La colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis ulcerosa es una enfermedad inflamatoria idiopática que afecta a la superficie de la mucosa del colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy. Es un tipo de enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal, junto con la enfermedad de Crohn. El recto siempre está afectado, y la inflamación puede extenderse proximalmente por el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy. La colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis ulcerosa provoca friabilidad difusa, erosiones con hemorragia y pérdida de haustras, que son visibles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la endoscopia. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar diarrea con sangre, dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal tipo cólico, tenesmo y urgencia fecal. El diagnóstico se establece mediante endoscopia con biopsia y descartando otras causas de diarrea sanguinolenta. El tratamiento se realiza principalmente mediante mesalamina tópica, 6-mercaptopurina o colectomía para los LOS Neisseria casos graves. Las complicaciones incluyen colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis fulminante, megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon tóxico, perforación intestinal y aumento del riesgo de cáncer colorrectal.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Un mayor riesgo de desarrollar colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis ulcerosa puede estar asociado a lo siguiente
Se desconoce la fisiopatología exacta, pero es probable que esté asociada a una combinación de desregulación del epitelio intestinal y del sistema inmunitario.
La inflamación afecta invariablemente el recto y puede extenderse proximalmente por el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy de forma continua.
La presentación típica de la colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis ulcerosa es un trastorno recidivante que incluye lo siguiente:
| Características | Leve | Moderada | Severa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frecuencia de las heces por día | < 4 | 4–6 | > 6 |
| Síntomas |
|
|
|
| Toxicidad sistémica | Hallazgos normales:
|
Anomalías de laboratorio:
|
Anomalías de laboratorio:
|
| Velocidad de eritrosedimentación (VES) | < 20 | 20–30 | > 30 |
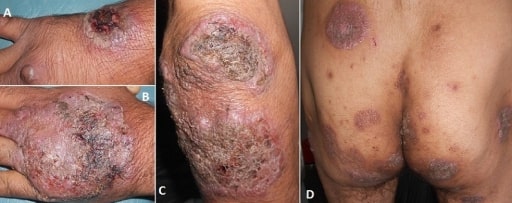
Pioderma gangrenoso
Imagen: “Vegetating idiopathic pyoderma gangrenosum” por Service de Dermatologie, CHU Ibn Sina, Rabat, Maroc. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Estudios de laboratorio:
Estudios de heces: pueden utilizarse para excluir otras causas de diarrea inflamatoria (e.g., infección)
Imágenes abdominales:
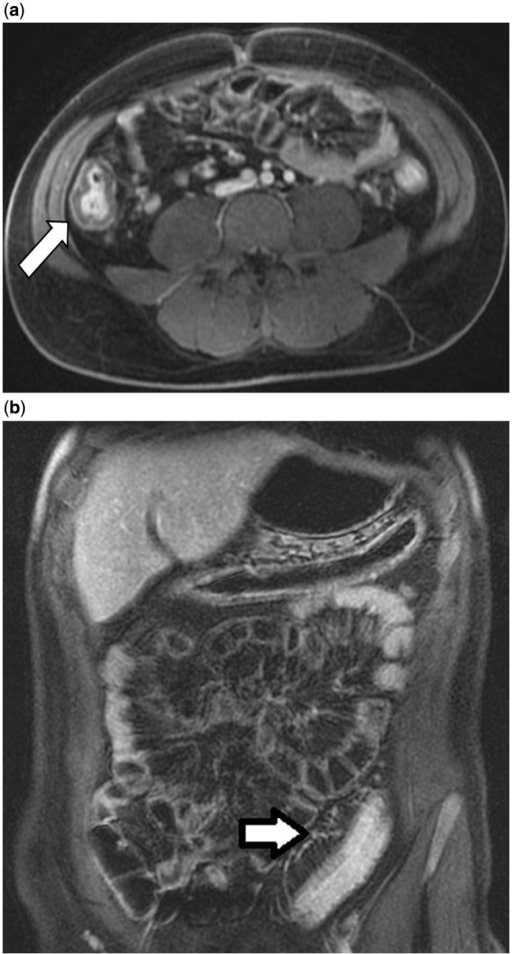
Enterografía por resonancia magnética en un varón de 24 años con colitis ulcerosa. 4a: engrosamiento de la pared colónica (flecha blanca) e hiperintensidad del colon derecho. 4b: engrosamiento de la vasa recta pericolónica (flecha blanca) con engrosamiento de la pared colónica e hiperintensidad en el colon sigmoide.
Imagen: “Magnetic resonance enterography” por Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Rochester MN, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0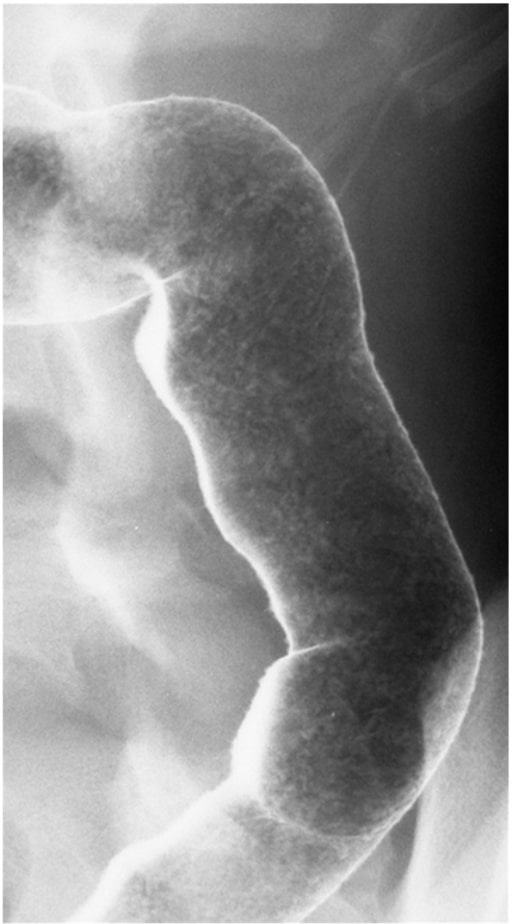
Enema de bario de doble contraste que ilustra la mucosa granular en un paciente con colitis ulcerosa activa
Imagen: “Double contrast barium enema” por Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Rochester MN, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0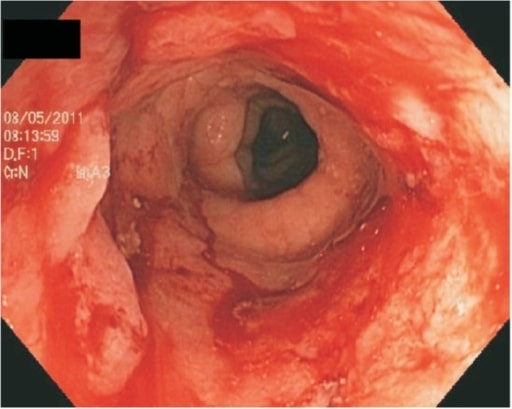
Vista endoscópica del colon que muestra una ulceración continua debida a una colitis ulcerosa grave
Imagen: “Ulcerative proctitis” por G.V. (Sonny) Montgomery VA Medical Center and Division of Digestive Diseases, Department of Medicine, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, MS, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0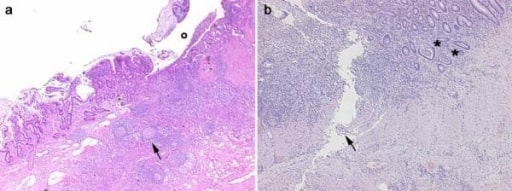
Imágenes histológicas obtenidas de 2 pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. Panel A, enfermedad de Crohn: en la sección transmural es claramente evidente una ulceración (o) en la mucosa y submucosa con infiltrados inflamatorios difusos, nódulos pseudofoliculares (flecha) y fibrosis de la pared intestinal. Panel B, colitis ulcerosa: la infiltración inflamatoria es más evidente en la mucosa y submucosa con abscesos de criptas (asteriscos). Es evidente una úlcera lineal serpiginosa (flecha).
Imagen: “Histological images obtained from two IBD patients enrolled in the study affected by CD” por Department of Surgery, Ospedale Maggiore di Milano, IRCCS, University of Milan, V. F. Sforza, 35 – 20122, Milan, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0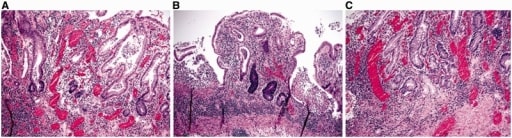
Características microscópicas de la colitis ulcerosa.
A y B: distorsión arquitectónica, incluyendo acortamiento de las criptas, variación en los tamaños y formas de las criptas y linfoplasmocitosis basal (A y B: tinción hematoxilina y eosina; 100X).
C: metaplasia de células de Paneth y metaplasia de la glándula pilórica en el colon izquierdo (tinción hematoxilina y eosina; 100X).
Las terapias médicas para la colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis ulcerosa dependen de la gravedad de la enfermedad. Los LOS Neisseria dos objetivos terapéuticos principales son:
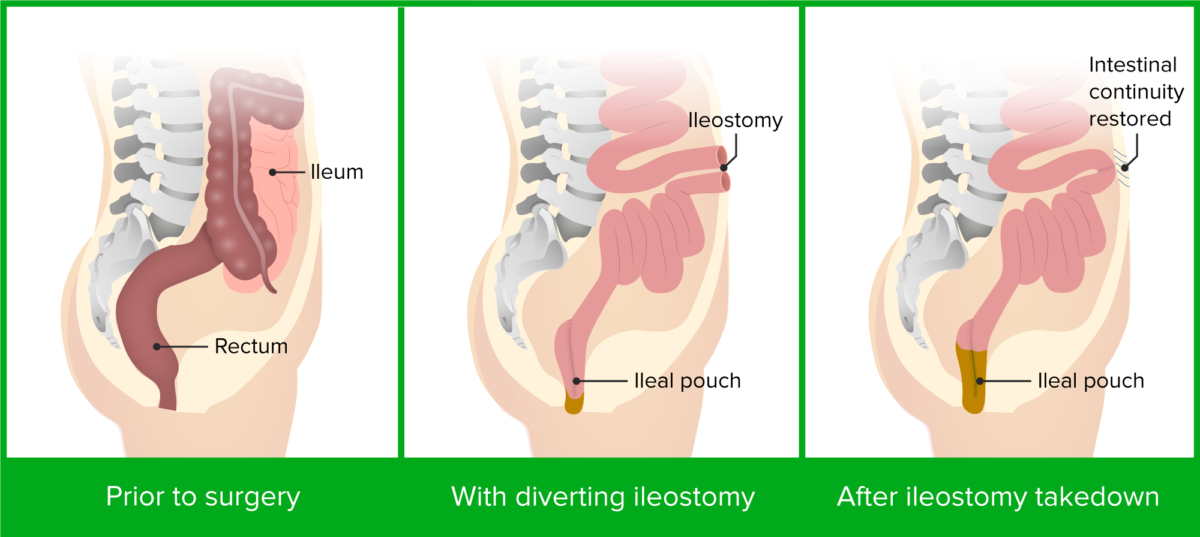
Colectomía y anastomosis en bolsa ileal-anal
Imagen por Lecturio.Las siguientes afecciones son diagnósticos diferenciales de la colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis ulcerosa:
| Enfermedad de Crohn | Colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis ulcerosa | |
|---|---|---|
| Patrón de compromiso | Lesiones
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum parches
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum cualquier parte del tracto gastrointestinal:
|
Lesiones continuas:
|
| Síntomas gastrointestinales | Generalmente diarrea no sanguinolenta, a veces puede ser sanguinolenta | Diarrea con sangre
|
| Manifestaciones extraintestinales | Colelitiasis y nefrolitiasis con cálculos de oxalato de calcio | Colangitis esclerosante primaria |
|
||
| Complicaciones |
|
|
|
||
| Hallazgos macroscópicos | Inflamación transmural
|
Inflamación de la mucosa y submucosa
|
| Hallazgos microscópicos |
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
|