Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos antimetabolitos quimioterapéuticos pertenecen a los LOS Neisseria medicamentos específicos del ciclo celular, que actúan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una fase específica del ciclo celular. Las células cancerosas se dividen (o ciclan) más rápidamente que las células normales, lo que las convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un objetivo fácil para la quimioterapia. Las diferentes fases del ciclo celular incluyen G1, S, G2 y M. Los LOS Neisseria antimetabolitos se dirigen a la fase S, cuando se produce la replicación del ADN, lo que inhibe la síntesis de ADN de las células tumorales. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum este grupo, los LOS Neisseria medicamentos incluyen antifolatos (que bloquean la actividad del ácido fólico, un componente esencial de los LOS Neisseria precursores de ADN y ARN), análogos de pirimidina y purina (que interfieren con el proceso de síntesis de ADN) e inhibidores de la ribonucleótido reductasa (que reducen la producción de desoxirribonucleótidos). Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos quimioterapéuticos específicos del ciclo celular no pueden diferenciar las células sanas de las cancerosas, por lo que se observan efectos secundarios. La mielosupresión es un hallazgo común durante el tratamiento.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
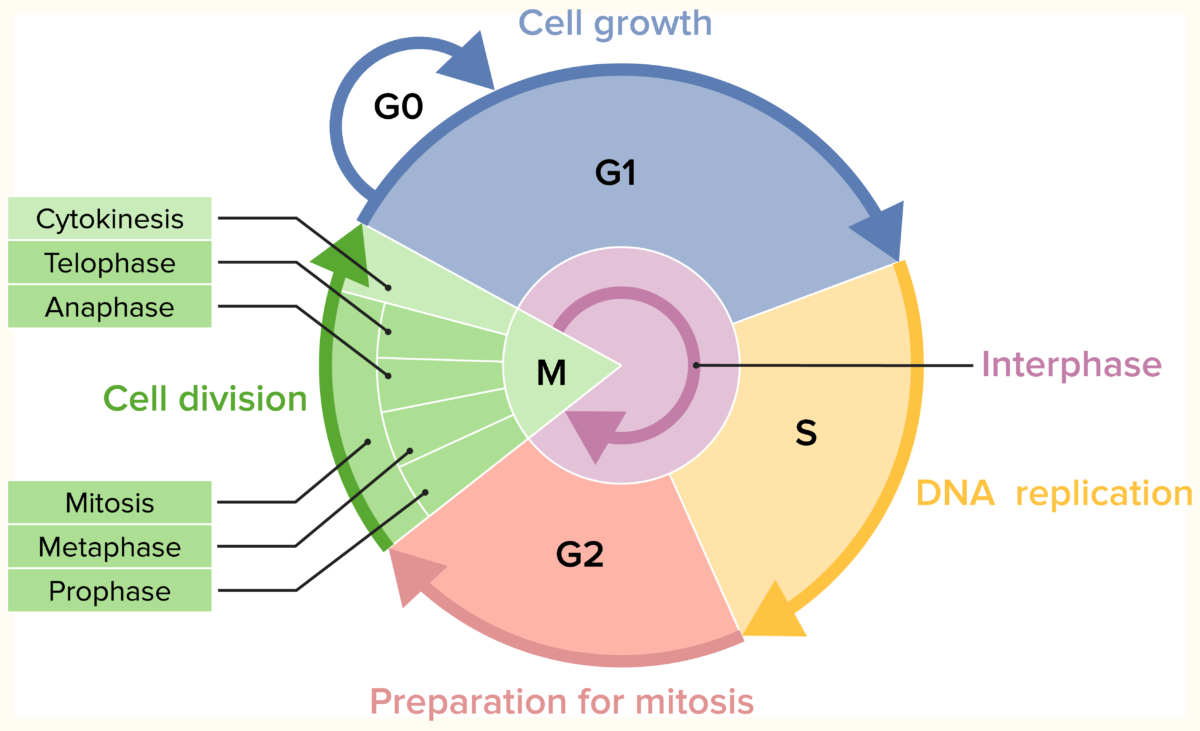
Fases del ciclo celular
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria subtipos de agentes de quimioterapia con antimetabolitos son:
| Medicamento | Mecanismo de acción | Indicaciones etiquetadas | Efectos secundarios | Consideraciones adicionales |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metotrexato | Inhibe la dihidrofolato reductasa |
|
|
Añadir leucovorina para rescatar a las células de la toxicidad. |
| Pemetrexed Pemetrexed A guanine-derived antineoplastic agent that functions as a nucleic acid synthesis inhibitor through its binding to, and inhibition of, thymidylate synthase. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy | Inhibe:
|
|
|
Agregar vitamina B12 y folato para ↓ toxicidad. |
| Pralatrexato |
|
Linfoma periférico de linfocitos T |
|
Agregar vitamina B12 y folato a ↓ toxicidad |
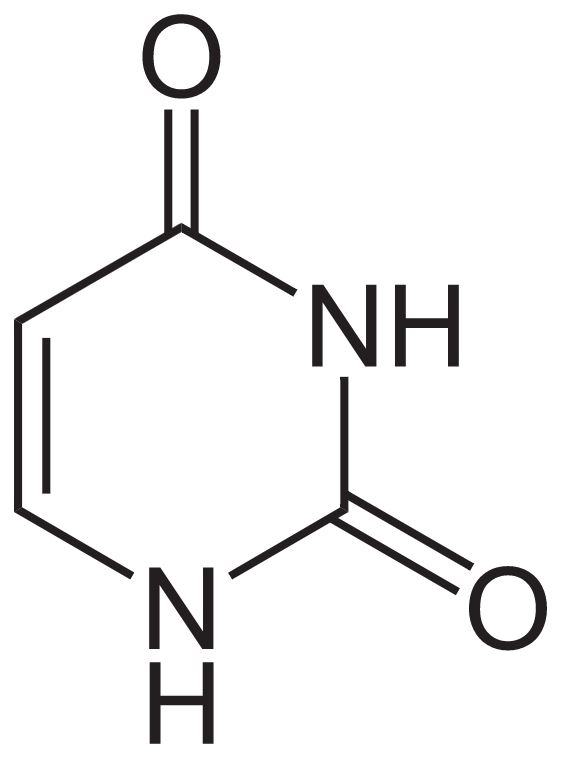
Estructura del uracilo
Imagen: “Uracil” por NEUROtiker. Licencia: Dominio Público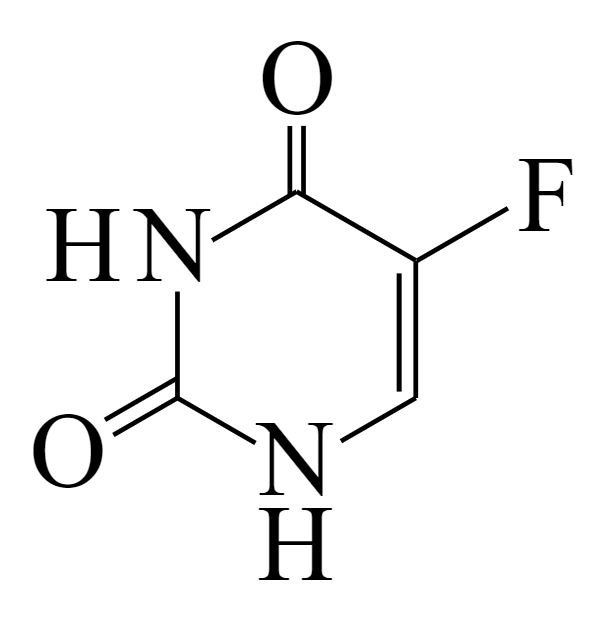
Estructura del 5-fluorouracilo
Imagen: “5-fluorouracil” por すじにくシチュー. Licencia: CC0 1.0
Estructura de la capecitabina
Imagen por Lecturio.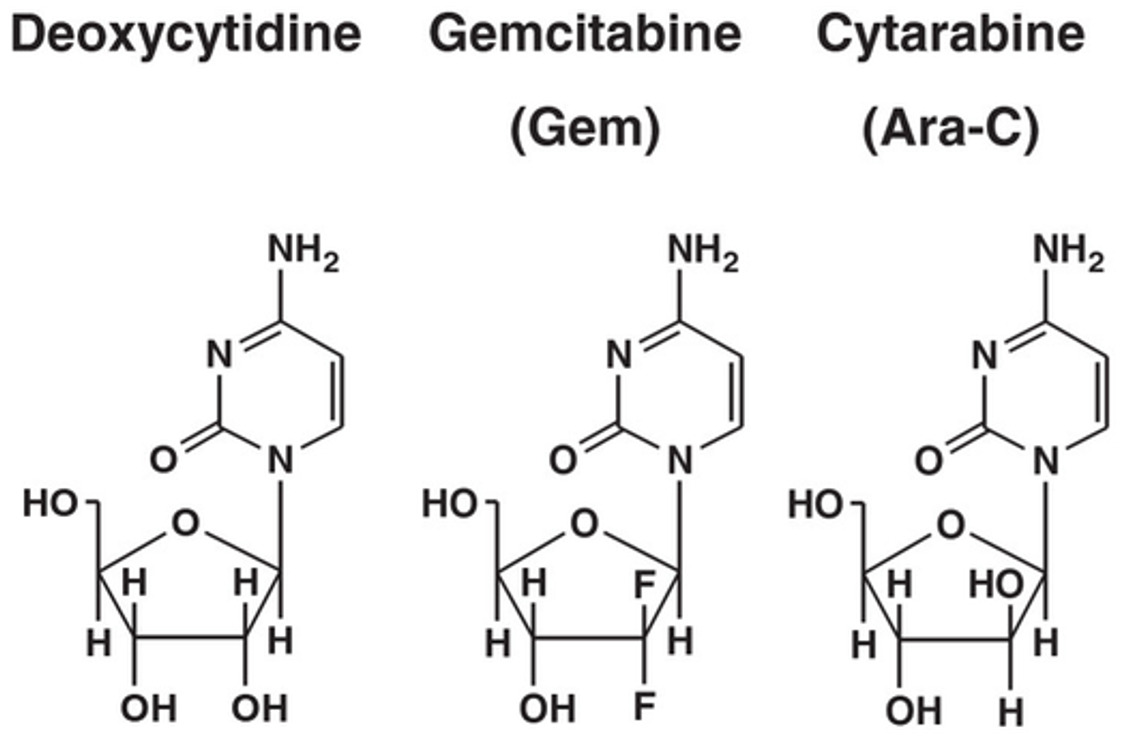
Desoxicitidina y análogos:
Gemcitabina (difluoroanálogo) y citarabina (citosina arabinósido)
| Medicamento | Mecanismo de acción | Indicaciones aprobadas | Efectos secundarios | Consideraciones adicionales |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-FU 5-FU A pyrimidine analog that is an antineoplastic antimetabolite. It interferes with DNA synthesis by blocking the thymidylate synthetase conversion of deoxyuridylic acid to thymidylic acid. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy | Inhibe la timidilato sintetasa |
|
|
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la deficiencia de dihidropirimidina deshidrogenasa: ↑ toxicidad |
| Capecitabina | Promedicamento del 5-FU 5-FU A pyrimidine analog that is an antineoplastic antimetabolite. It interferes with DNA synthesis by blocking the thymidylate synthetase conversion of deoxyuridylic acid to thymidylic acid. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy (inhibe la timidilato sintetasa) |
|
|
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la deficiencia de dihidropirimidina deshidrogenasa: ↑ toxicidad |
| Citarabina | Inhibe la ADN polimerasa |
|
|
|
| Gemcitabina | Inhibe la ADN polimerasa y la ribonucleótido reductasa |
|
|
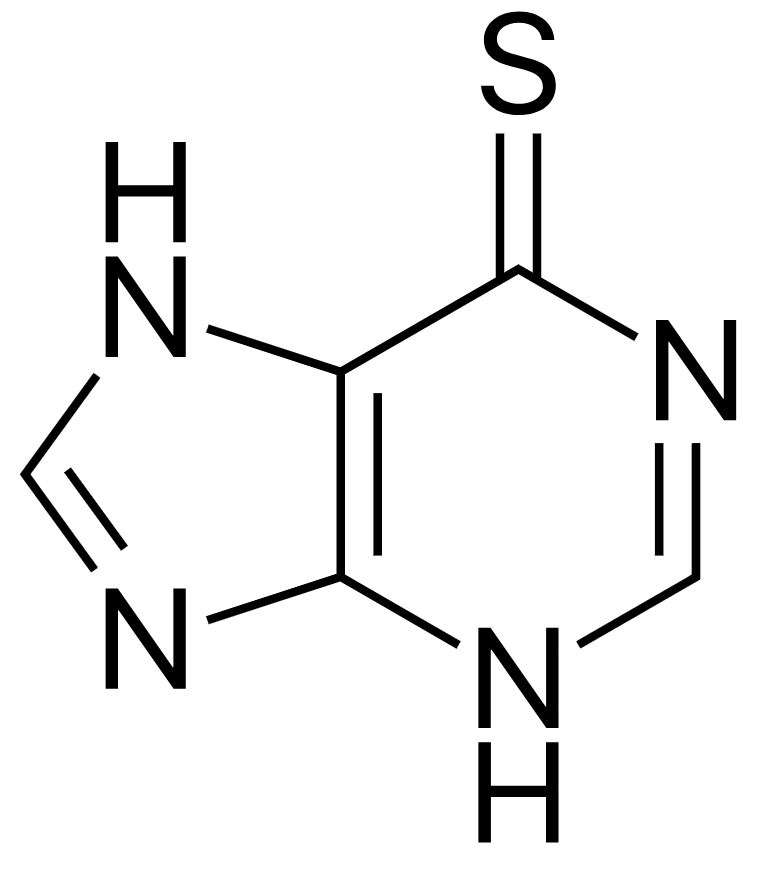
Estructura de la 6-mercaptopurina
Imagen: “Mercaptopurine” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio Público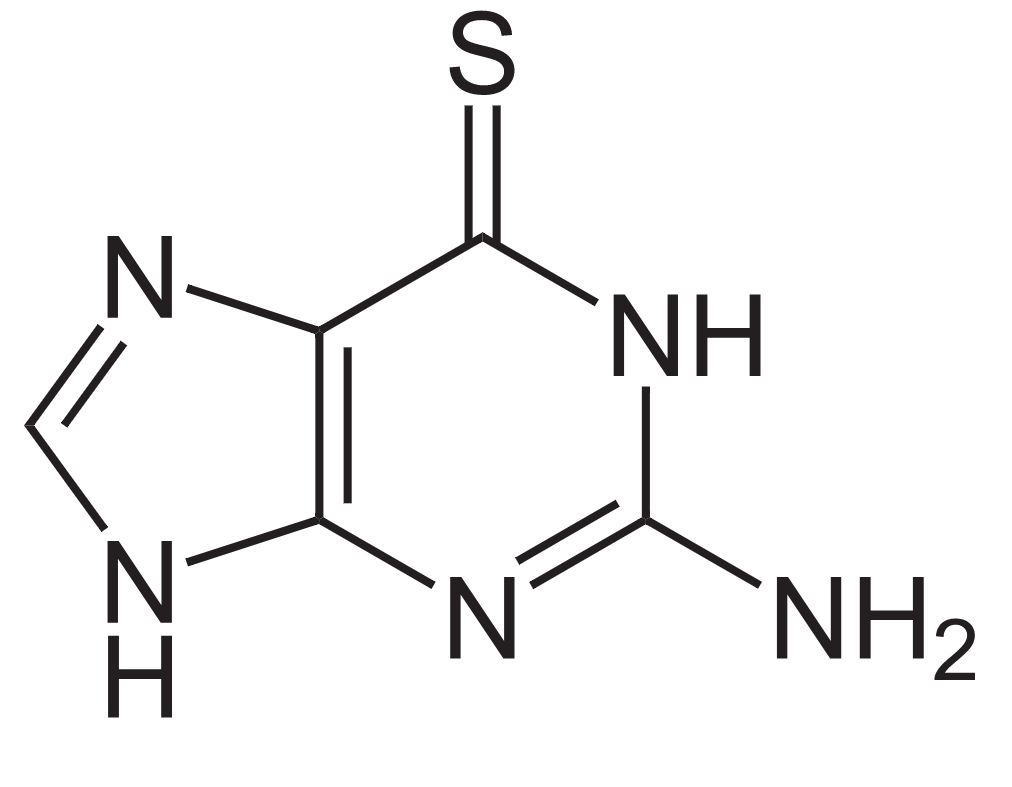
Estructura de la 6-tioguanina
Imagen: “6-Thioguanin” por NEUROtiker. Licencia: Dominio Público
Estructura de fludarabina
Imagen: “Fludarabine” por Yikrazuul. Licencia: Dominio Público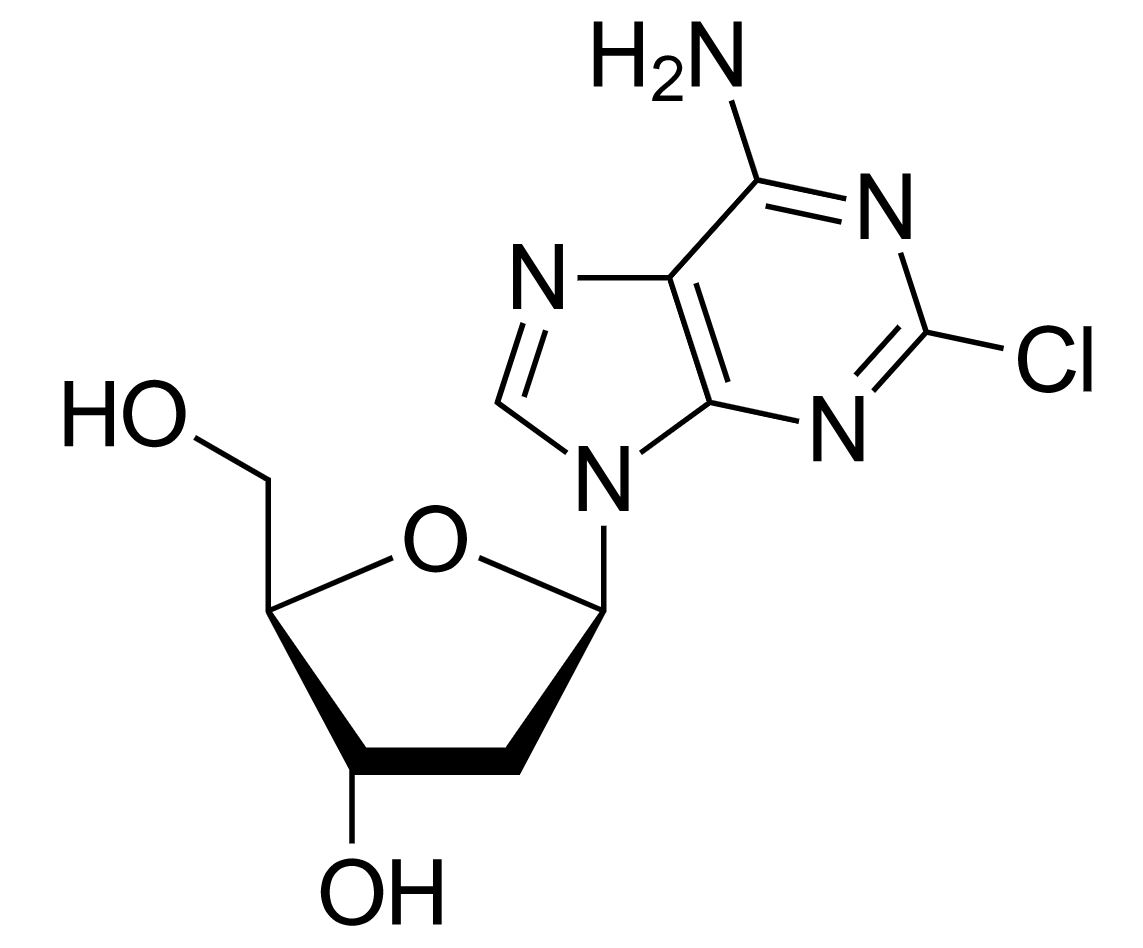
Estructura de la cladribina
Imagen: “Cladribine” por Yikrazuul. Licencia: Dominio Público
Estructura de la pentostatina
Imagen: “Pentostatin” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio Público| Medicamento | Mecanismo de acción | Indicaciones aprobadas | Efectos secundarios | Consideraciones adicionales |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-Mercaptopurina | Antagonista de la purina (inhibe la síntesis de nucleótidos de purina) | Leucemia linfocítica aguda |
|
↓ Dosis si se está administrando alopurinol |
| 6-TG 6-TG An antineoplastic compound which also has antimetabolite action. The drug is used in the therapy of acute leukemia. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy | Antagonista de la purina | Leucemia mieloide aguda |
|
|
| Fludarabina | Inhibe:
|
Leucemia linfocítica crónica |
|
Evitar la pentostatina (↑ toxicidad pulmonar) |
| Cladribina | Inhibe:
|
Leucemia de células pilosas |
|
|
| Pentostatina | Inhibe la adenosina desaminasa (↓ síntesis de ADN) | Leucemia de células pilosas |
|
Evitar la fludarabina (↑ toxicidad pulmonar) |
Estructura de la hidroxiurea
Imagen: “Hydroxyurea-2D-skeletal” por Chem Sim 2001. Licencia: Dominio Público| Clase del medicamento | Fase del ciclo celular afectada | Mecanismo de acción |
|---|---|---|
| Antifolatos | Detención del ciclo celular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fase S | Inhiben:
|
| Fluoropirimidinas | Detención del ciclo celular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fase S | Inhiben la timidilato sintasa |
| Análogos de desoxicitidina | Detención del ciclo celular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fase S | Inhiben:
|
| Análogos de purinas | Detención del ciclo celular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fase S | Inhiben la síntesis de purinas de novo |
| Inhibidores de la topoisomerasa II | Detención del ciclo celular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las fases S y G2 | Inhiben la topoisomerasa II |
| Taxanos | Detención del ciclo celular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la metafase de la fase M | Hiperestabilizan los LOS Neisseria microtúbulos |
| Alcaloides de vinca | Detención celular durante la metafase de la fase M | Se unen a la beta-tubulina y previenen la polimerización de los LOS Neisseria microtúbulos |
Diversos medicamentos quimioterapéuticos y sus efectos sobre el ciclo celular
Imagen por Lecturio.