Como la causa más común de demencia, la enfermedad de Alzheimer afecta no solo a muchas personas, sino también a sus familias. La enfermedad de Alzheimer es una enfermedad neurodegenerativa progresiva que causa atrofia cerebral y se presenta con una disminución de la memoria, cognición y habilidades sociales. Se han descrito varios defectos genéticos y factores de riesgo, aunque en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos no existe una causa clara de la enfermedad. Las principales características patológicas observadas son placas neuríticas, depósitos extracelulares de péptidos amiloides y ovillos neurofibrilares. Las características clínicas son deterioro de la memoria, pérdida de la función ejecutiva y del juicio, deterioro de la función cognitiva y cambios de comportamiento. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el examen clínico, las pruebas neuropsiquiátricas y mediante imagenología. No existe una terapia curativa, pero el tratamiento sintomático con medicamentos puede retrasar la progresión de la enfermedad; estos incluyen inhibidores de la colinesterasa, el antagonista del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de N-metil-D-aspartato memantina y un anticuerpo monoclonal anti-amiloide aprobado recientemente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La enfermedad de Alzheimer es una enfermedad neurodegenerativa progresiva que causa atrofia cerebral y una disminución de la cognición, memoria y habilidades sociales.
Aunque se desconoce la causa de la enfermedad de Alzheimer, se han identificado varios defectos genéticos y múltiples factores de riesgo.
La patogenia de la enfermedad de Alzheimer no está clara; sin embargo, hay un aumento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria péptidos beta-amiloides y agregación de la proteína tau.
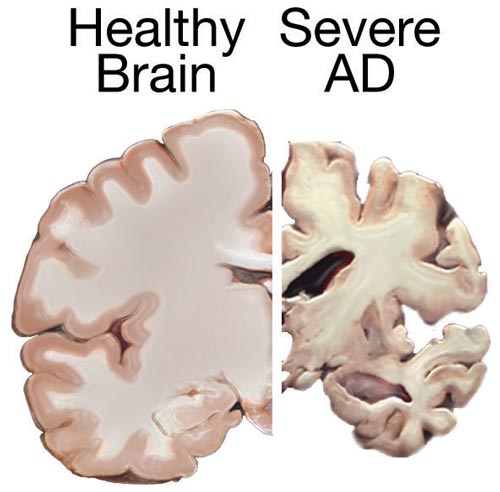
Representación de la patología macroscópica observada con la enfermedad de Alzheimer
Imagen: “Alzheimers brain” por National Institutes of Health. Licencia: Dominio Público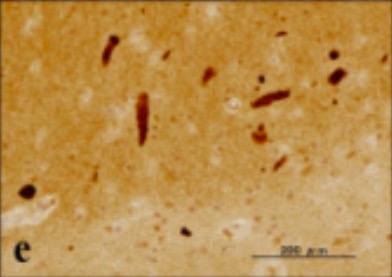
Tinción de plata que muestra ovillos neurofibrilar dentro del citoplasma neuronal
Imagen: “UBQLN1 single labeling” por Department of Bioinformatics and Molecular Neuropathology, Meiji Pharmaceutical University, 2-522-1 Noshio, Kiyose, Tokyo 204-8588, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, recortado por Lecturio.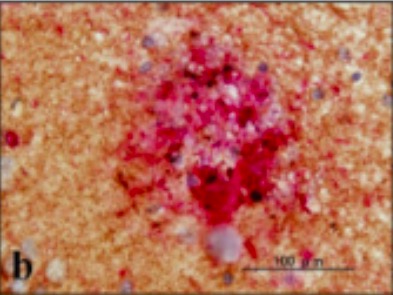
Placa neurítica con un borde de neuritas distróficas rodeando un núcleo amiloide
Imagen: “UBQLN1 single labeling” por Department of Bioinformatics and Molecular Neuropathology, Meiji Pharmaceutical University, 2-522-1 Noshio, Kiyose, Tokyo 204-8588, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, recortado por Lecturio.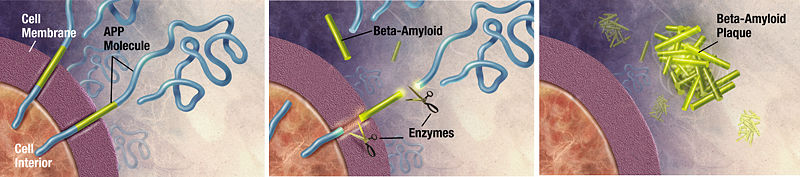
Formación de placas de beta-amiloide:
APP: proteína precursora de beta-amiloide
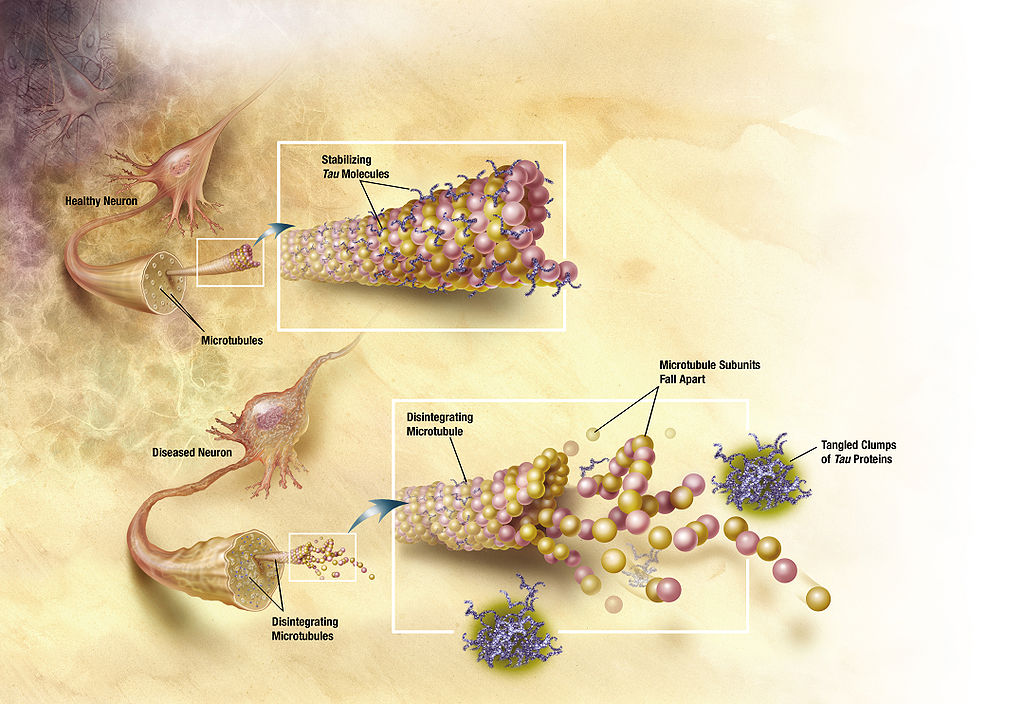
Ovilos neurofibrilares como se observa en la enfermedad de Alzheimer
Imagen: “Diagram of how microtubules desintegrate with Alzheimer’s disease” por ADEAR. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEntrevistar a los LOS Neisseria miembros de la familia es esencial para obtener antecedentes de cambios cognitivos y conductuales.
El deterioro de la memoria es el síntoma temprano más común de la enfermedad de Alzheimer.
La duración típica de la enfermedad de Alzheimer sintomática es de 8–10 años, pero el curso varía de 1 a 25 años.
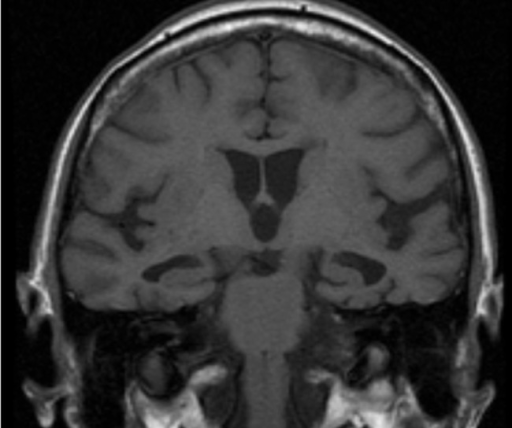
Enfermedad de Alzheimer:
RMN ponderada en T1 que muestra la atrofia bilateral del hipocampo típica de la enfermedad de Alzheimer
No existe una cura para la enfermedad de Alzheimer, pero los LOS Neisseria medicamentos pueden retrasar el deterioro funcional. Las decisiones de tratamiento individualizado se toman en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum conjunto con los LOS Neisseria pacientes y los LOS Neisseria cuidadores después de discutir los LOS Neisseria posibles beneficios, riesgos y costos.