El tobillo es una articulación sinovial en bisagra formada entre las superficies articulares de la tibia distal, el peroné distal y el astrágalo. El tobillo permite principalmente la flexión plantar y la dorsiflexión del pie. La articulación subastragalina y los otros huesos del tarso crean muchas articulaciones sinérgicas, lo que permite un amplio rango de movimiento—flexión plantar, dorsiflexión, eversión, inversión, abducción y aducción. Los movimientos son generados por grandes grupos de músculos que se originan en la pierna y se insertan y actúan sobre los huesos del pie y el tarso.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El tobillo es una articulación sinovial que consta de articulaciones entre la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy, el peroné y el astrágalo, reforzadas por los LOS Neisseria ligamentos medial, lateral y sindesmótico. Generalmente, la articulación del tobillo tiene una forma más ancha superior y anteriormente para acomodar el astrágalo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de cuña, lo que contribuye a la estabilidad de la articulación.
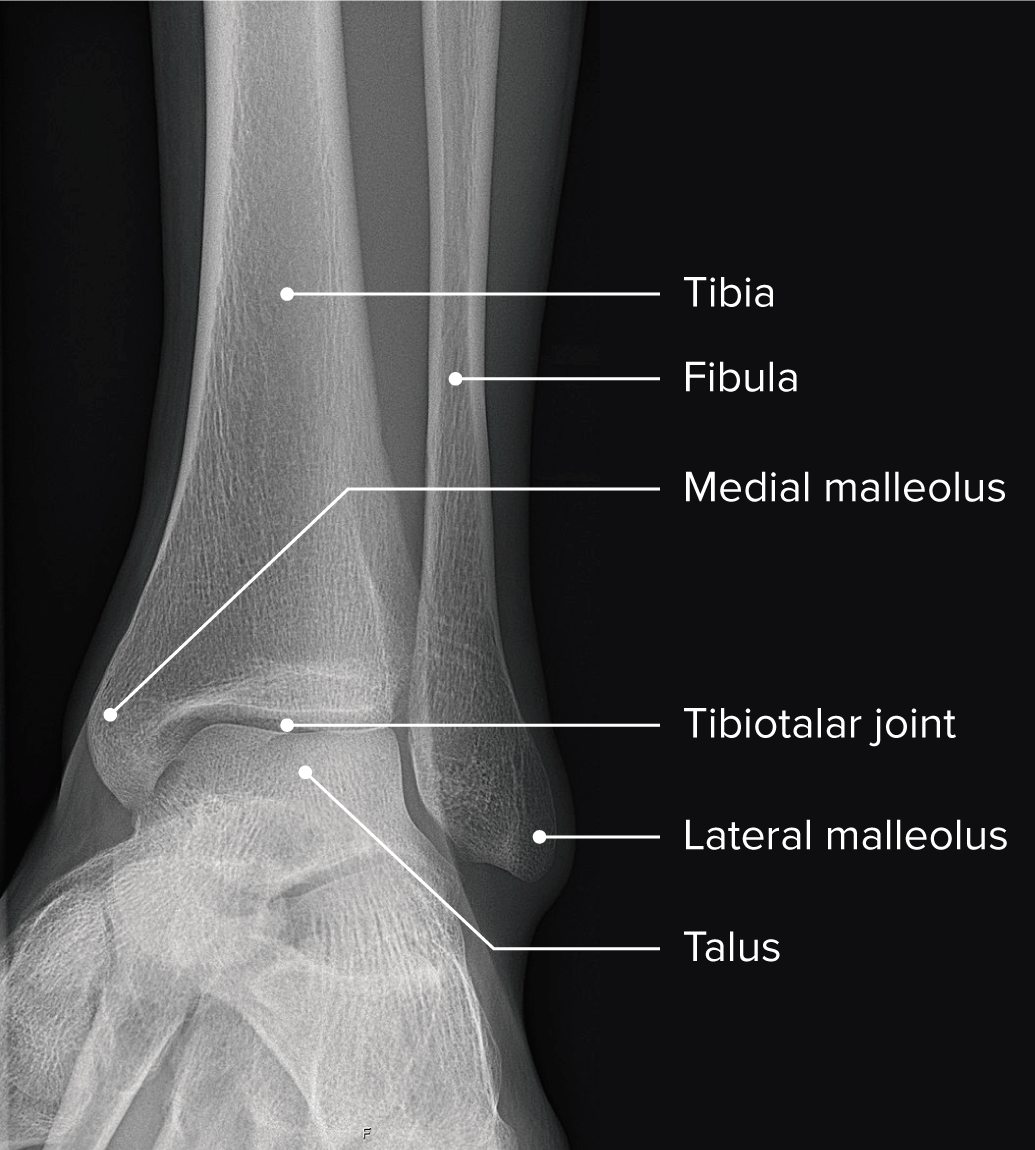
Radiografía del tobillo que muestra la anatomía normal del tobillo y la relación de los huesos y las articulaciones
Imagen por Lecturio.La tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy, el peroné y el astrágalo forman la articulación del tobillo y, junto con las articulaciones subastragalina y astragalina, contribuyen al AL Amyloidosis movimiento coordinado del tobillo.
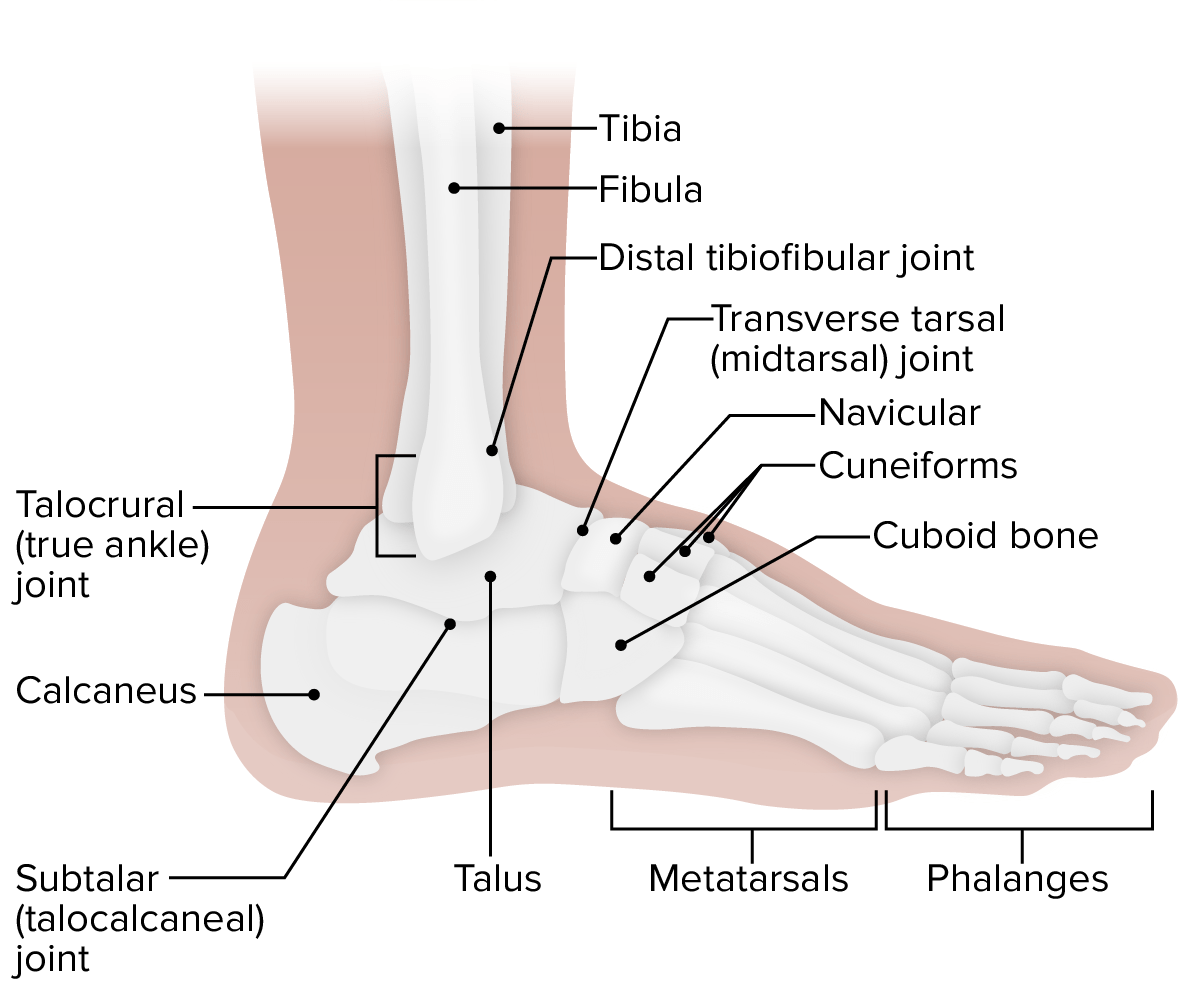
Vista lateral del tobillo: obsérvese las 4 articulaciones diferentes que funcionan sinérgicamente para lograr el rango completo de movimiento del tobillo.
Imagen por Lecturio.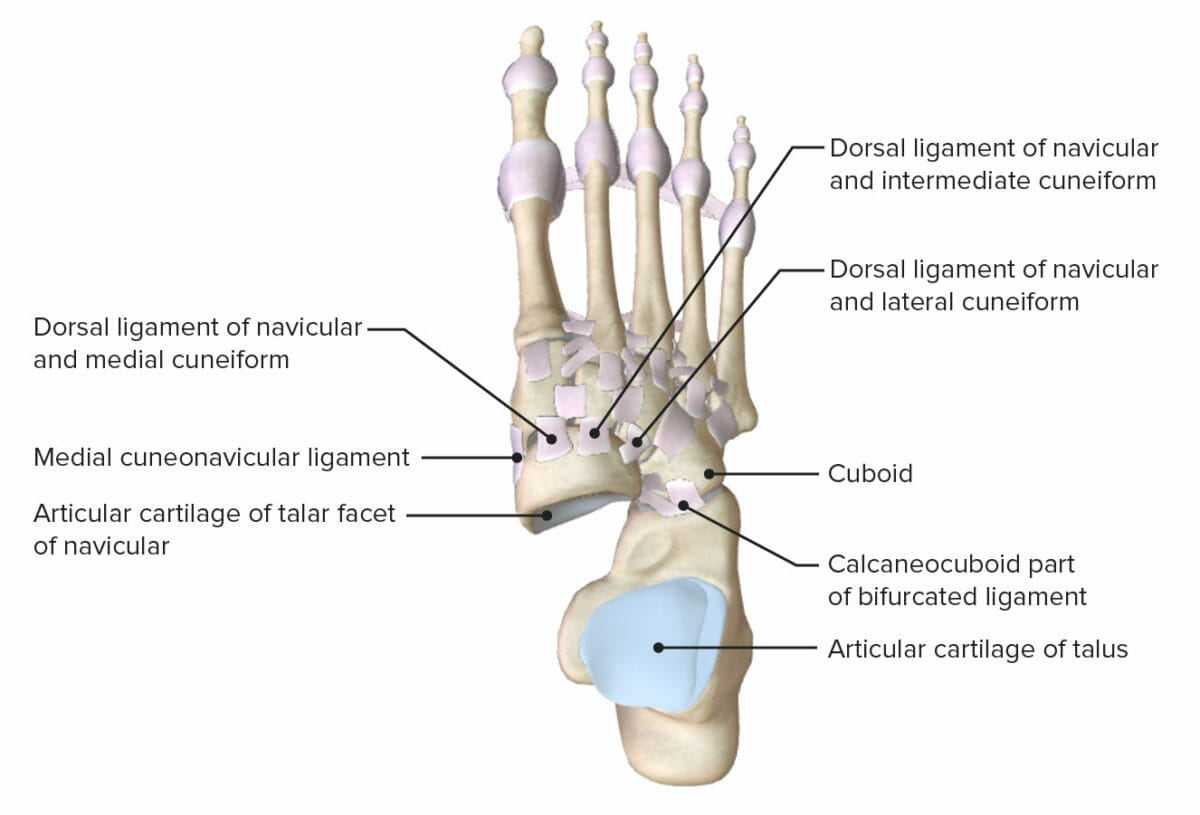
Vista superior del tobillo con el astrágalo extraído, que muestra las superficies articulares y los ligamentos de soporte de las articulaciones subastragalina y transversa del tarso
Imagen por Lecturio.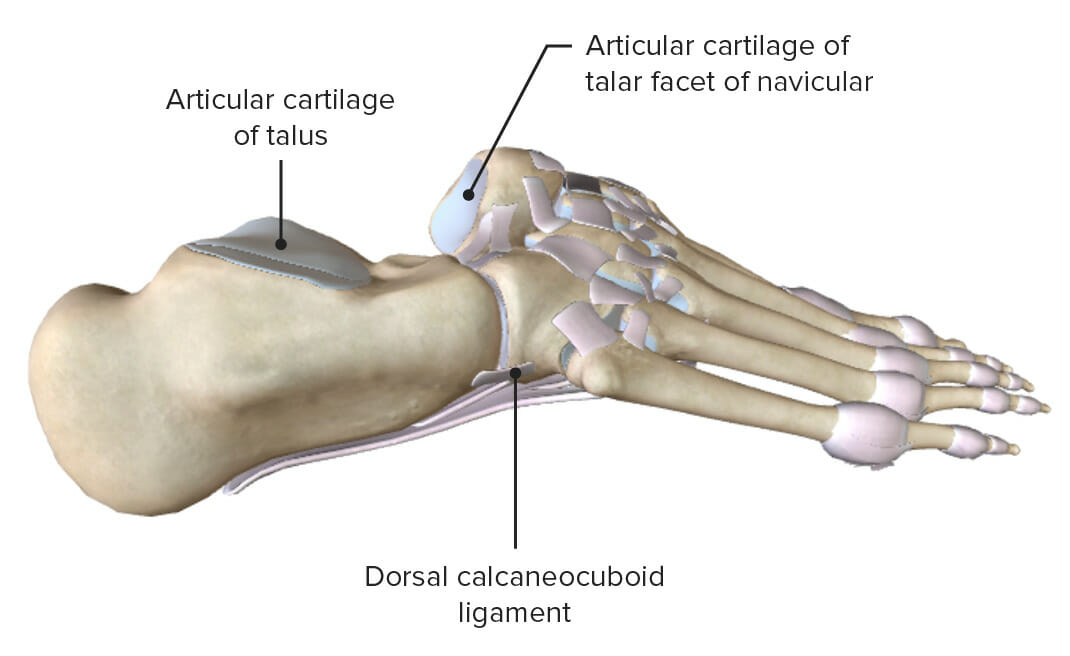
Vistas laterales (derecha) del tobillo con el astrágalo extraído, que muestran las superficies articulares y los ligamentos de soporte de las articulaciones subastragalina y transversa del tarso.
Imagen por Lecturio.Existen varios complejos de ligamentos principales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tobillo para proporcionar estabilidad y soporte.
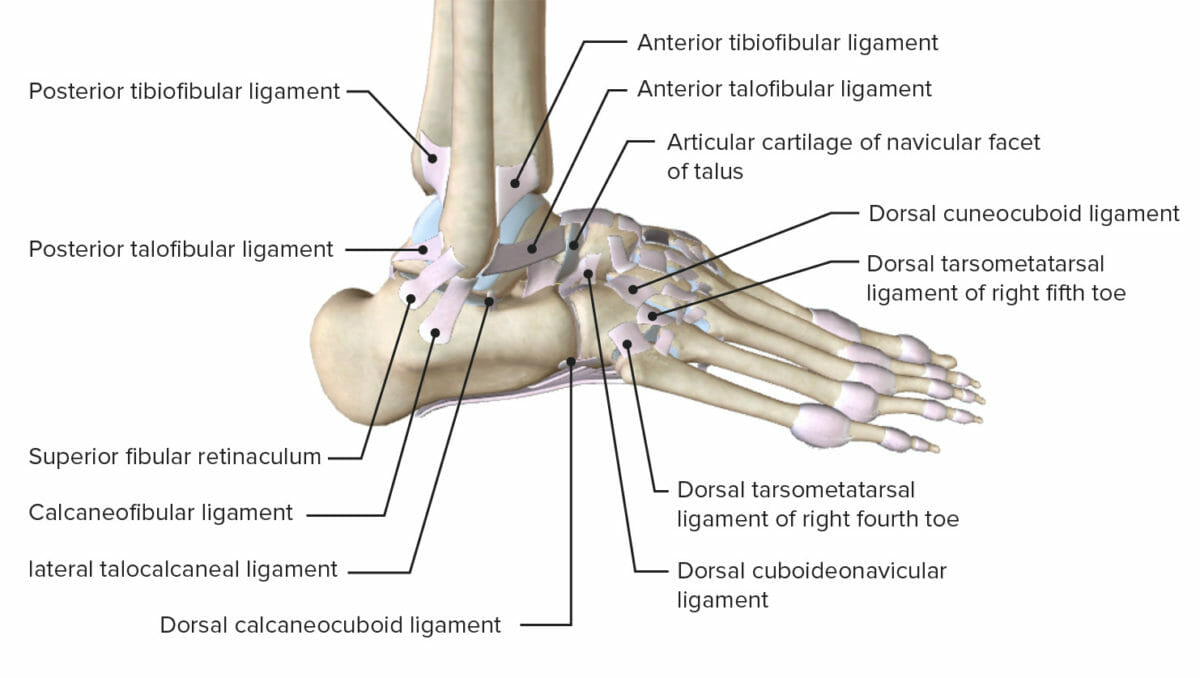
Vista lateral del tobillo con los ligamentos de soporte de las articulaciones astragalocrural y subastragalina
Imagen por Lecturio.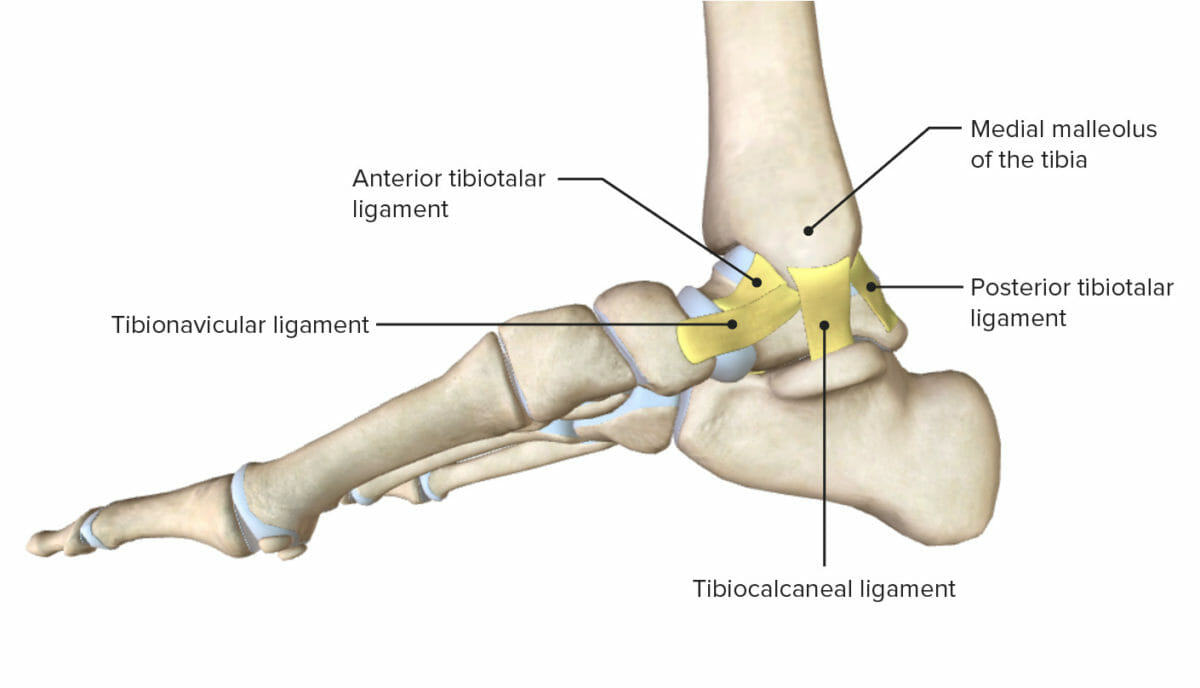
Vista medial del tobillo destacando los diversos ligamentos de la articulación medial del tobillo
Imagen por Lecturio.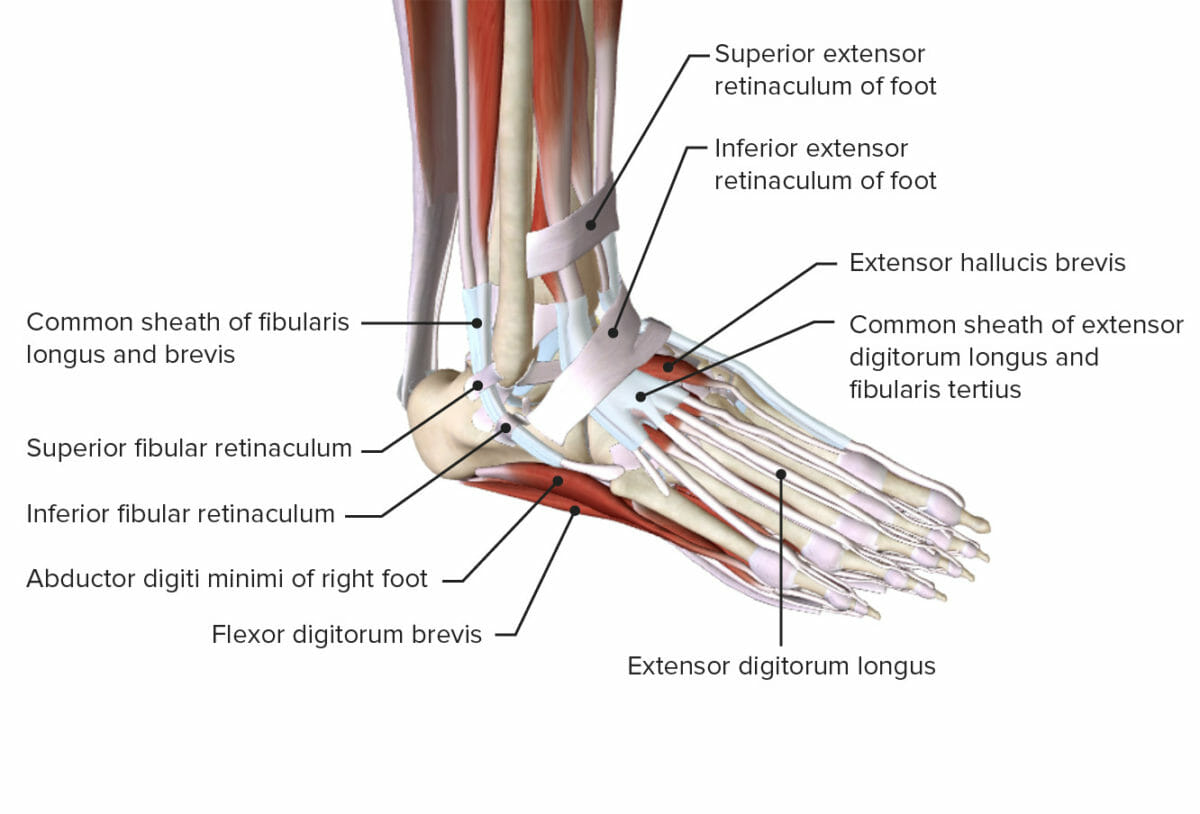
Vista oblicua del tobillo que muestra los retináculos y varios músculos
Imagen por Lecturio.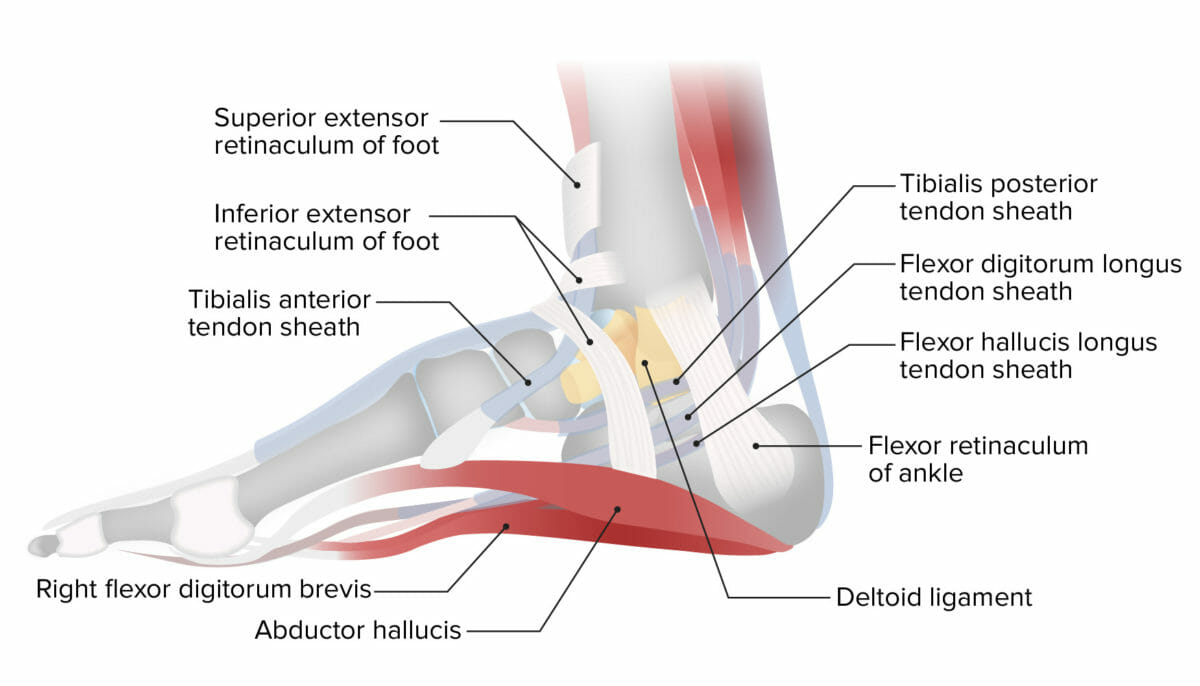
Proyección lateral del tobillo que muestra el retináculo medial del tobillo
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria músculos de la pierna se insertan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria huesos del tobillo para crear movimiento y este ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria planos cardinales.
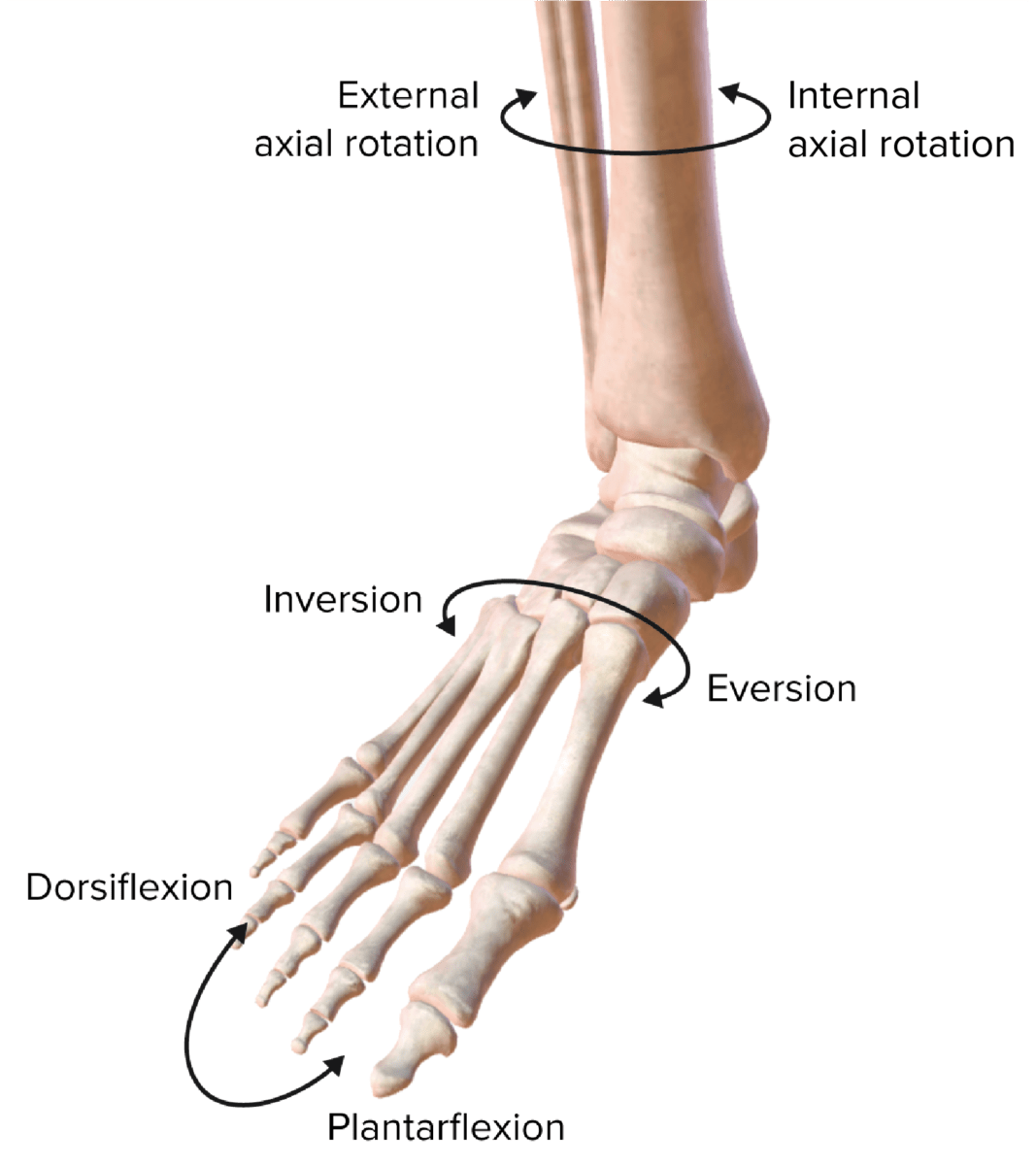
Los planos de movimiento de la articulación del tobillo
Imagen por Lecturio.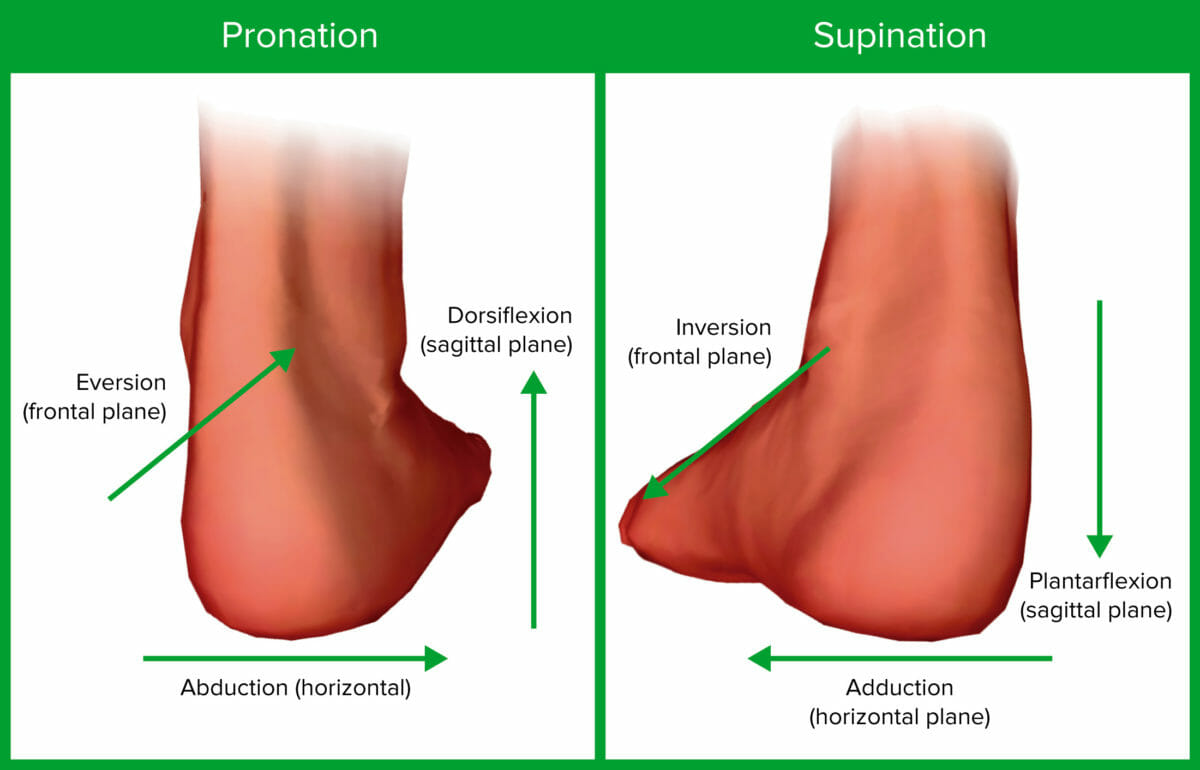
Los diversos planos y movimientos de la articulación del tobillo
Imagen por Lecturio.| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Acción | Inervación |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibial anterior |
|
Superficie interior del cuneiforme medial | Dorsiflexión | Nervio peroneo (fibular) profundo |
| Extensor largo del hallux |
|
Falange distal del hallux | Dorsiflexión | Nervio peroneo (fibular) profundo |
| Extensor largo de los LOS Neisseria dedos |
|
Falanges media y distal 2–5 | Dorsiflexión | Nervio peroneo (fibular) profundo |
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Acción | Inervación |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peroneo largo | Parte supero-lateral del peroné | 1er metatarsiano, cuneiforme medial |
Flexión plantar,
eversión |
Peroneo superficial |
| Peroneo corto | Eje distal del peroné | Extremo proximal del 5to metatarsiano | Flexión plantar,
eversión |
Peroneo superficial |
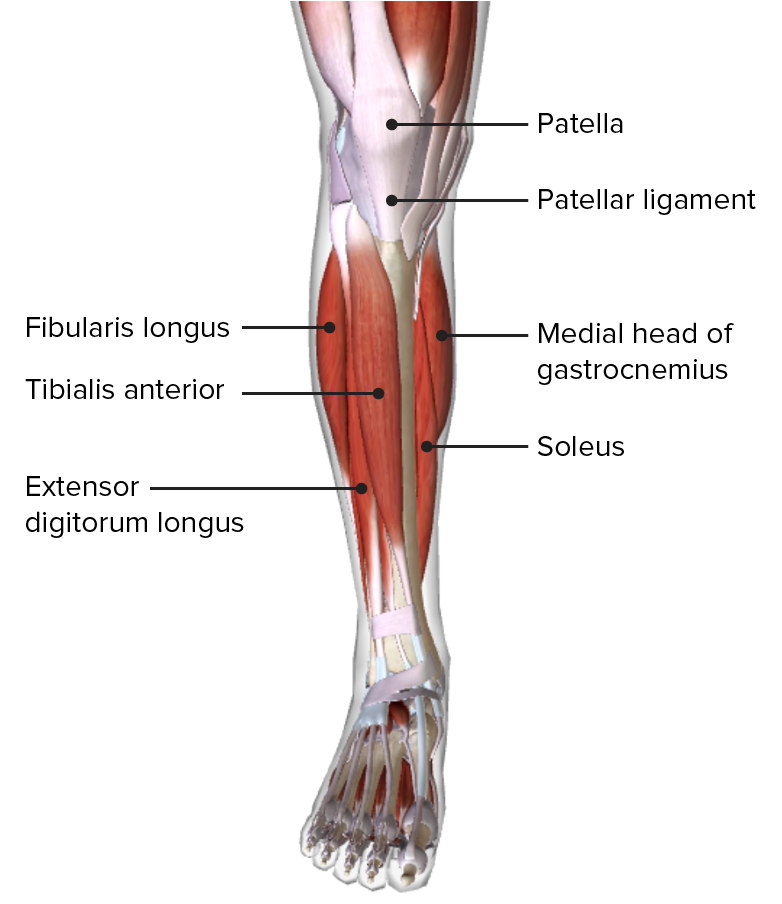
Vista anterior de la pierna, mostrando los músculos del compartimento anterior y sus relaciones con otros músculos y entre sí
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio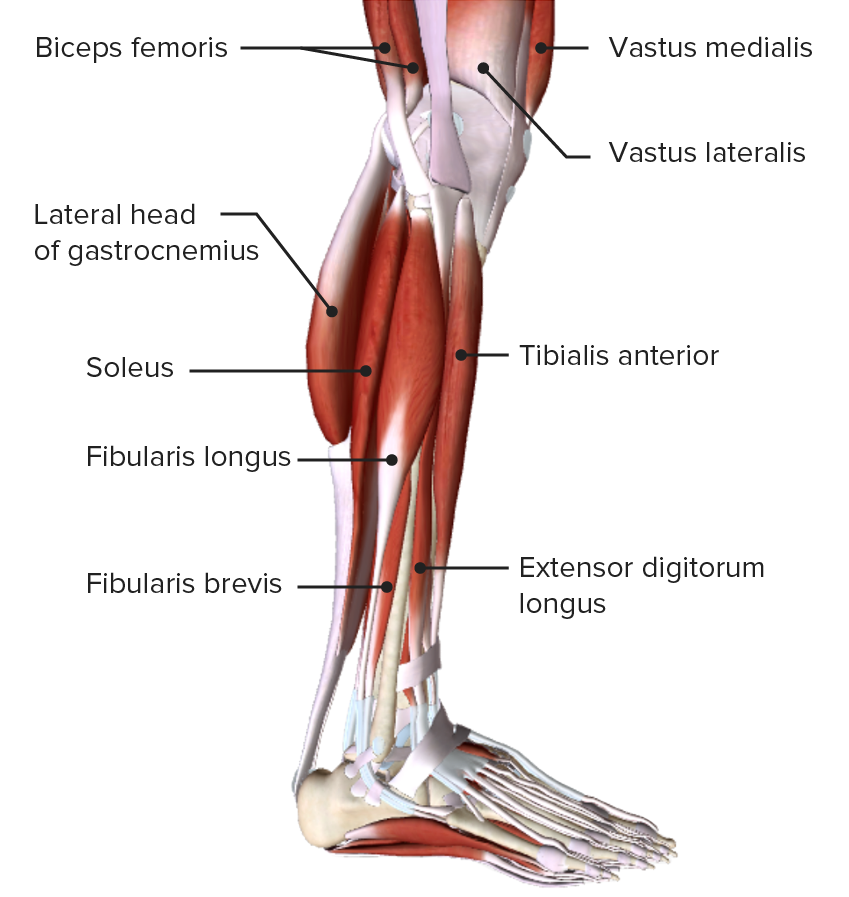
Vista lateral de la pierna, mostrando los músculos del compartimiento lateral o eversor y sus relaciones con otros músculos y entre sí
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Acción | Inervación |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrocnemio | Cóndilos medial y lateral | Calcáneo posterior | Flexión plantar | Nervio tibial |
| Sóleo | Tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy superior, peroné, membrana interósea | Calcáneo posterior | Flexión plantar | Nervio tibial |
| Plantar | Fémur posterior por encima del cóndilo lateral | Tendón calcáneo o calcáneo | Flexión plantar | Tibial desde ramas anteriores S1 S1 Heart Sounds– S2 S2 Heart Sounds |
| Tibial posterior | Tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy y peroné superiores, membrana interósea | Varios tarsianos y metatarsianos 2–4 | Inversión y flexión plantar | Nervio tibial |
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Acción | Inervación |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexor largo de los LOS Neisseria dedos | Tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy posterior | Falanges distales 2–5 | Flexión plantar, inversión | Nervio tibial |
| Flexor largo del hallux | Parte media del peroné, membrana interósea | Falange distal del hallux | Flexión plantar, inversión | Nervio tibial |
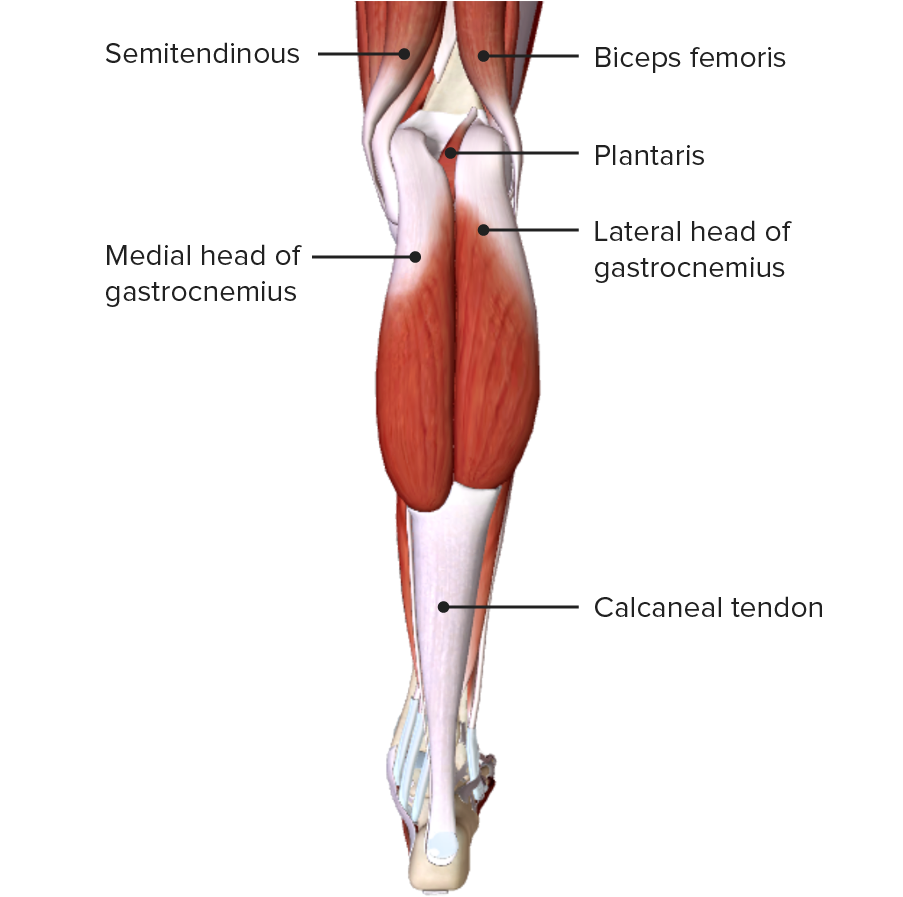
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando los músculos gastrocnemios de la capa superficial del compartimento posterior
Imagen por BioDigita, editado por Lecturio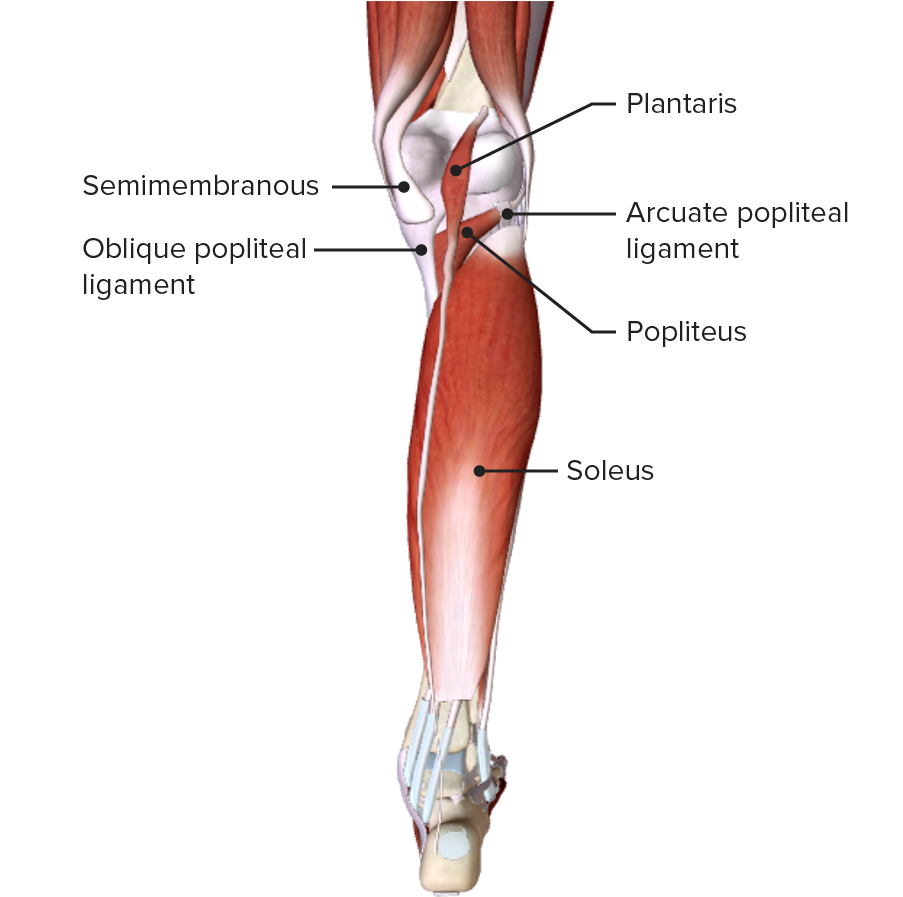
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando los músculos plantar y sóleo de la capa superficial del compartimento posterior
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio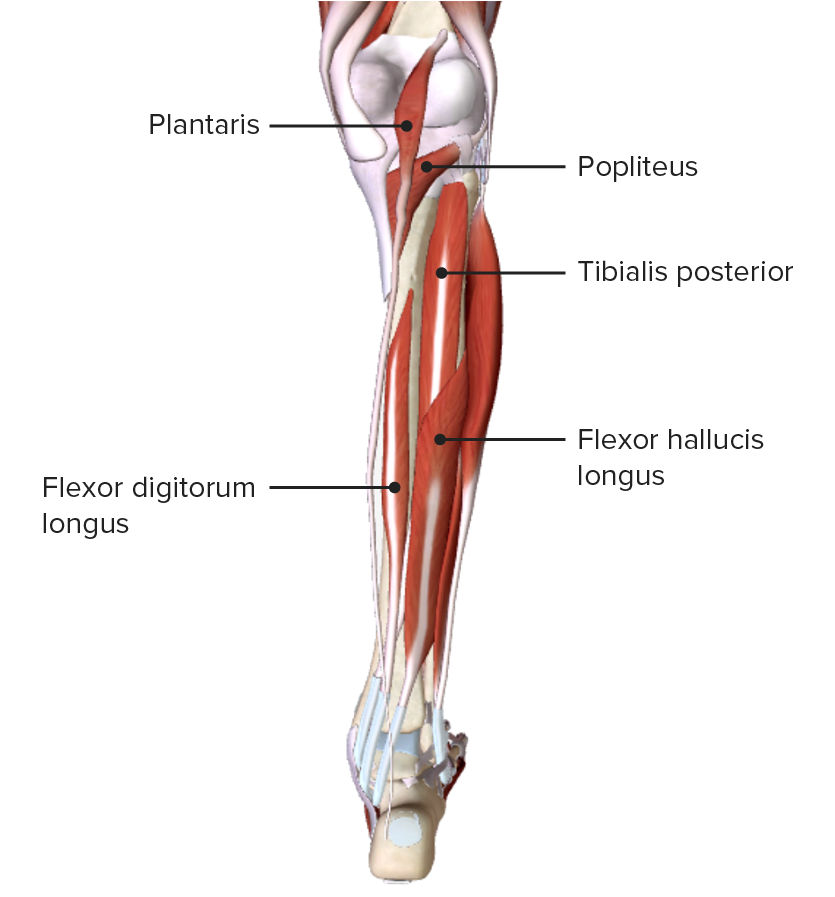
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando los músculos de la capa profunda del compartimiento posterior y sus relaciones espaciales con otros músculos y entre sí
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio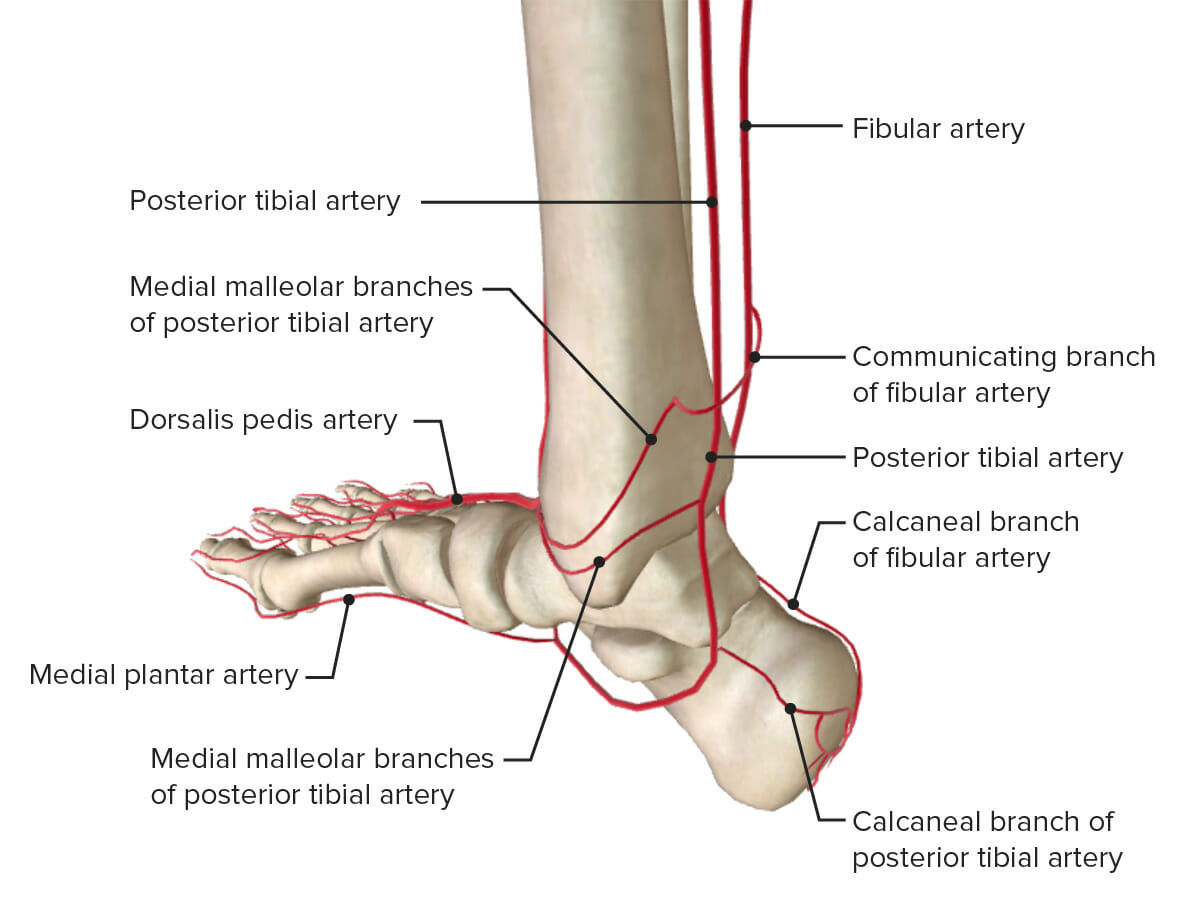
La irrigación arterial del tobillo: obsérvese que la arteria tibial anterior se muestra como su continuación, la arteria dorsal del pie.
Imagen por Lecturio.La inervación del tobillo la proporcionan las raíces desde el nivel L4 a S2 S2 Heart Sounds de la médula espinal. Los LOS Neisseria siguientes nervios también dan ramas a la articulación del tobillo:
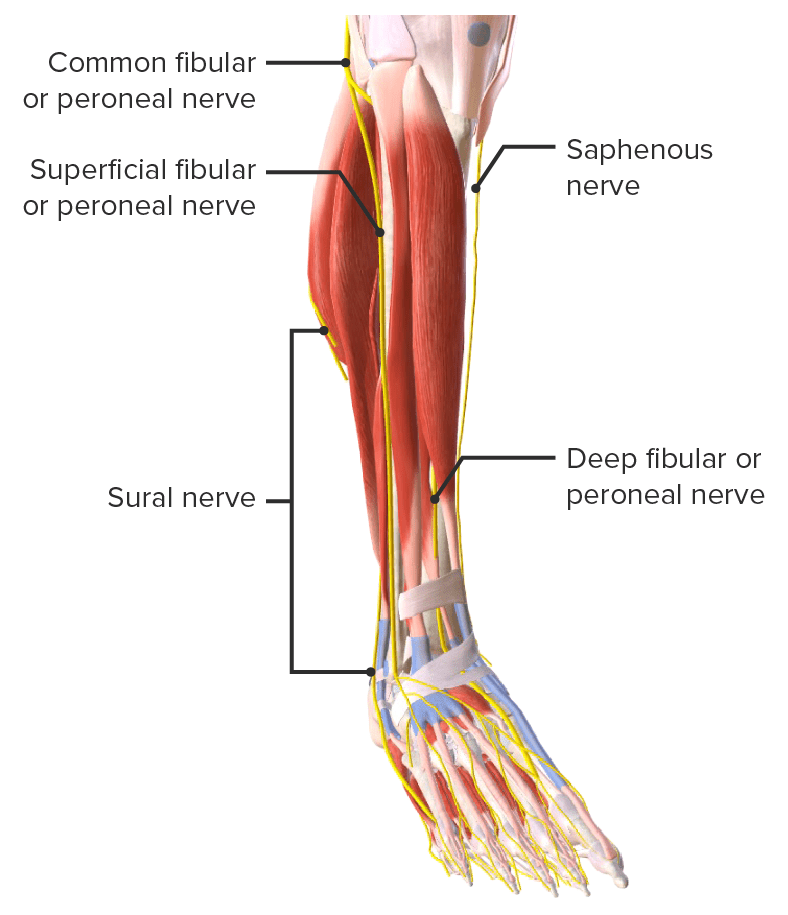
Vista anterior de los nervios de la articulación del tobillo
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio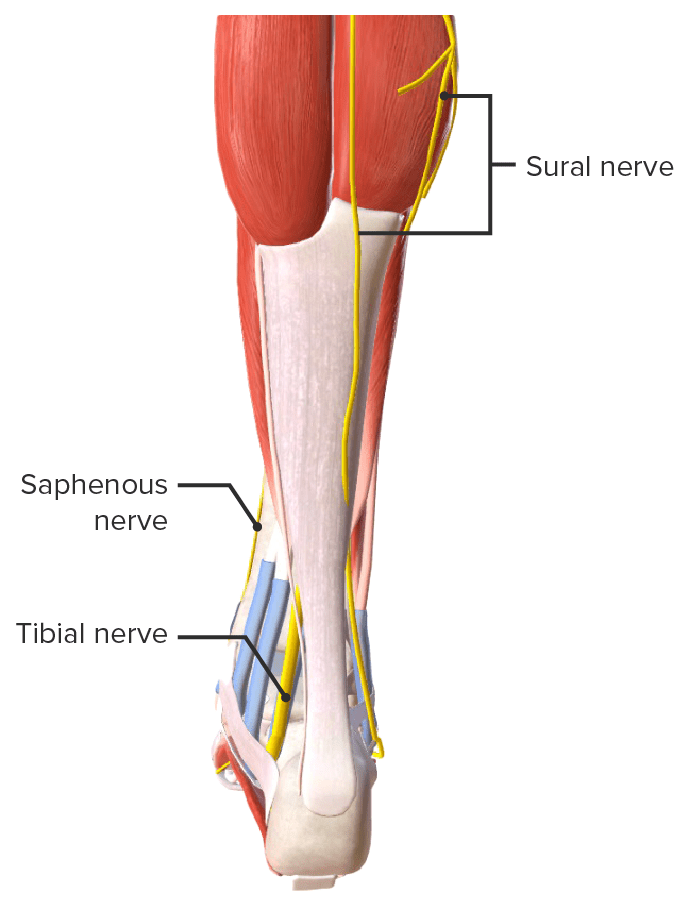
Vista posterior de los nervios de la articulación del tobillo
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio