Los LOS Neisseria carbohidratos almacenan energía y son uno de los LOS Neisseria 3 macronutrientes principales (además de las proteínas y los LOS Neisseria lípidos). Los LOS Neisseria carbohidratos están presentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum numerosos alimentos, como los LOS Neisseria cereales, las frutas, las legumbres y muchas verduras. Los LOS Neisseria polisacáridos, sobre todo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de almidón, son la principal fuente dietética de carbohidratos para el ser humano. Para ser utilizados como energía por los LOS Neisseria seres humanos, la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria carbohidratos deben ser digeridos (descompuestos) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum monosacáridos que puedan ser absorbidos y luego metabolizados. La digestión de los LOS Neisseria carbohidratos comienza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la boca con la acción de las amilasas salivales. El resto del almidón es descompuesto por la amilasa pancreática y las enzimas del borde en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cepillo de los LOS Neisseria enterocitos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria intestinos. La oxidación de 1 g de carbohidratos proporciona 4 kcal de energía
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
| Nombre | Definición | Ejemplos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos |
|---|---|---|
| Monosacáridos | Moléculas formadas por un solo grupo de azúcares |
|
| Disacáridos | Una combinación de 2 monosacáridos |
|
| Oligosacáridos | Una combinación de 3‒10 monosacáridos | Usualmente unidos a:
|
| Polisacáridoss | Una combinación de > 10 monosacáridos |
|
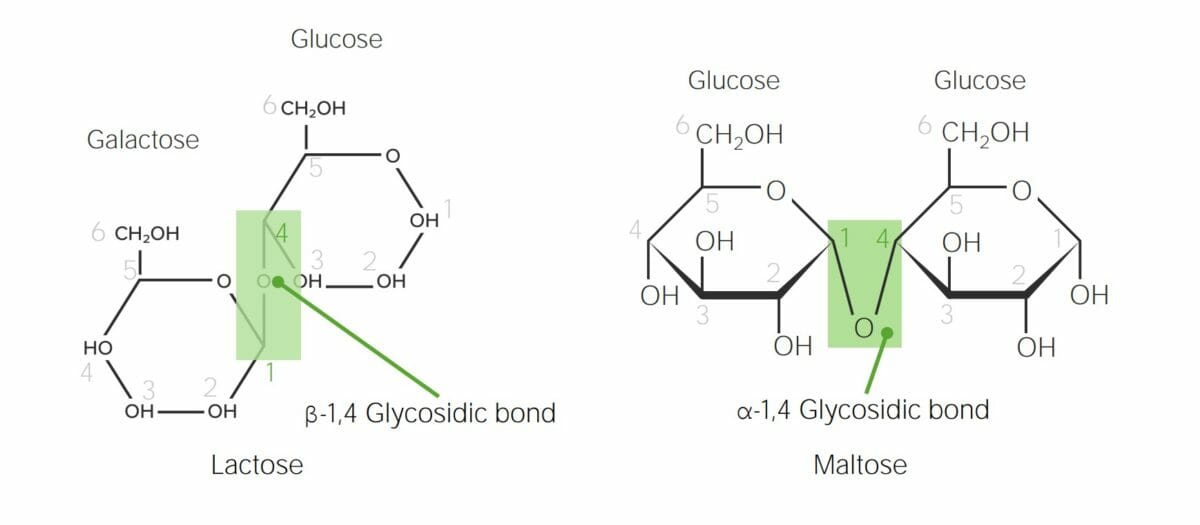
Estructura química de la lactosa y la maltosa que demuestra los enlaces glicosídicos α versus los β:
En la lactosa, el carbono anomérico de la galactosa (C1) está en la configuración β (el grupo hidroxilo apunta hacia arriba); por lo tanto, cuando la galactosa se une al C4 de la glucosa, se forma un enlace β-1,4-glicosídico. La maltosa está formada por 2 moléculas de glucosa. El carbono anomérico de la glucosa (C1) tiene la configuración α (el grupo hidroxilo apunta hacia abajo); por lo tanto, el enlace en la maltosa es un enlace α-1,4-glicosídico entre 2 moléculas de glucosa.
Los
LOS
Neisseria carbohidratos son digeridos principalmente por las amilasas y las enzimas del borde
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum cepillo de
los
LOS
Neisseria enterocitos.
Los
LOS
Neisseria carbohidratos solo pueden ser absorbidos como monosacáridos, por lo que estas enzimas rompen las grandes moléculas de almidón
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum monosacáridos individuales.
Nota: Muchos de los LOS Neisseria carbohidratos de la dieta se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de almidón, que es una mezcla de amilosa y amilopectina (ambos están hechos completamente de moléculas de glucosa):
La amilopectina es parcialmente digerida por la amilasa. Las moléculas de amilopectina son cadenas de glucosa, unidas por enlaces α-1,4-glicosídicos (crean una cadena recta de moléculas de glucosa) y enlaces α-1,6-glicosídicos (crean una ramificación de la cadena recta). La amilasa rompe los enlaces α-1,4-glicosídicos.
Imagen por Lecturio.Las enzimas del borde en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cepillo son proteínas unidas a la membrana en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la superficie luminal de los LOS Neisseria enterocitos del intestino delgado. Hay 4 enzimas principales del borde en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cepillo que participan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la digestión de los LOS Neisseria carbohidratos.
Digestión del borde en cepillo:
Diagrama del disacárido lactosa que se hidroliza en sus monosacáridos constituyentes (galactosa y glucosa) para ser absorbido por los enterocitos. El borde en cepillo es empleado en la digestión de muchos otros disacáridos.
SGLT1: transportador de sodio-glucosa 1
La isomaltasa rompe los enlaces α-1,6-glicosídicos presentes en la amilopectina. Los enlaces α-1,6-glicosídicos crean ramificaciones de las “cadenas rectas” de glucosa al unir el primer carbono de una cadena (estructura anular superior) con el sexto carbono de otra cadena (estructura anular inferior). La isomaltasa hidroliza estos enlaces.
Imagen por Lecturio.Después de la digestión, los LOS Neisseria carbohidratos se absorben y se transportan a través de la sangre hacia la circulación portal. El transporte puede ser un mecanismo activo, facilitado o pasivo.
Los LOS Neisseria transportadores tienen roles específicos y sus funciones pueden ser activas, facilitadas o pasivas.
La absorción pasiva de glucosa representa una minoría de las capacidades de absorción. La mayor parte de la absorción ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la 1ra parte del intestino delgado (duodeno, yeyuno).
Orden de los LOS Neisseria acontecimientos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la absorción de monosacáridos:
Absorción de monosacáridos a través de los enterocitos
SGLT1: transportador de sodio-glucosa
GLUT5: transportador de glucosa 5
GLUT2: transportador de glucosa 2
Una vez en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre, los LOS Neisseria monosacáridos son transportados a las células de todo el cuerpo y absorbidos por las células periféricas por medio de diferentes transportadores. Varios transportadores importantes de glucosa incluyen:
| Transportador | Localización | Función |
|---|---|---|
| GLUT1 | La mayoría de las células humanas: eritrocitos, SNC, córnea, placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity, tejido fetal |
|
| GLUT2 GLUT2 A glucose transport facilitator that is expressed primarily in pancreatic beta cells; liver; and kidneys. It may function as a glucose sensor to regulate insulin release and glucose homeostasis. Digestion and Absorption | ||
| GLUT3 |
|
|
| GLUT4 |
|
|
| GLUT5 GLUT5 A hexose transporter that mediates fructose transport in skeletal muscle and adipocytes and is responsible for luminal uptake of dietary fructose in the small intestine. Digestion and Absorption |
|
Transporta fructosa |
| SGLT1 | Membrana apical de los LOS Neisseria enterocitos del intestino delgado | Absorción de glucosa y galactosa del lumen intestinal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria enterocitos |
| SGLT2 | Túbulo contorneado proximal |
|