La degeneración macular asociada a la edad es una alteración visual debida a cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mácula, la zona responsable de mayor agudeza visual. Se caracteriza por la pérdida de la visión central, mientras que la visión periférica está relativamente respetada. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo incluyen la edad avanzada, el tabaquismo, los LOS Neisseria antecedentes familiares y enfermedad cardiovascular. Los LOS Neisseria dos tipos de degeneración macular asociada a la edad son exudativa (húmeda) o no exudativa (seca). La diferencia entre estos 2 tipos es la presencia de neovascularización coroidea en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la degeneración macular asociada a la edad húmeda, que se manifiesta como distorsión o pérdida visual. La degeneración macular asociada a la edad seca, que es la más frecuente, suele ser asintomática, pero en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una minoría de casos provoca la pérdida de visión. No hay tratamiento para la degeneración macular asociada a la edad seca temprana, pero se recomiendan los LOS Neisseria suplementos del Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS 2, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) para la enfermedad avanzada. Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores del factor de crecimiento endotelial vascular se utilizan para la degeneración macular asociada a la edad húmeda.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Degeneración macular asociada a la edad:
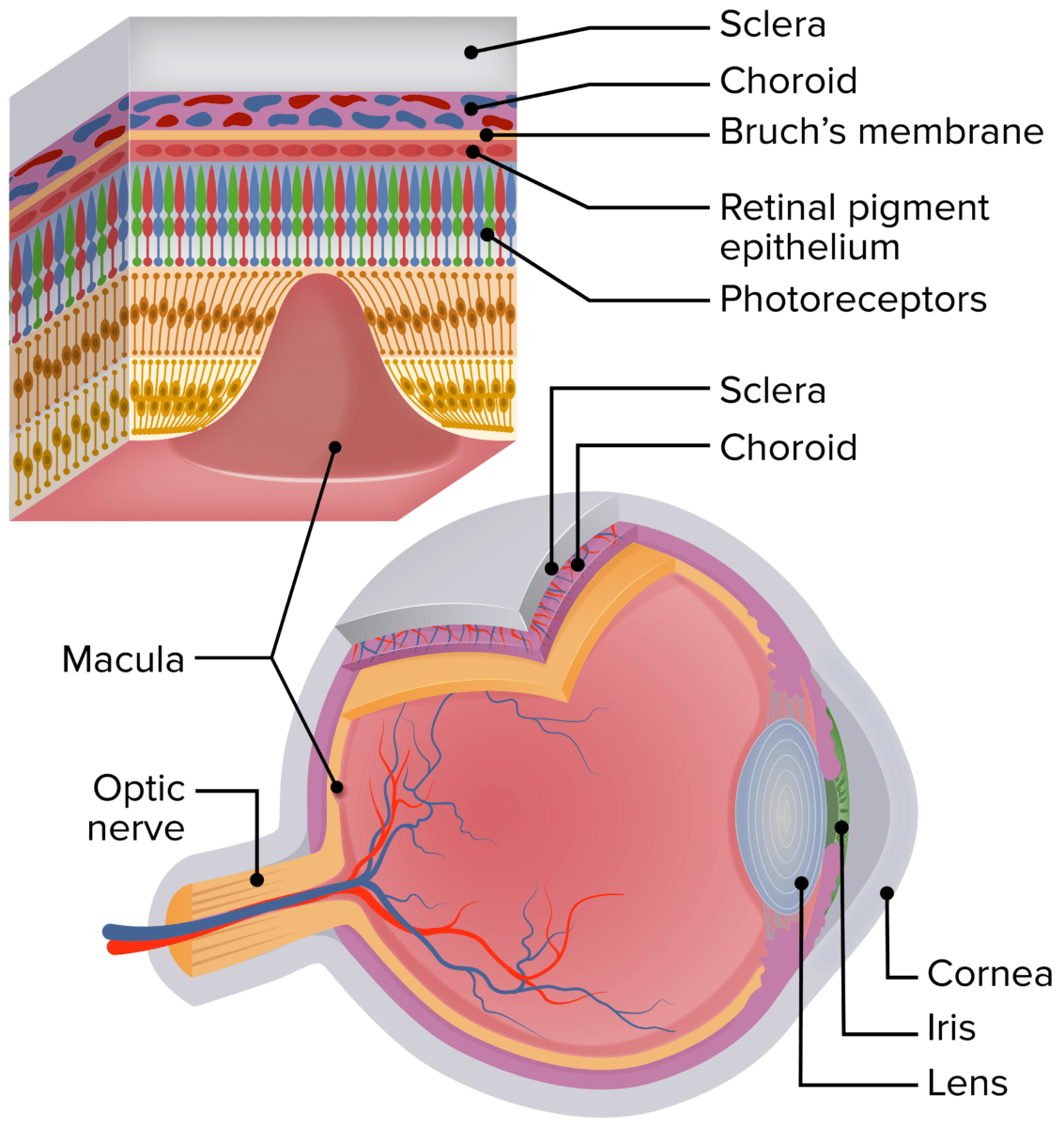
Esquema del ojo humano que muestra la ubicación de la mácula. La sección ampliada de la retina muestra las capas de la retina y la relación de los fotorreceptores con el epitelio pigmentario de la retina, la membrana de Bruch y la coriocapilar.
Image by Lecturio.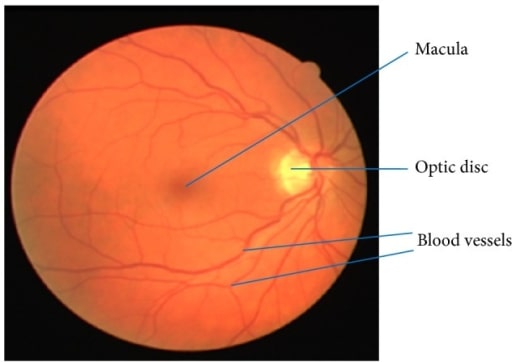
Imagen de la retina que muestra la mácula, los vasos sanguíneos y el disco óptico
Imagen: “Retinal image showing blood vessels and OD” por Department of ECE, SACS MAVMM Engineering College, Madurai, Tamil Nadu 625 301, India. Licencia: CC BY 3.0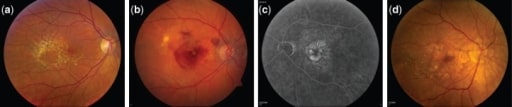
Fotografías del fondo de ojo que muestran las diferentes etapas de progresión de la degeneración macular asociada a la edad.
(a) Drusas grandes e intermedias en la fase intermedia de la degeneración macular asociada a la edad
(b) Degeneración macular asociada a la edad neovascular: ojo derecho con líquido subretiniano, hemorragia y exudado duro en presencia de neovascularización coroidea
(c) Angiografía con fluoresceína de la degeneración macular asociada a la edad neovascular: ojo izquierdo que muestra la hiperfluorescencia del angiograma con fluoresceína correspondiente a la zona de la neovascularización coroidea
(d) Atrofia geográfica central: ojo derecho con evidencia de atrofia geográfica que involucra el centro de la fóvea con evidencia de grandes drusas en la retina temporal
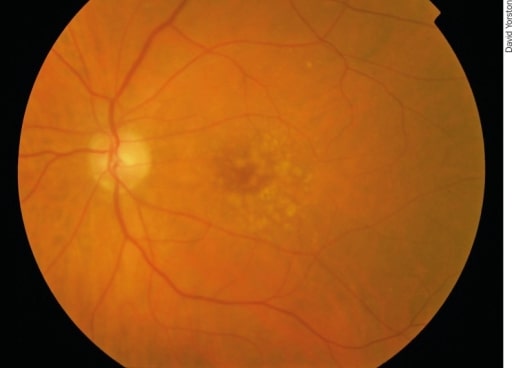
Degeneración macular asociada a la edad precoz: hay puntos pálidos irregulares en la mácula, que se llaman drusas. Se producen por la acumulación de productos de desecho del metabolismo de los fotorreceptores. Aunque las drusas están asociadas a la degeneración macular asociada a la edad, la mayoría de los pacientes con drusas no desarrollarán una degeneración macular asociada a la edad grave.
Imagen: “Early AMD” por Africa Regional Medical Advisor: Fred Hollows Foundation, Kigali, Rwanda. Licencia: CC BY 2.0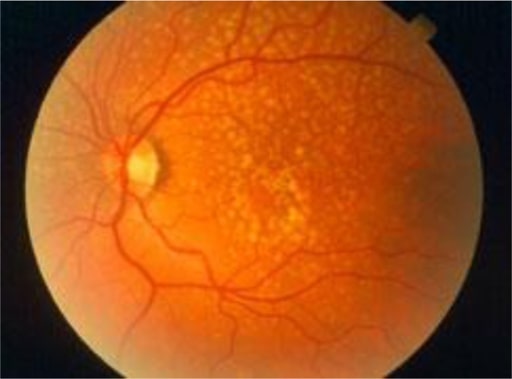
Las drusas son depósitos amarillos bajo la retina, el tejido sensible a la luz situado en la parte posterior del ojo. Las drusas están formadas por lípidos y proteínas grasas.
Imagen: “Oxidative stress, innate immunity, and age-related macular degeneration” por Department of Ophthalmology and Shiley Eye Institute, University of California San Diego, San Diego, CA, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Ejemplo de visión normal
Imagen: “An example of normal vision” por National Eye Institute. Licencia: Dominio Público
Visión afectada por la degeneración macular asociada a la edad
Imagen: “The same view with age-related macular degeneration” por National Eye Institute. Licencia: Dominio Público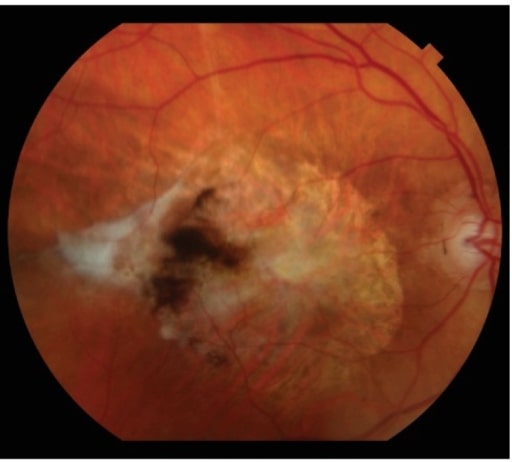
La cicatrización fibrótica subretiniana es la manifestación final de la degeneración macular asociada a la edad neovascular.
Imagen: “Subretinal fibrotic scarring” por Retina Service, Department of Ophthalmology, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0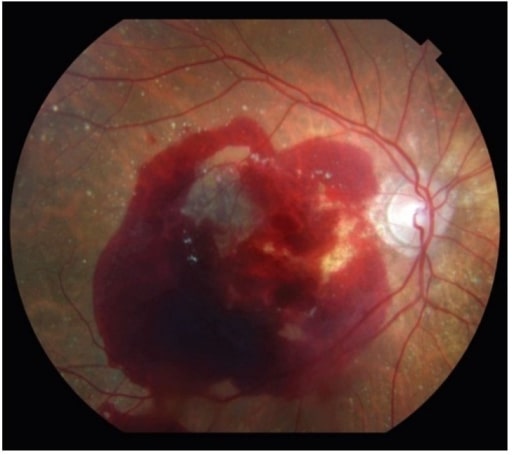
La degeneración macular asociada a la edad neovascular también puede presentarse con una importante hemorragia retiniana.
Imagen: “Neovascular age-related macular degeneration” por Retina Service, Department of Ophthalmology, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0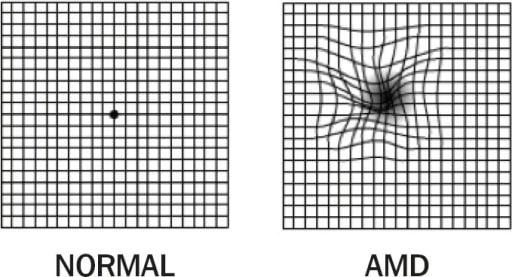
1. Rejilla de Amsler: visión normal (izquierda); 2. Rejilla de Amsler: degeneración macular asociada a la edad con metamorfopsia (derecha). Observe las líneas distorsionadas.
Imagen: “Amsler Grid” por Africa Regional Medical Advisor: Fred Hollows Foundation, Kigali, Rwanda. Licencia: CC BY 2.0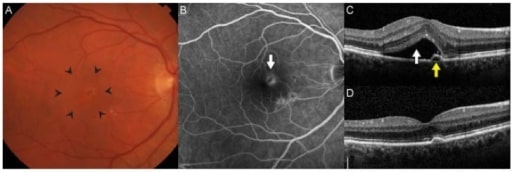
La neovascularización coroidea es el sello distintivo de la degeneración macular asociada a la edad neovascular. (A): A menudo hay un engrosamiento o elevación de la retina que se observa clínicamente a través de la biomicroscopía estereoscópica (área dentro de las puntas de las flechas). (B): En la angiografía con fluoresceína, las membranas neovasculares aparecen como lesiones hiperfluorescentes en la profundidad de la retina (flecha) que presentan fuga de contraste con el tiempo. (C): La tomografía óptica de coherencia de dominio espectral permite obtener imágenes transversales detalladas de la anatomía de la retina. En este paciente, había líquido subretiniano (flecha blanca) y un pequeño desprendimiento epitelial pigmentario adyacente. La agudeza visual era de 20/32. (D): Después de 3 inyecciones intravítreas mensuales de ranibizumab, el líquido se resolvió y la agudeza visual mejoró a 20/20.
Imagen: “Age-Related Macular Degeneration” por Retina Service, Department of Ophthalmology, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0