La cetoacidosis diabética y el estado hiperglucémico hiperosmolar son complicaciones graves y agudas de la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus. La cetoacidosis diabética se caracteriza por una hiperglucemia y una cetoacidosis debidas a un déficit absoluto de insulina. El estado hiperglucémico hiperosmolar se produce debido a una deficiencia relativa de insulina o a una resistencia a la insulina, lo que provoca una hiperglucemia grave y una osmolalidad sérica elevada. Los LOS Neisseria factores desencadenantes incluyen terapia de insulina inadecuada, infección subyacente, enfermedad concurrente o efectos secundarios de los LOS Neisseria medicamentos. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con cetoacidosis diabética suelen ser más jóvenes, con diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus tipo 1, que presentan síntomas agudos, como dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, náuseas y vómitos. Por otro lado, los LOS Neisseria pacientes con estado hiperglucémico hiperosmolar suelen ser mayores, con diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus tipo 2, y tendrán una aparición gradual de los LOS Neisseria síntomas, incluyendo alteración del estado mental y cambios neurológicos. Ambos grupos de pacientes tendrán poliuria, polidipsia y evidencia de deshidratación severa. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria valores de laboratorio que demuestran una hiperglucemia con cetoacidosis o hiperosmolalidad. El tratamiento implica una rehidratación agresiva con líquidos, terapia con insulina y corrección de las anomalías electrolíticas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La cetoacidosis diabética y el estado hiperglucémico hiperosmolar son complicaciones graves y agudas de la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus.
La respuesta normal al AL Amyloidosis aumento de la glucosa sérica implica la liberación de insulina por parte de las células beta del páncreas. Esto conlleva a:
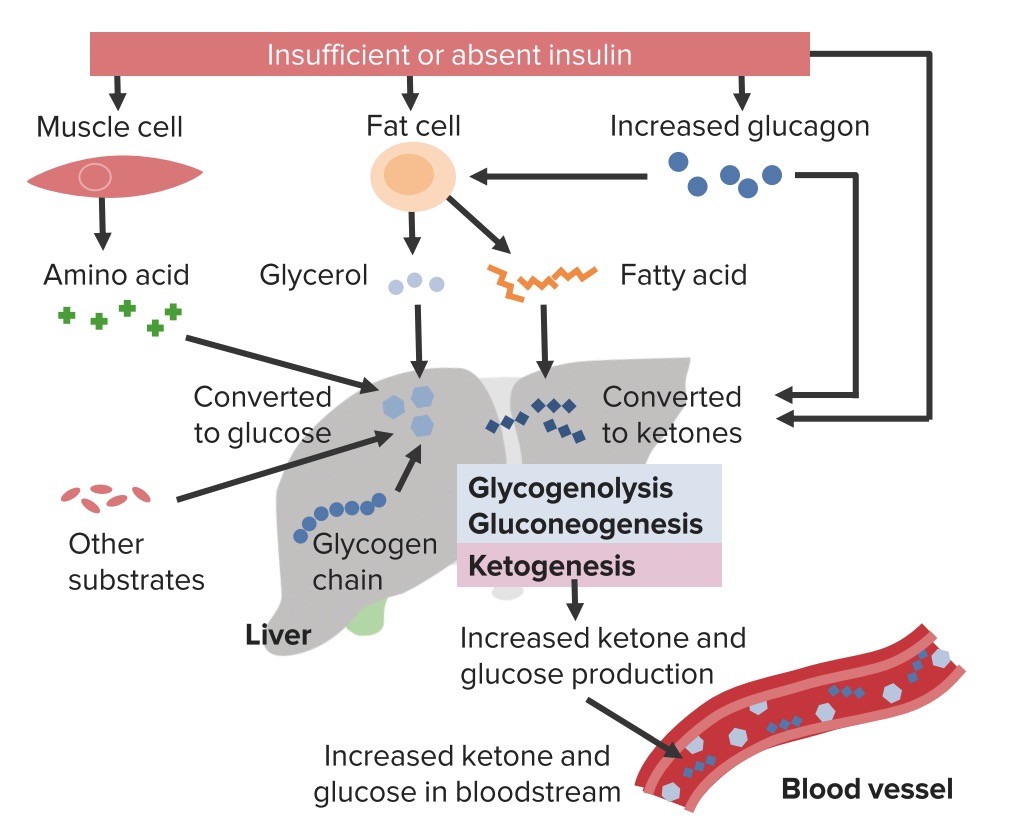
Fisiopatología de la cetoacidosis diabética
Imagen por Lecturio.| Análisis de laboratorio | Cetoacidosis diabética | Estado hiperglucémico hiperosmolar |
|---|---|---|
| Glucosa sérica | > 250 mg/dL | > 600 mg/dL |
| Bicarbonato sérico | ↓↓ | > 18 mEq/L |
| Brecha aniónica | ↑ | Generalmente normal |
| Osmolalidad sérica | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables | > 320 mOsm/L |
| Cetonas séricas (beta-hidroxibutirato, acetona) | Positivas | Pocas o negativas |
| Cetonas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la orina | Positivas | Pocas o negativas |
| Gasometría arterial |
|
pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance: > 7,3 |
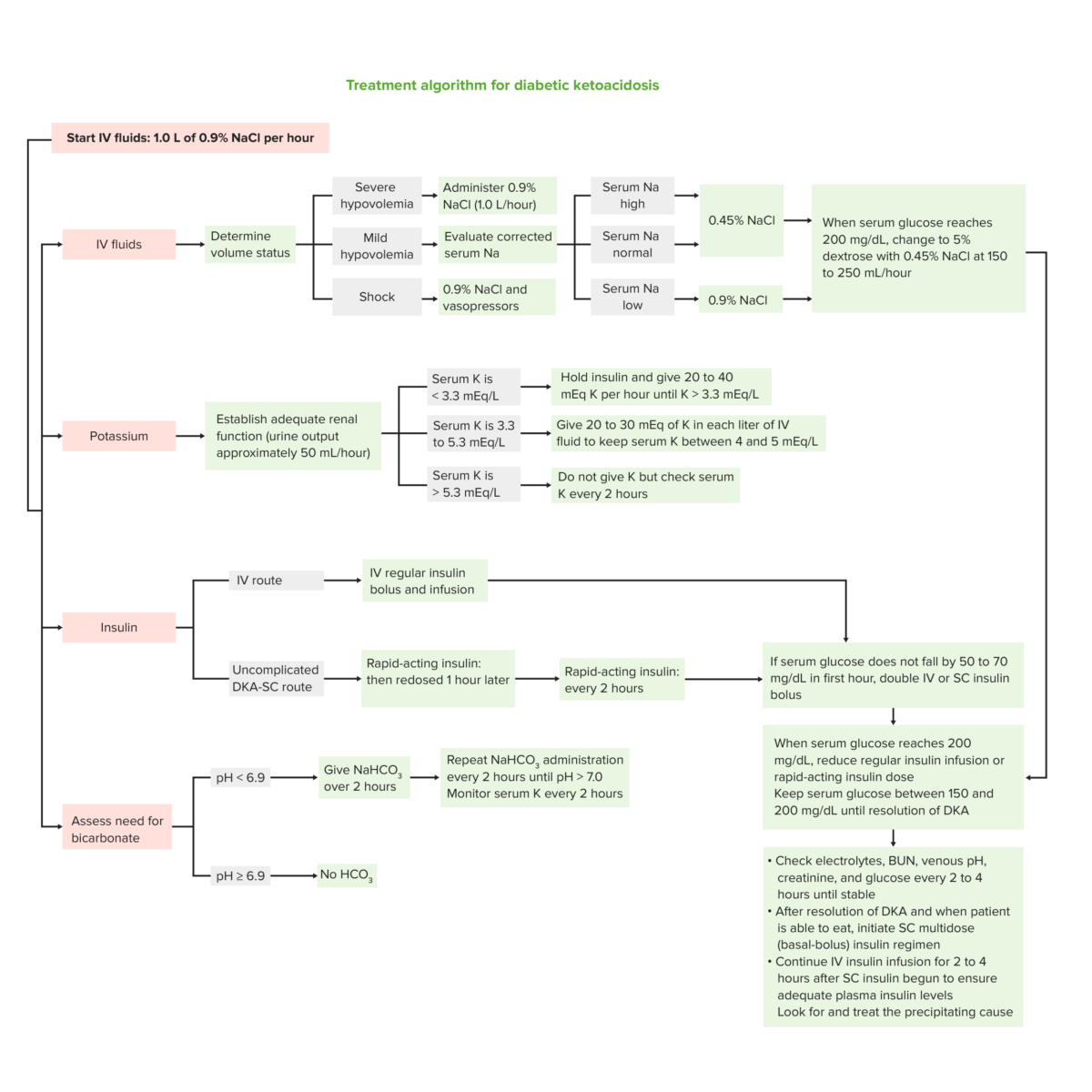
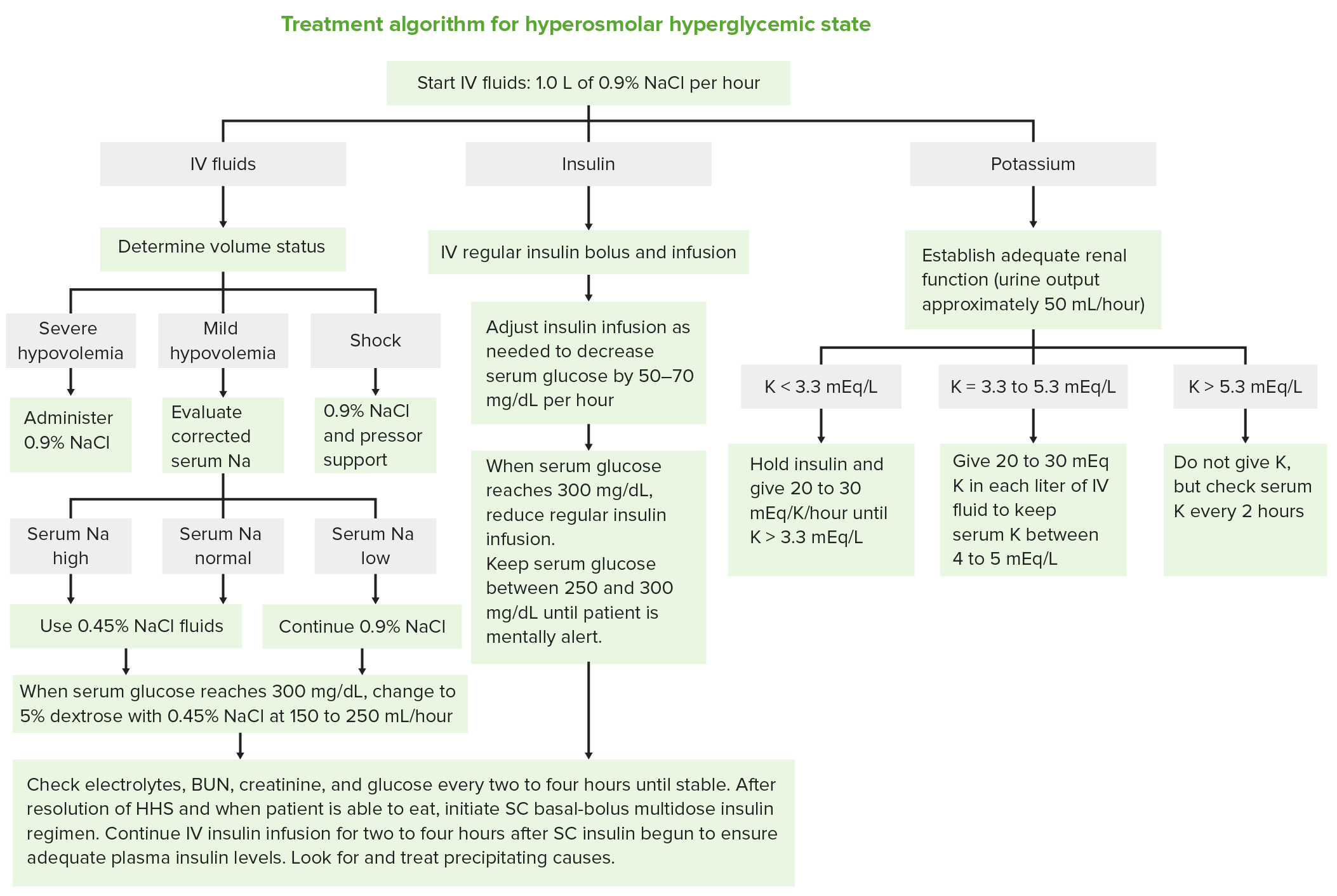
Algoritmo de tratamiento del estado hiperglucémico hiperosmolar
Imagen por Lecturio.