El sistema urogenital se deriva del mesodermo intermedio. El mesodermo intermedio se diferencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cordones nefrogénicos (que pasarán a formar el sistema urinario) y un área adyacente conocida como cresta gonadal (que pasará a formar las gónadas). Los LOS Neisseria cordones nefrogénicos se alargan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum dirección caudal y desarrollan secuencialmente 3 estructuras diferentes: el pronefros (rudimentario y no funcional), el mesonefros (forma el sistema urinario primitivo) y el metanefros (forma el riñón permanente). Al AL Amyloidosis mismo tiempo, el sistema genital se desarrolla en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estrecha asociación con el sistema urinario. El desarrollo genital depende del sexo cromosómico, que determina si las gónadas primitivas se diferencian en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum testículos u ovarios. Las gónadas luego secretan ciertas hormonas, que dirigen un mayor desarrollo de las estructuras genitales internas y externas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Se desarrolla alrededor de la semana 2 de vida embrionaria:
Capas:
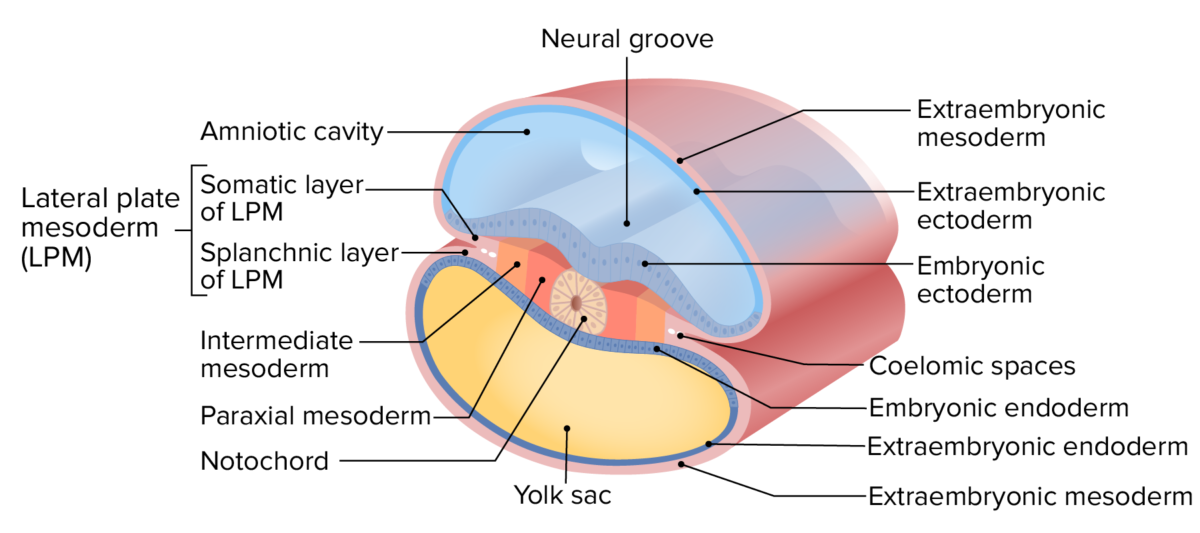
Capas del disco trilaminar
Imagen por Lecturio.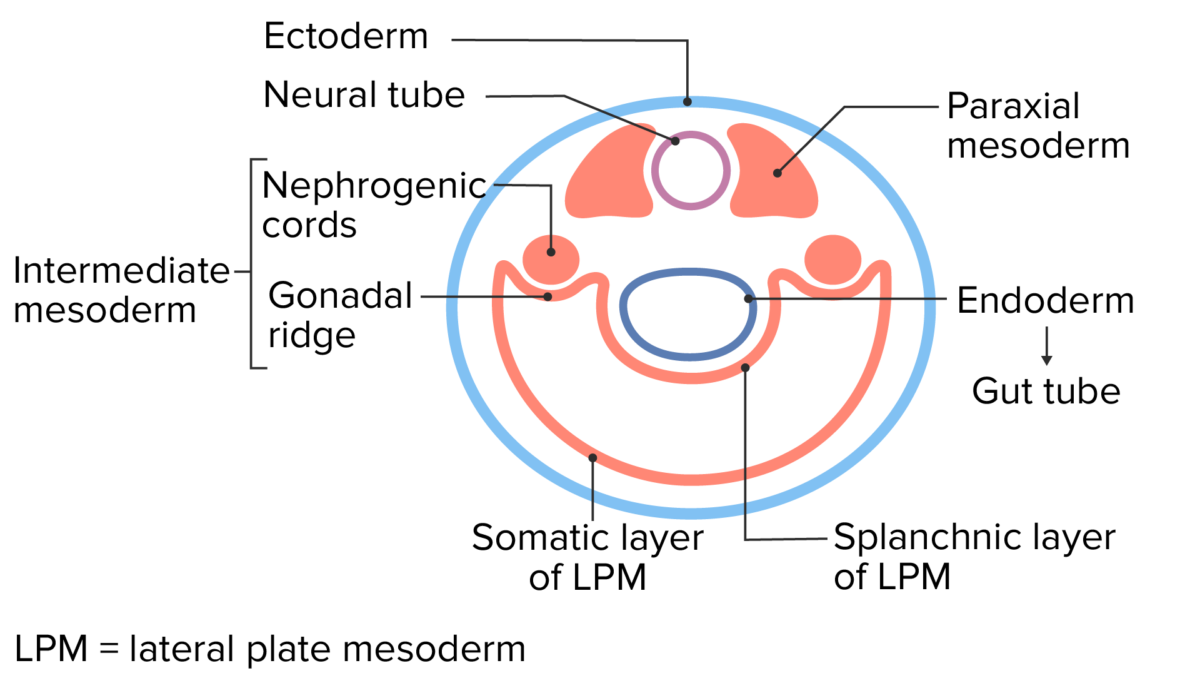
Vista transversal del embrión temprano
Imagen por Lecturio.El riñón se desarrolla a partir del mesodermo embrionario en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 formas sucesivas a partir de los LOS Neisseria cordones nefrogénicos a medida que los LOS Neisseria cordones se alargan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una dirección de craneal a caudal.
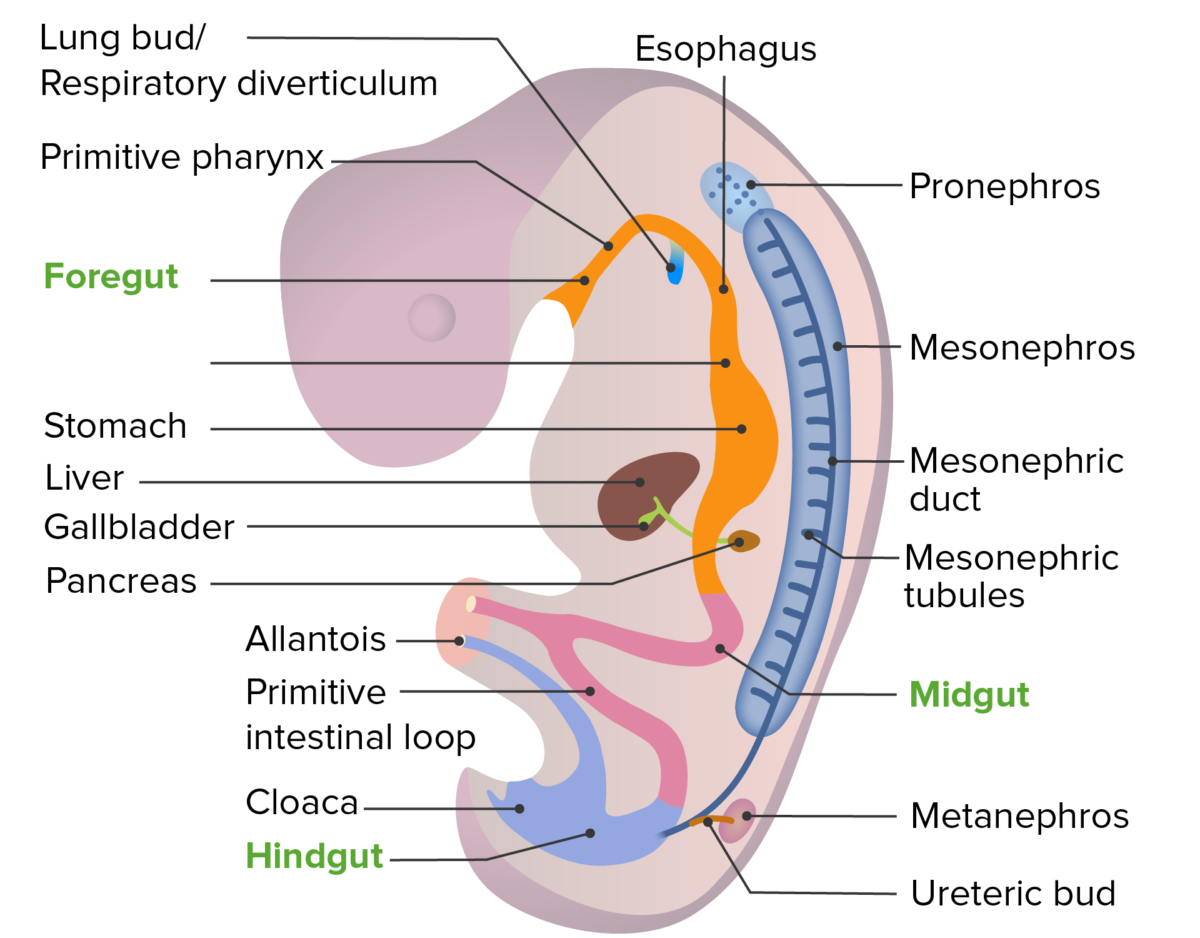
Localización del desarrollo del pronefros, mesonefros y metanefros en el embrión en desarrollo
Imagen por Lecturio.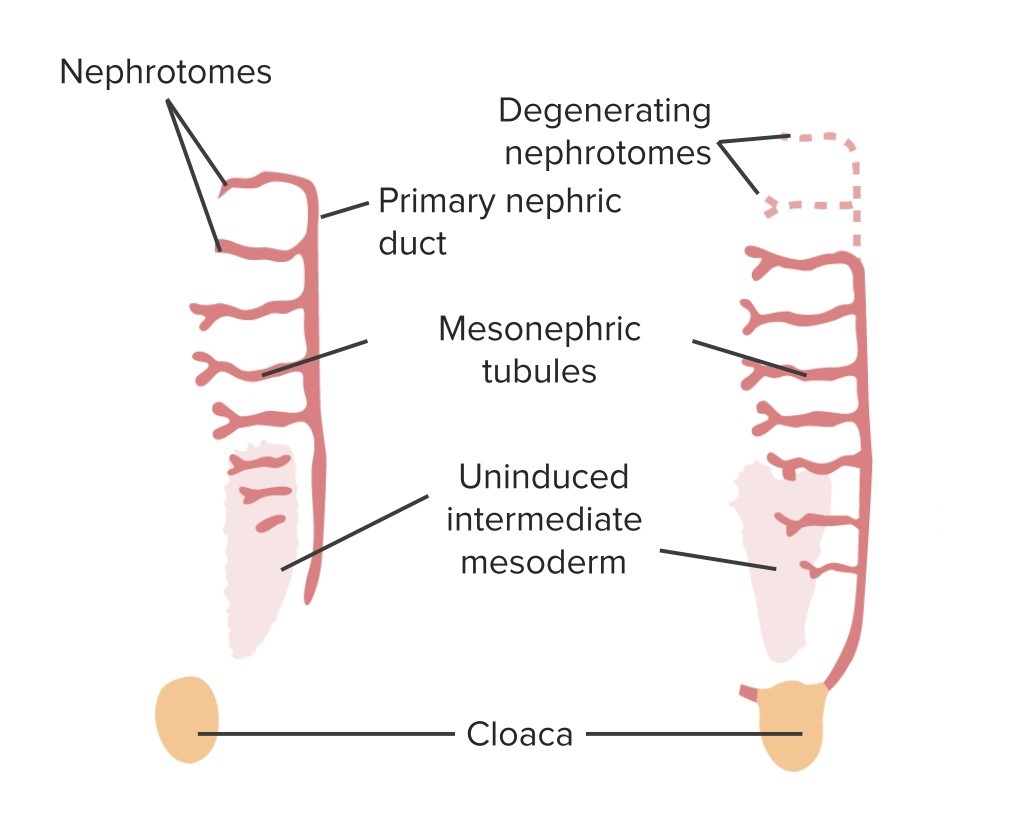
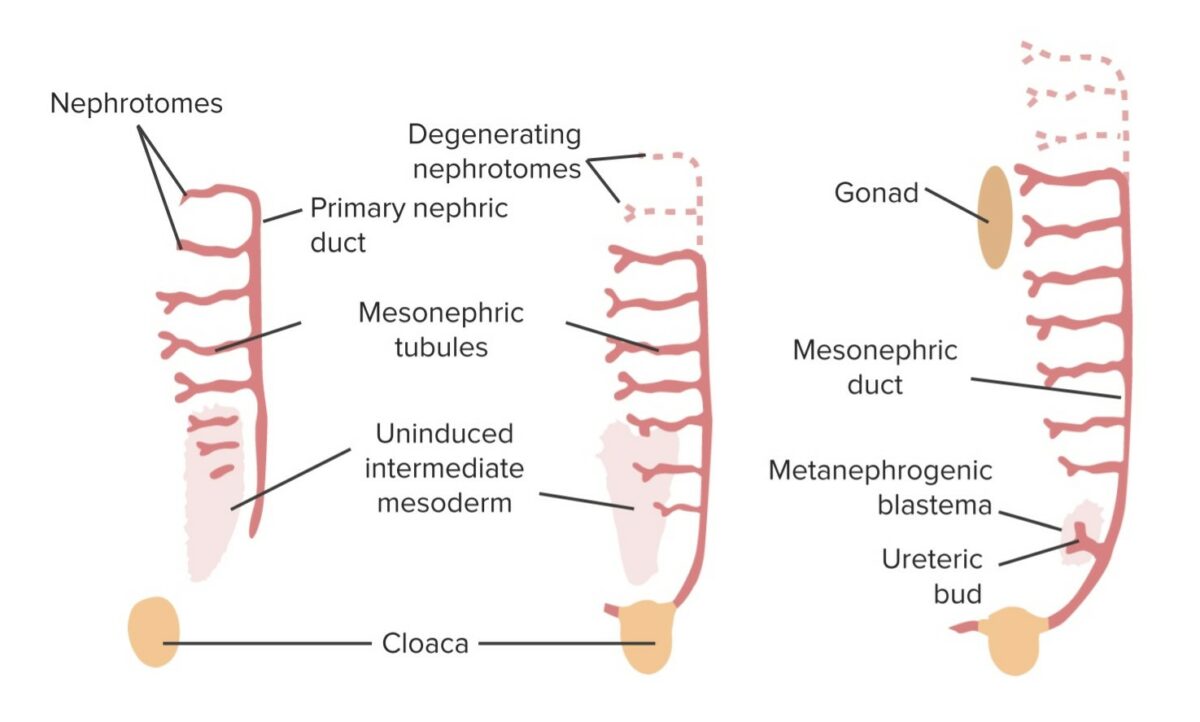
Resumen gráfico de los mesonefros:
Obsérvese que los cordones nefrogénicos (conductos néfricos primarios) se alargan y se unen con la cloaca. Los túbulos mesonéfricos crecen en un patrón similar a una escalera y funcionan como un sistema urinario primitivo, mientras que el riñón definitivo se desarrolla a partir de los metanefros más abajo en la pelvis en crecimiento.
El riñón permanente se forma a partir de los LOS Neisseria metanefros.
Resumen gráfico del riñón en desarrollo:
El brote ureteral crece fuera del conducto mesonéfrico e invade una colección de células mesodérmicas intermedias conocidas como blastema metanéfrico. Juntos, estos se conocen como mesonefros, que se convierte en el riñón. Los túbulos mesonéfricos retroceden. En los hombres, el conducto mesonéfrico persiste en el sistema eyaculatorio.
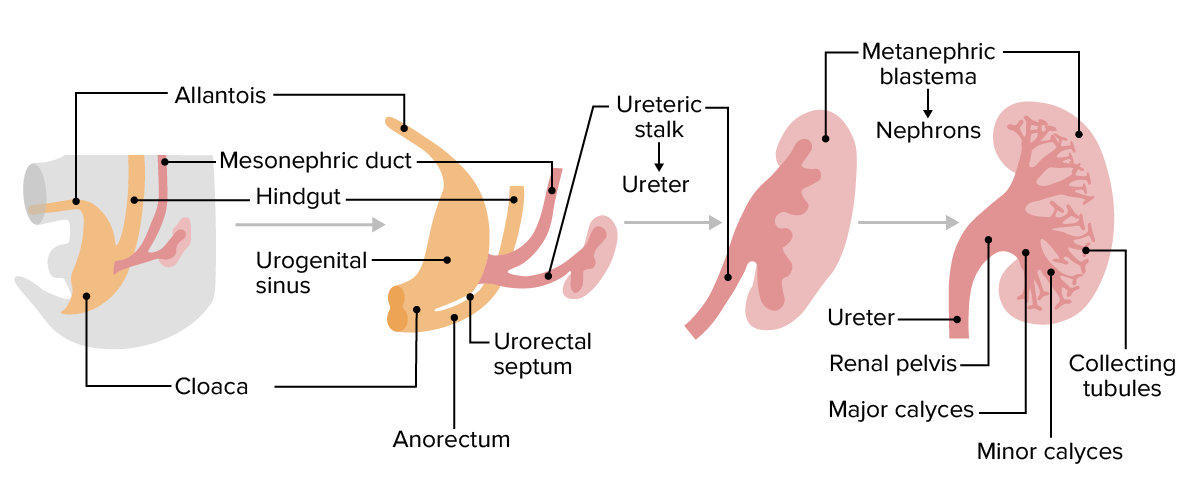
Crecimiento, alargamiento y división de los brotes ureterales, que forman los uréteres, la pelvis renal, los cálices mayor y menor y el túbulo colector.
Imagen por Lecturio.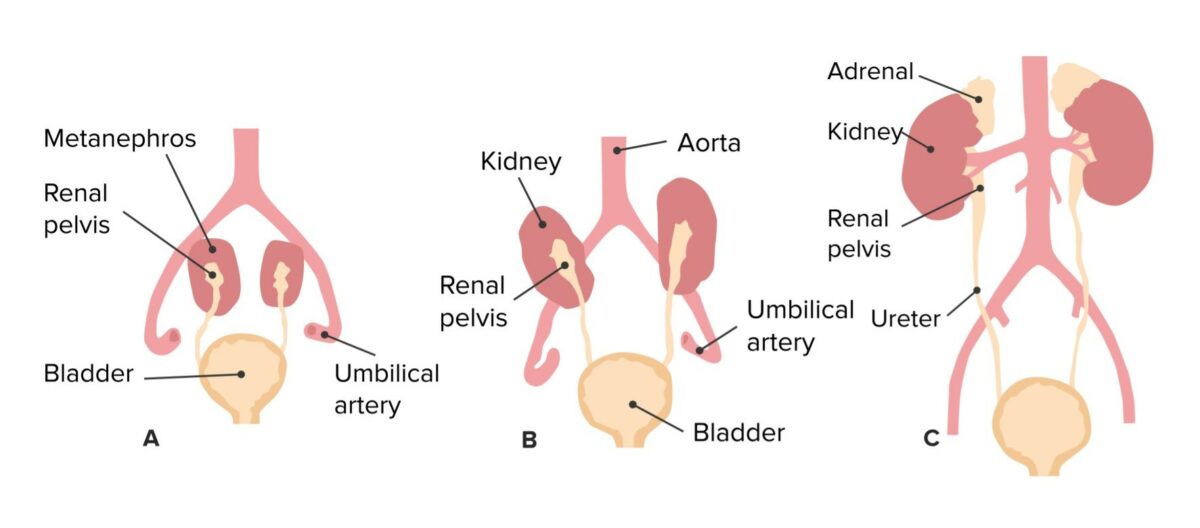
Ascenso de los riñones y cambios correspondientes en la irrigación
Imagen por Lecturio.Entre la 4ta y la 7ma semana de desarrollo, la cloaca Cloaca A dilated cavity extended caudally from the hindgut. In adult birds, reptiles, amphibians, and many fishes but few mammals, cloaca is a common chamber into which the digestive, urinary and reproductive tracts discharge their contents. In most mammals, cloaca gives rise to large intestine; urinary bladder; and genitalia. Development of the Abdominal Organs se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
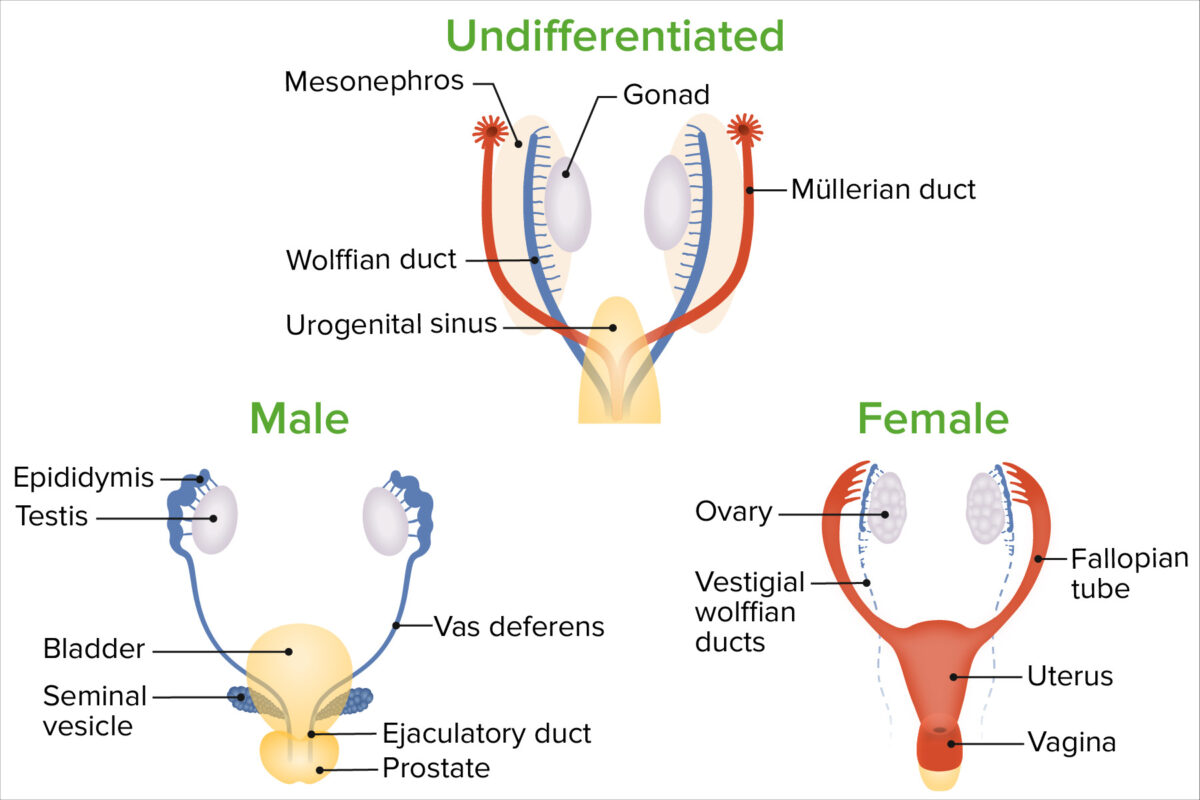
Diferenciación sexual de los conductos mesonéfricos (de Wolff) y paramesonéfricos (de Müller):
En las mujeres, los conductos mesonéfricos retroceden, mientras que los conductos paramesonéfricos persisten. Los conductos paramesonéfricos permanecen abiertos al celoma intraembrionario (la eventual cavidad peritoneal) cerca de las gónadas, y los extremos inferior/medial se fusionan en un cuerpo común en la línea media, formando el útero y la vagina superior.
En los hombres, los conductos mesonéfricos están estrechamente asociados con las gónadas; entran en el seno urogenital por separado en cada lado y se convierten en partes del sistema eyaculatorio, mientras que el seno urogenital se convierte en vejiga y próstata.
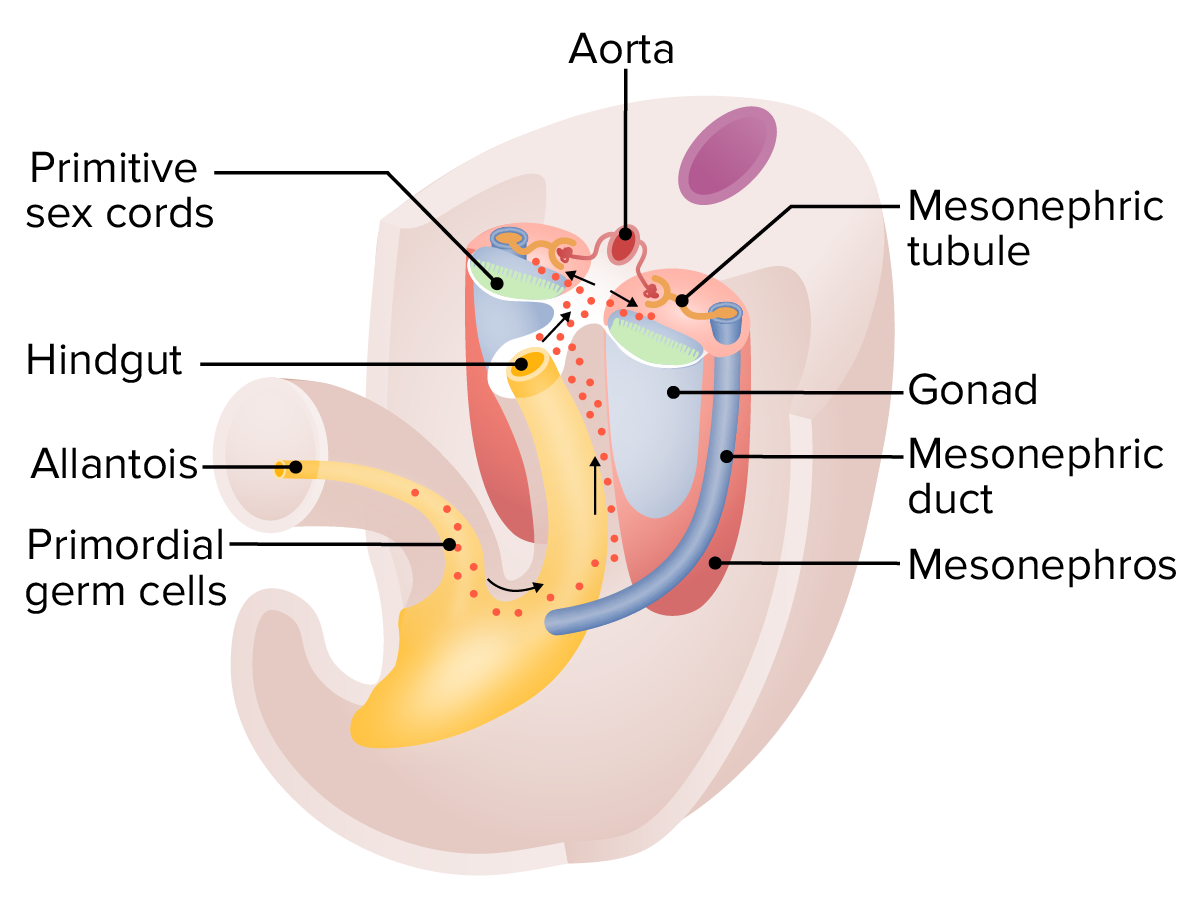
Migración de las células germinales primordiales alrededor de las 5 semanas:
Estas células germinales comienzan como células del epiblasto y comienzan a desarrollarse dentro del saco vitelino. Las células luego migran hacia abajo por la alantoides, a lo largo del mesenterio dorsal del intestino posterior, y luego invaden las crestas gonadales, que están comenzando a formar las primeras gónadas.
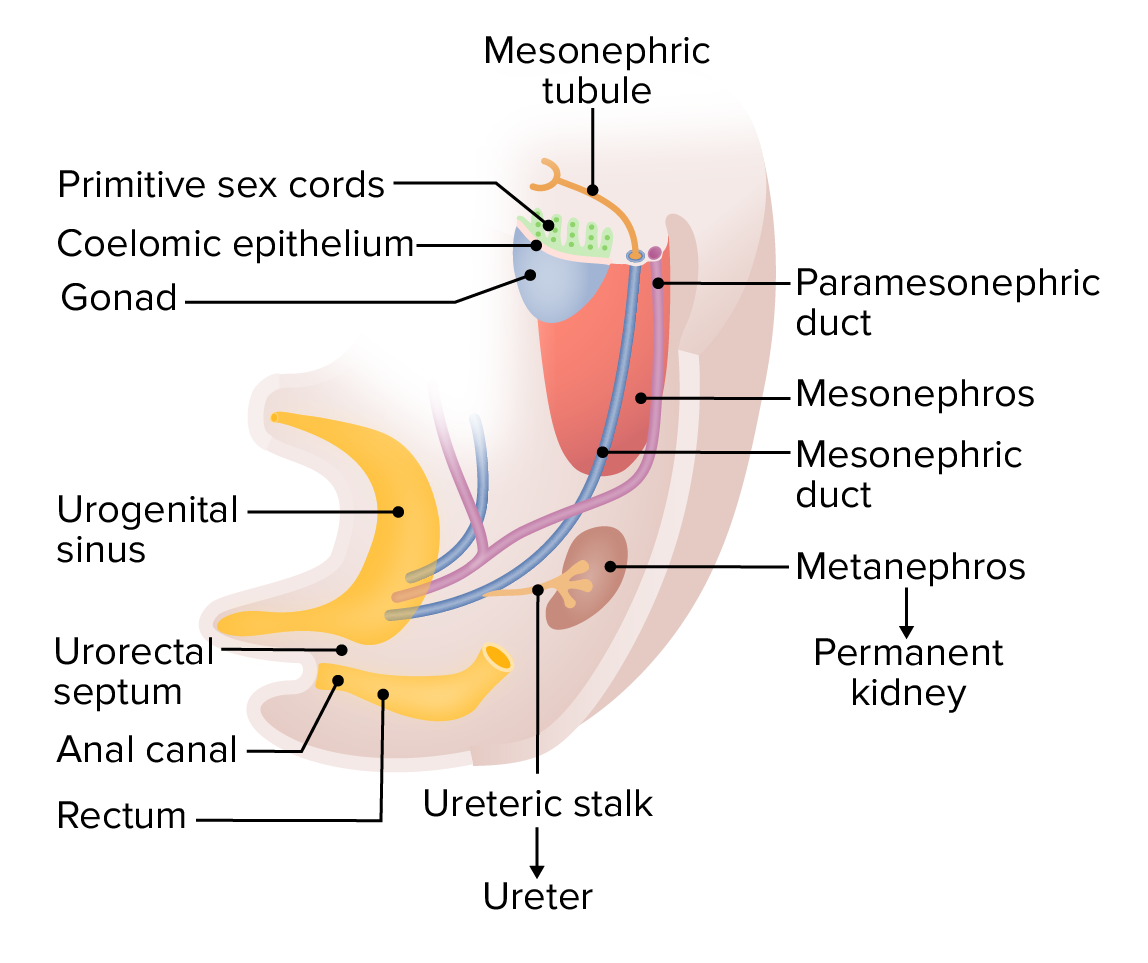
Formación de cordones sexuales primitivos:
Alrededor de las 6 semanas, el mesotelio de las gónadas invade el mesodermo subyacente y forma los cordones sexuales primitivos. Los conductos paramesonéfricos se desarrollan simultáneamente a los conductos mesonéfricos. En esta etapa, los conductos mesonéfricos funcionan como parte del sistema urinario primitivo (mesonefros); sin embargo, a medida que el riñón definitivo (del metanefros) asume el control, los conductos mesonéfricos comenzarán a diferenciarse en estructuras genitales masculinas en los hombres o retrocederán en las mujeres.
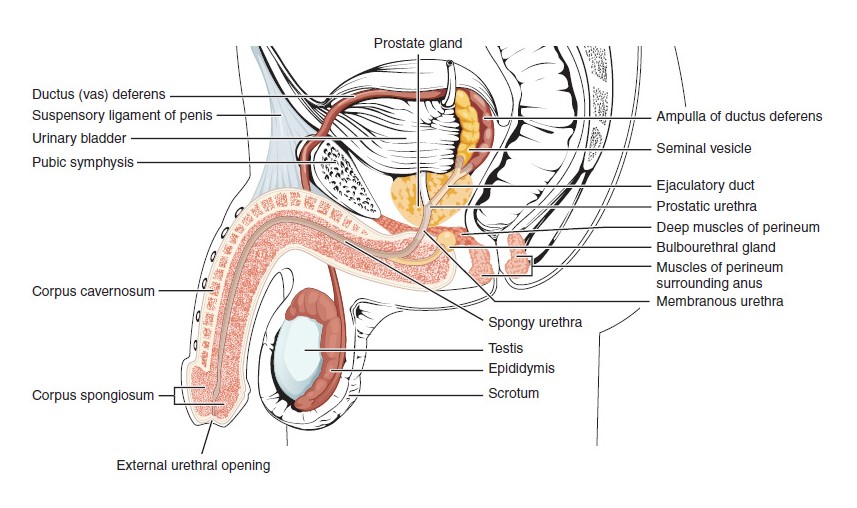
Estructuras del sistema reproductor masculino
Imagen: “Male Reproductive System” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, recortado por Lecturio.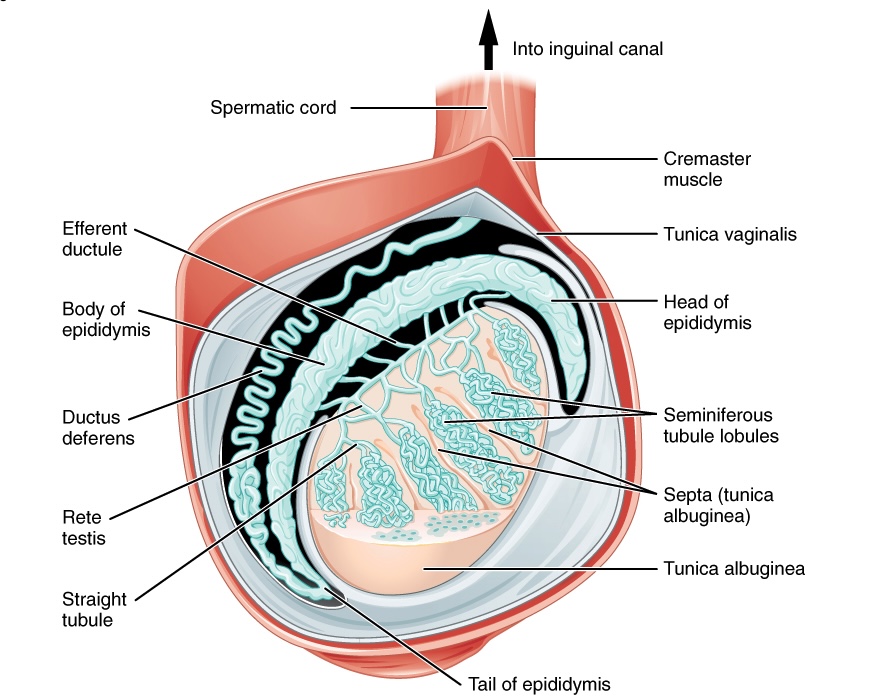
Anatomía del testículo
Imagen: “Anatomy of the testis” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 4.0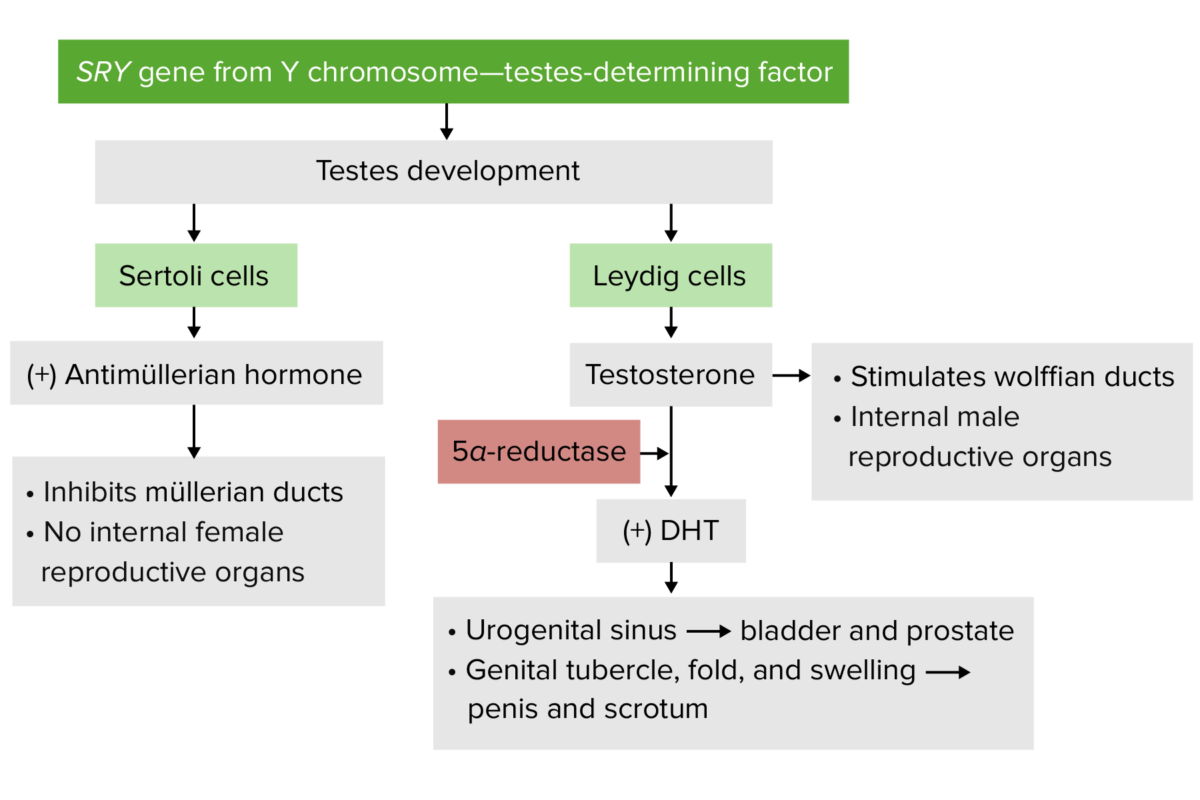
Desarrollo masculino
Imagen por Lecturio.Paso 1: fusión de los LOS Neisseria conductos paramesonéfricos
Paso 2: conexión de los LOS Neisseria conductos paramesonéfricos fusionados al AL Amyloidosis seno urogenital
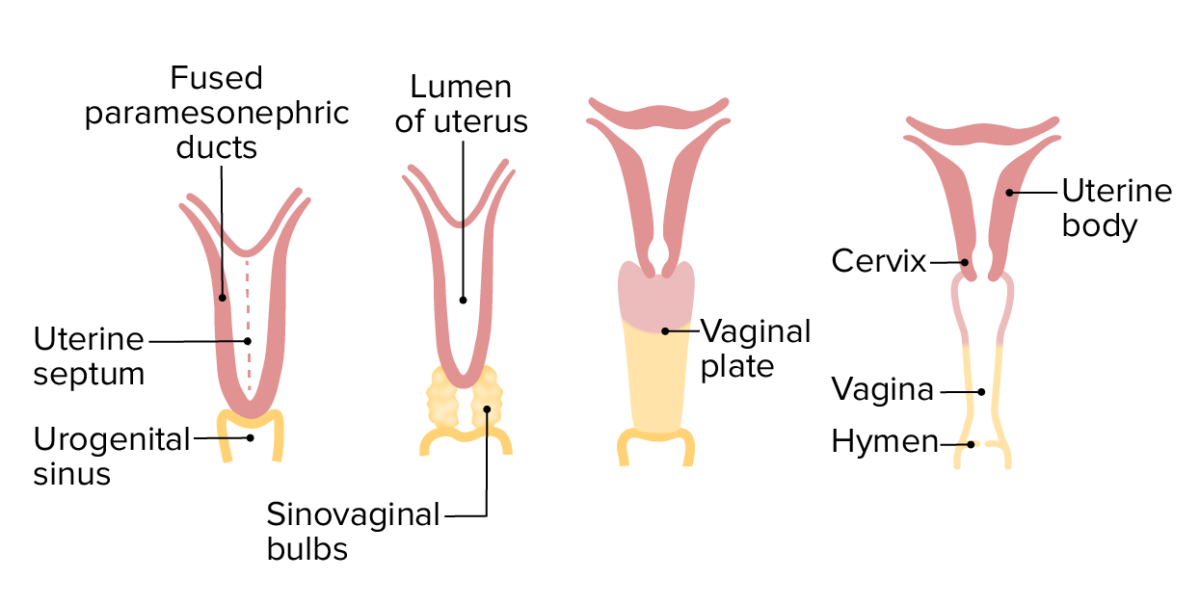
Desarrollo del útero, cuello uterino y vagina (vista anterior)
Imagen por Lecturio.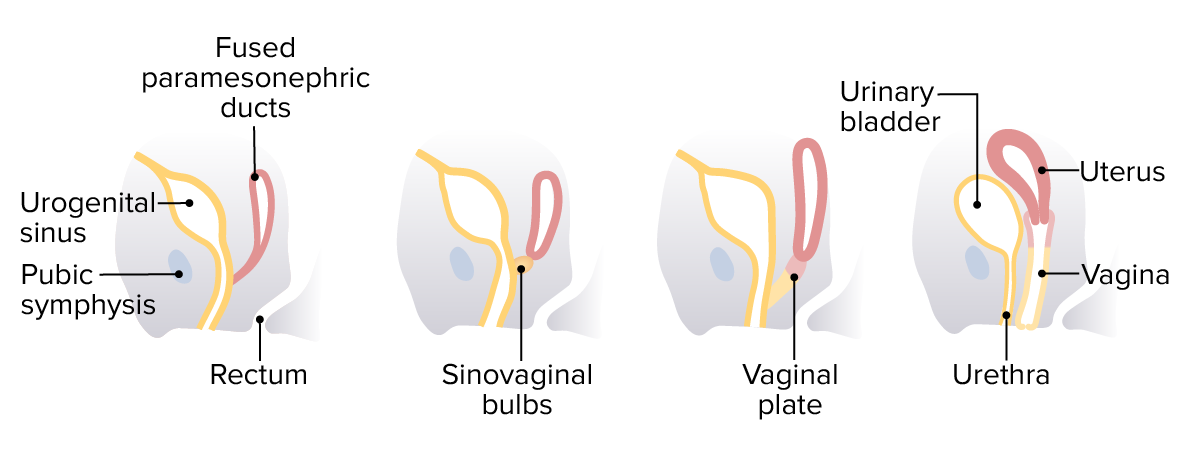
Desarrollo del útero, cuello uterino y vagina (vista lateral)
Imagen por Lecturio.| Estructura indiferenciada | En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum presencia de testosterona | Estrógeno/falta de testosterona |
|---|---|---|
| Seno urogenital |
|
|
| Tubérculo genital (forma tejido eréctil) |
|
|
| Pliegues genitales |
|
Labios menores |
| Protuberancia genital | Escroto | Labios mayores |
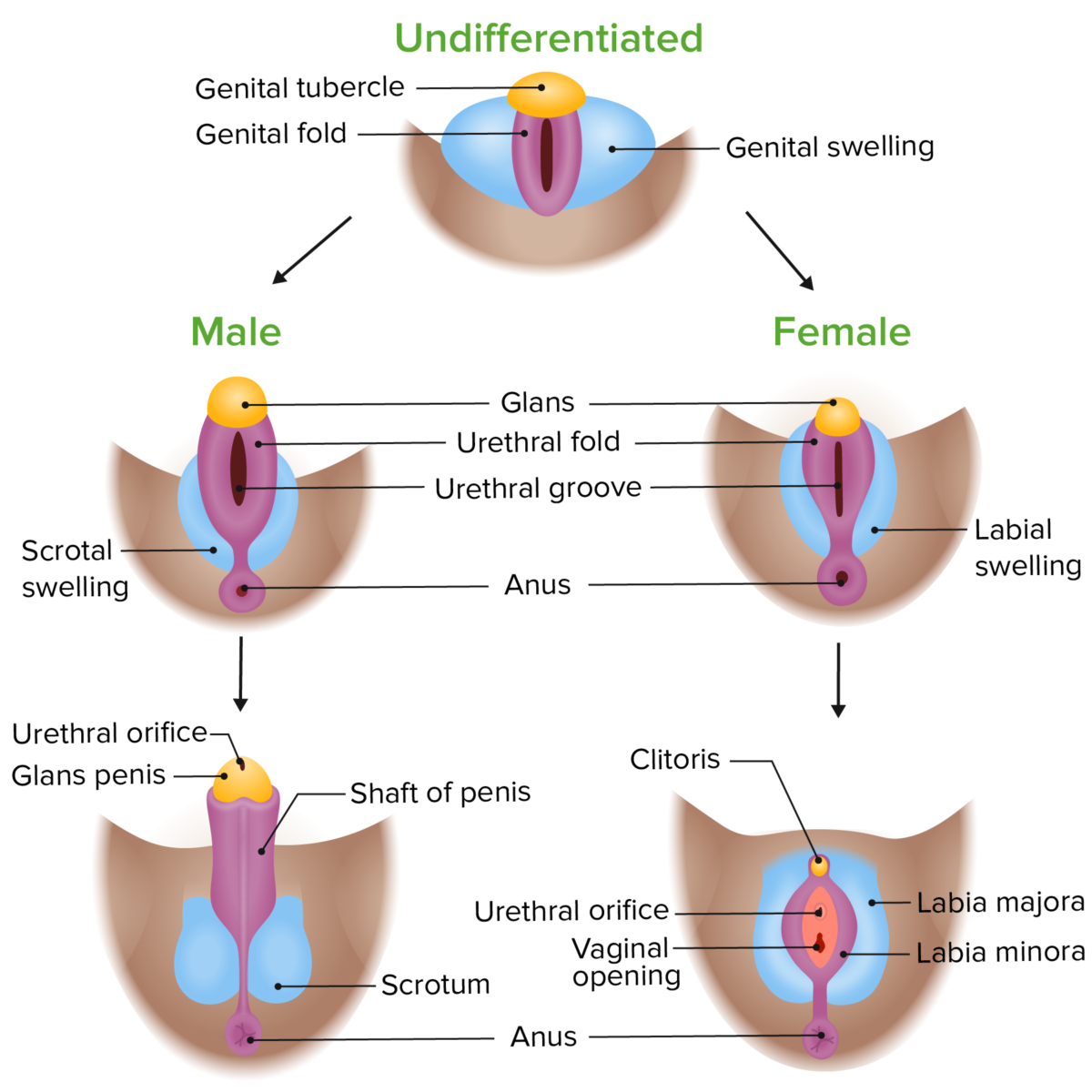
Diferenciación fenotípica de los genitales externos en embriones masculinos y femeninos:
Tanto los genitales externos masculinos como femeninos se desarrollan a partir de las mismas estructuras iniciales, pero divergen ya que están expuestos a diferentes niveles de andrógenos y estrógenos.
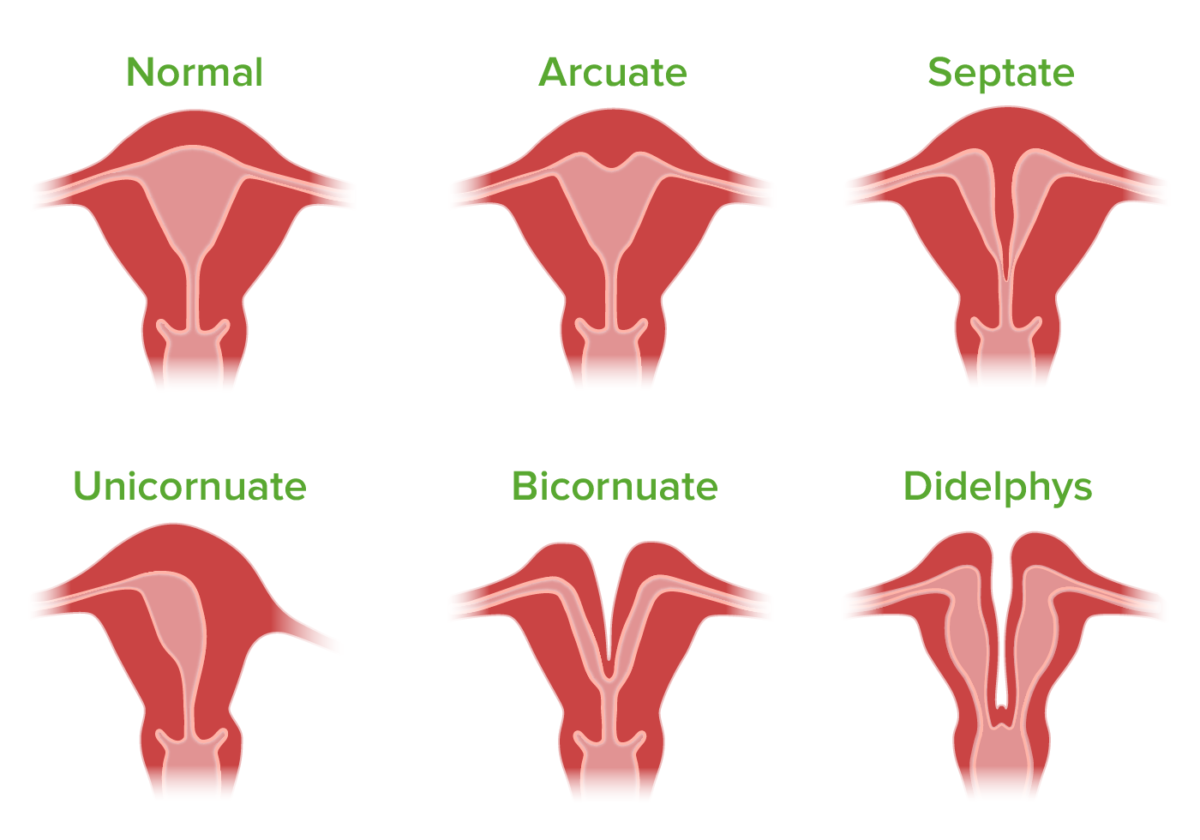
Ilustración que muestra los tipos de malformaciones congénitas del útero
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0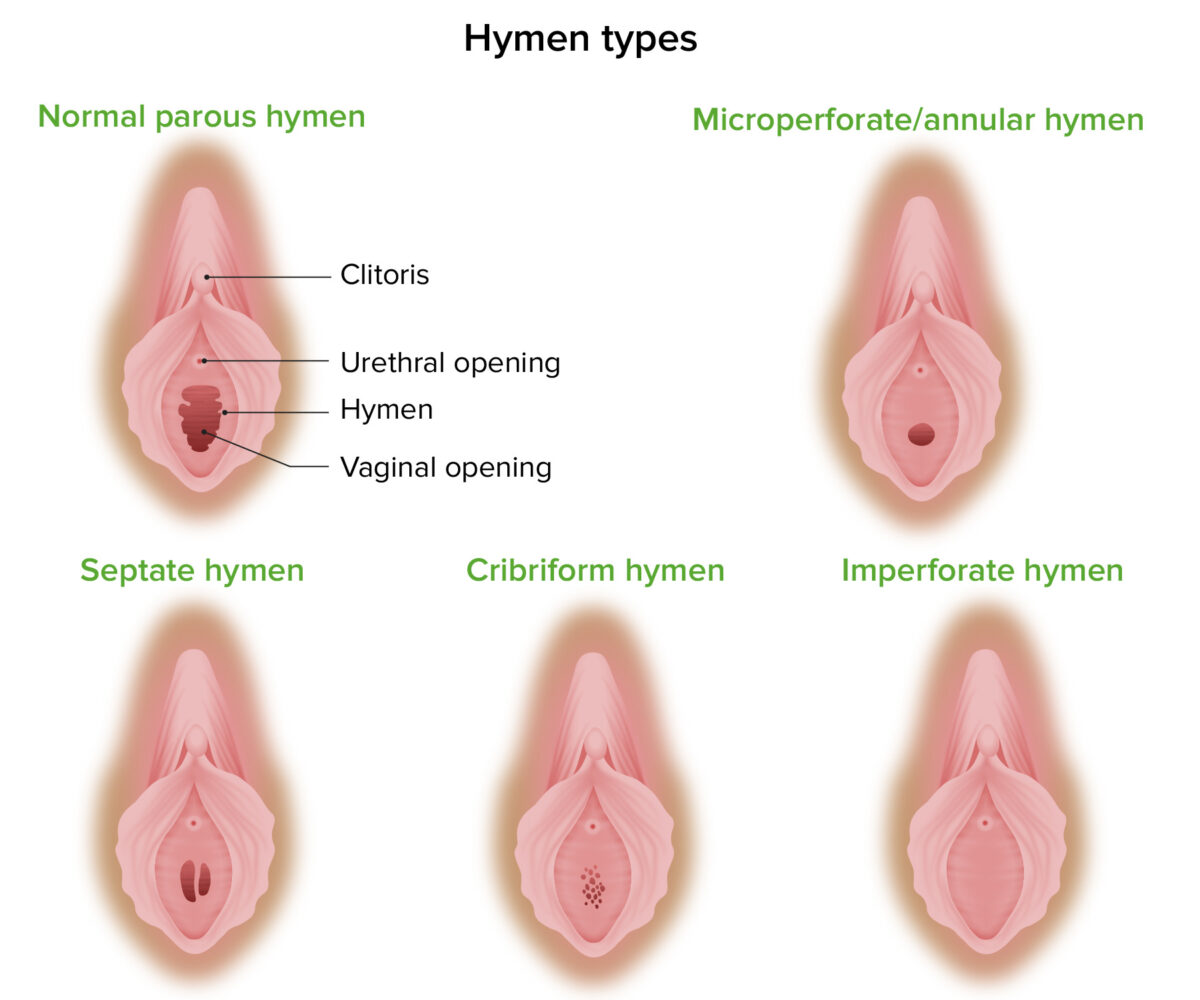
Himen poroso normal en comparación con las malformaciones comunes del himen, incluidos himen microperforado, tabicado, cribiforme e imperforado
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Los LOS Neisseria trastornos del desarrollo sexual son un grupo de afecciones caracterizadas por un desarrollo sexual atípico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un individuo, que puede involucrar anomalías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la estructura y/o función de los LOS Neisseria órganos reproductores internos y/o genitales externos.