Ascaris Ascaris Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The infection, ascariasis, is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. Transmission occurs primarily via ingestion of water or food contaminated with Ascaris eggs. Most patients with ascariasis are asymptomatic. Ascaris/Ascariasis es un género de nemátodos parásitos. La infección, ascariasis Ascariasis Ascariasis is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. If symptomatic, characteristics typically follow 2 phases, which correlate with the migration of the parasite through the body. The early phase may include cough, dyspnea, and wheezing. The late phase typically includes abdominal discomfort, bloating, nausea, and intermittent diarrhea. Ascaris/Ascariasis, es causada con mayor frecuencia por A. lumbricoides A. lumbricoides A species of parasitic nematode that is the largest found in the human intestine. Its distribution is worldwide, but it is more prevalent in areas of poor sanitation. Human infection with a. Lumbricoides is acquired by swallowing fully embryonated eggs from contaminated soil. Ascaris/Ascariasis. La transmisión ocurre principalmente a través de la ingestión de agua o alimentos contaminados con huevos de Ascaris Ascaris Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The infection, ascariasis, is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. Transmission occurs primarily via ingestion of water or food contaminated with Ascaris eggs. Most patients with ascariasis are asymptomatic. Ascaris/Ascariasis. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes con ascariasis Ascariasis Ascariasis is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. If symptomatic, characteristics typically follow 2 phases, which correlate with the migration of the parasite through the body. The early phase may include cough, dyspnea, and wheezing. The late phase typically includes abdominal discomfort, bloating, nausea, and intermittent diarrhea. Ascaris/Ascariasis son asintomáticos. Si es sintomático, las características suelen seguir 2 fases, que se correlacionan con la migración del parásito a través del cuerpo. La fase temprana puede incluir tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, disnea y sibilancias. La fase tardía generalmente incluye molestias abdominales, distensión abdominal, náuseas y diarrea intermitente. Las infecciones graves pueden causar obstrucción intestinal y retraso del crecimiento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños. El diagnóstico se realiza recuperando un parásito adulto de las heces del paciente o encontrando huevos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las heces del paciente durante un examen microscópico. El tratamiento incluye terapia antihelmíntica con albendazol, mebendazol o pamoato de pirantel.
Last updated: Mar 13, 2025
Ascaris Ascaris Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The infection, ascariasis, is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. Transmission occurs primarily via ingestion of water or food contaminated with Ascaris eggs. Most patients with ascariasis are asymptomatic. Ascaris/Ascariasis es un género de nemátodos parásitos (helmintos redondos).
Adultos:
Huevos:
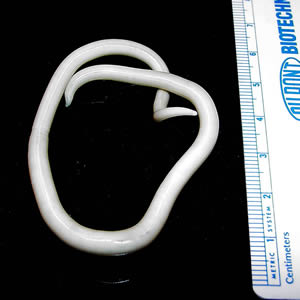
Helminto adulto Ascaris lumbricoides
Imagen: “An adult Ascaris lumbricoides worm” por CDC Division of Parasitic Diseases. Licencia: Dominio Público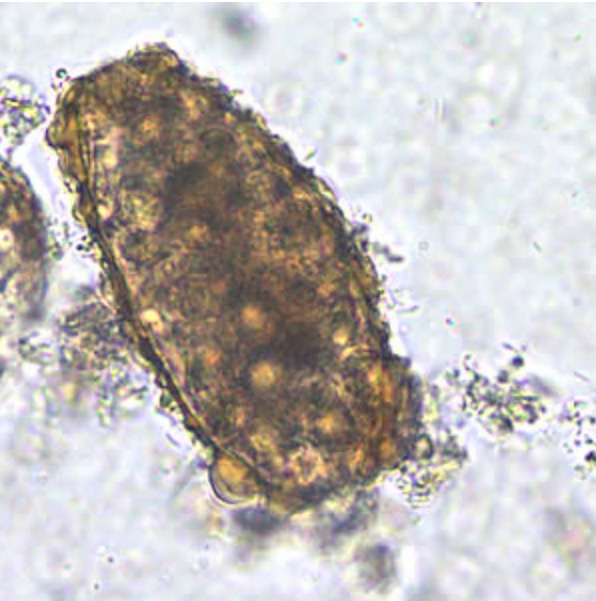
Huevo no fertilizado de Ascaris lumbricoides en una preparación húmeda sin teñir
Imagen:“Ascaris egg” por Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa ascariasis Ascariasis Ascariasis is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. If symptomatic, characteristics typically follow 2 phases, which correlate with the migration of the parasite through the body. The early phase may include cough, dyspnea, and wheezing. The late phase typically includes abdominal discomfort, bloating, nausea, and intermittent diarrhea. Ascaris/Ascariasis es causada por:
La ascariasis Ascariasis Ascariasis is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. If symptomatic, characteristics typically follow 2 phases, which correlate with the migration of the parasite through the body. The early phase may include cough, dyspnea, and wheezing. The late phase typically includes abdominal discomfort, bloating, nausea, and intermittent diarrhea. Ascaris/Ascariasis es una de las infecciones parasitarias más comunes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos.
A. lumbricoides A. lumbricoides A species of parasitic nematode that is the largest found in the human intestine. Its distribution is worldwide, but it is more prevalent in areas of poor sanitation. Human infection with a. Lumbricoides is acquired by swallowing fully embryonated eggs from contaminated soil. Ascaris/Ascariasis:
A. suum A. suum A species of parasitic nematode usually found in domestic pigs and a few other animals. Human infection can also occur, presumably as result of handling pig manure, and can lead to intestinal obstruction. Ascaris/Ascariasis:
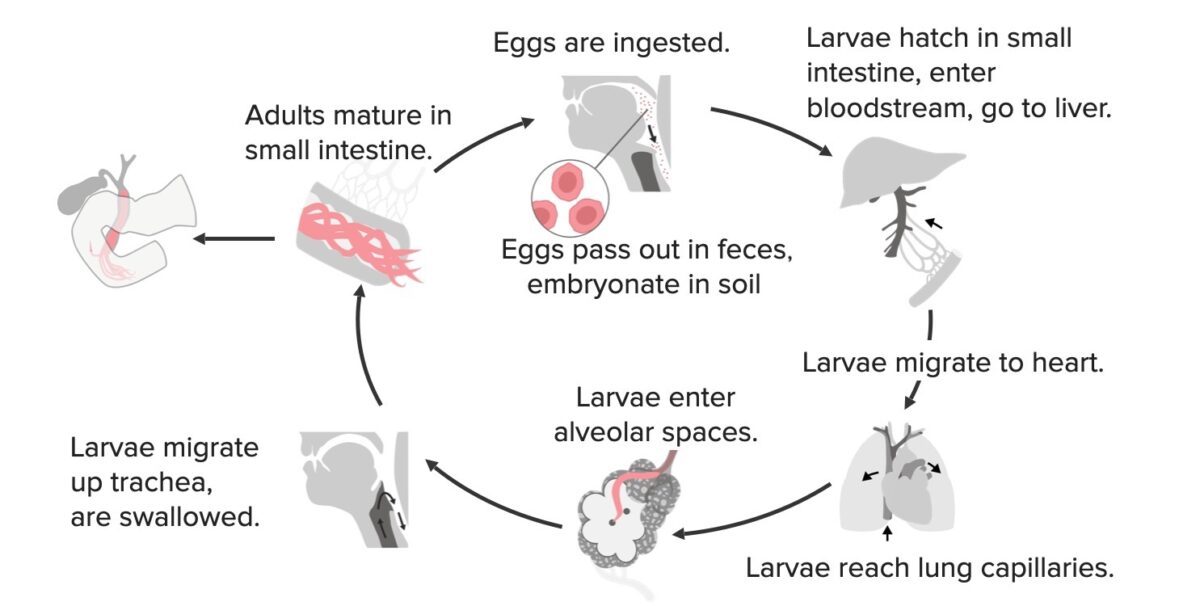
Diagrama que resume el ciclo de vida de Ascaris lumbricoides
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Efecto de la migración de larvas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria pulmones → síndrome de Löffler:
Efecto de los LOS Neisseria helmintos adultos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal:
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas del síndrome de Löffler incluyen:
Definitivo:
Evaluación de apoyo:
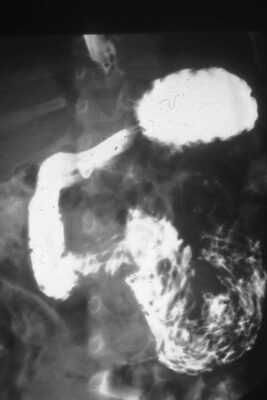
Una radiografía de abdomen con trago de bario en un paciente con ascariasis:
Los helmintos adultos aparecen en el duodeno como una masa enredada (áreas negras) dentro del blanco del medio de contraste.
| Organismo | Enterobius vermicularis Enterobius Vermicularis Enterobius/Enterobiasis | Toxocara canis Toxocara canis A species of parasitic nematode found in the intestine of dogs. Lesions in the brain, liver, eye, kidney, and lung are caused by migrating larvae. In humans, these larvae do not follow normal patterns and may produce visceral larva migrans (larva migrans, visceral). Toxocariasis | Ascaris Ascaris Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The infection, ascariasis, is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. Transmission occurs primarily via ingestion of water or food contaminated with Ascaris eggs. Most patients with ascariasis are asymptomatic. Ascaris/Ascariasis lumbricoides | Strongyloides stercoralis Strongyloides stercoralis A species of parasitic nematode widely distributed in tropical and subtropical countries. The females and their larvae inhabit the mucosa of the intestinal tract, where they cause ulceration and diarrhea. Strongyloidiasis | Trichinella spiralis Trichinella spiralis A parasite of carnivorous mammals that causes trichinellosis. It is especially common in rats and in swine fed uncooked garbage. Human infection is initiated by the consumption of raw or insufficiently cooked pork or other meat containing the encysted larvae. Trichinella/Trichinellosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reservorio | Humanos | Perros | Humanos |
|
Cerdos |
| Transmisión | Fecal-oral | Fecal-oral | Fecal-oral | Contacto de la piel con tierra contaminada | Comer carne cruda o poco cocida |
| Hallazgos clínicos |
|
|
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
Análisis de heces |
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
|
|
|
|
| Prevención | Buena higiene |
|
|
|
Vista microscópica de baja potencia de Enterobius vermicularis
Imagen: “Enterobius vermicularis, under low power” por Kaniyarakkal V et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
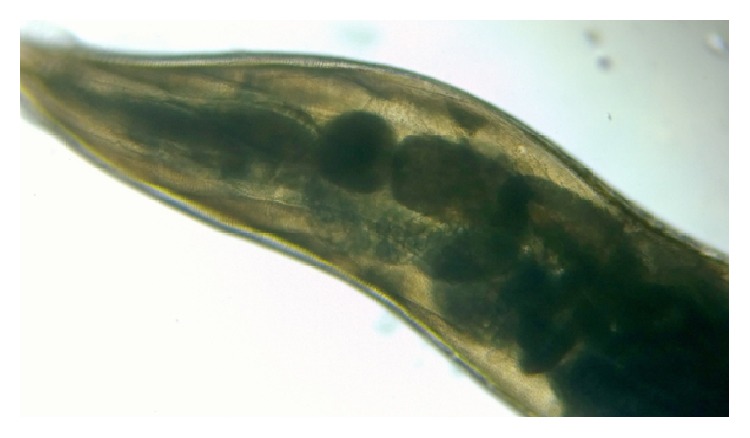
Helminto adulto Ascaris lumbricoides
Imagen: “An adult Ascaris lumbricoides worm” por CDC Division of Parasitic Disease. Licencia: Dominio Público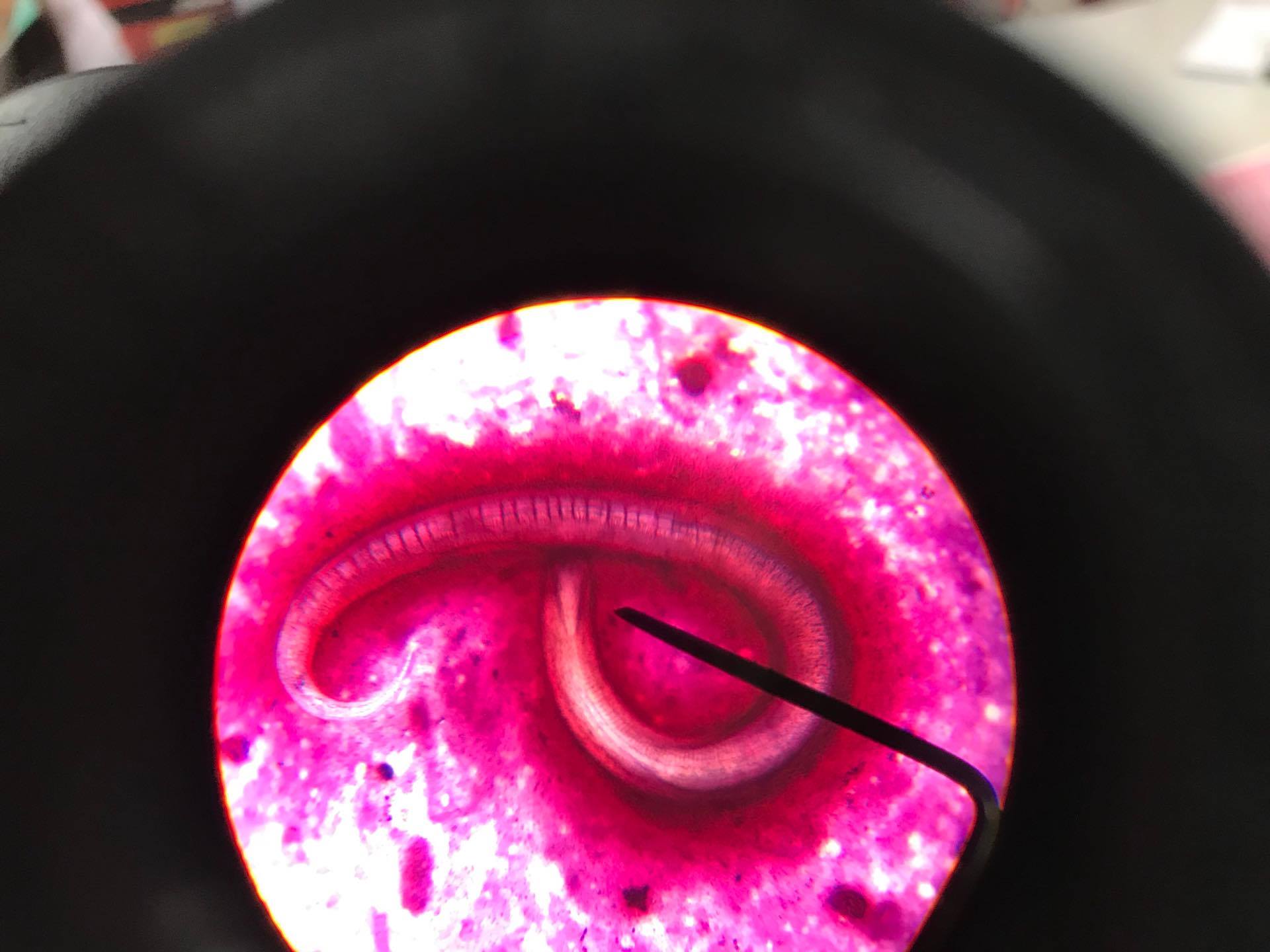
Parásito Strongyloides stercoralis
Imagen: “Strongyloides stercoralis in sputum” por CDC Division of Parasitic Diseases. Licencia: CC BY 4.0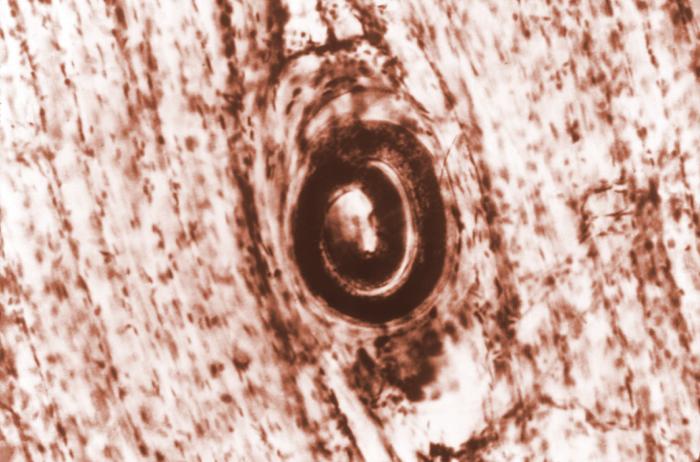
Quiste de Trichinella spiralis incrustado en tejido muscular en un caso de triquinelosis:
La triquinelosis se adquiere al ingerir carne que contiene quistes (larvas enquistadas) del parásito nemátodo.