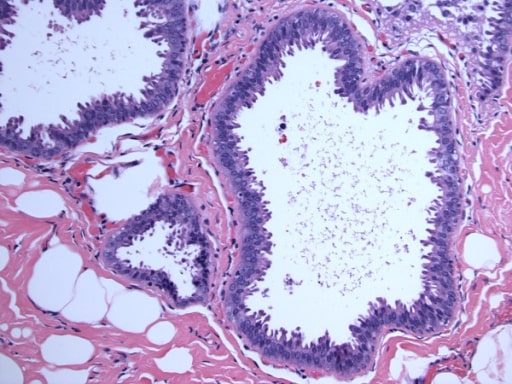
Lesiones de células columnares con atipia (atipia epitelial plana)
Imagen: “Flat epithelial atypia” por Department of Pathology, Wilford Hall Medical Center, Lackland AFB, TX, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0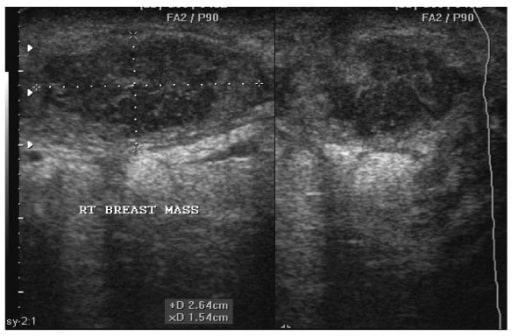
Ultrasonido de una mujer de 22 años que muestra un absceso en la mama derecha. Obsérvese la forma ovalada del absceso, que mide 2,64 cm por 1,54 cm antes de la aspiración bajo guía por ultrasonido.
Imagen: “Breast abscess” por Department of Surgery, Weil Bugando University College of Health Sciences, Mwanza, Tanzania. Licencia: CC BY 2.0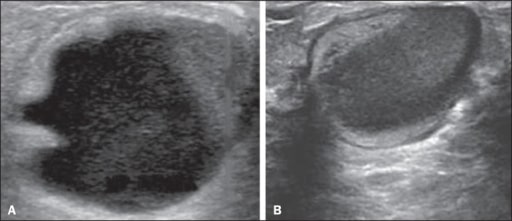
Galactocele:
A: Lesión paralela a la piel con bordes bien definidos que muestra componentes anecoicos (quísticos) y ecogénicos (sólidos), con discreto realce acústico posterior y bordes bien definidos.
B: Lesión predominantemente hipoecoica paralela a la piel con bordes bien definidos, áreas periféricas de hiperecogenicidad y realce acústico posterior.
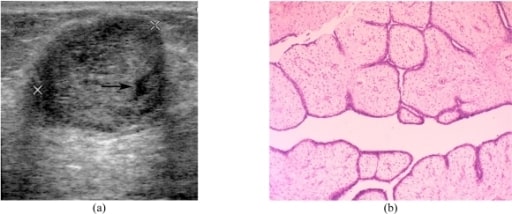
Tumor filoides de la mama
(a) Imagen de ultrasonido transversal que muestra un eco heterogéneo circunscrito con un pequeño espacio quístico (flecha) y un ligero realce acústico posterior.
(b) Microfotografía que muestra procesos en forma de hoja que contienen estroma celular revestido de células epiteliales ductales benignas que se proyectan en el espacio quístico (tinción de hematoxilina y eosina; x100).