Zellweger syndrome (ZWS), also called cerebrohepatorenal syndrome, is a rare congenital peroxisome biosynthesis Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of peptides and proteins on ribosomes, directed by messenger RNA, via transfer RNA that is charged with standard proteinogenic amino acids. Virology disorder and is considered an inborn error Error Refers to any act of commission (doing something wrong) or omission (failing to do something right) that exposes patients to potentially hazardous situations. Disclosure of Information of metabolism. Zellweger syndrome is the most severe form of a spectrum of conditions called Zellweger spectrum disorder (ZSD), and is characterized by the reduction or absence of functional peroxisomes Peroxisomes Microbodies which occur in animal and plant cells and in certain fungi and protozoa. They contain peroxidase, catalase, and allied enzymes. The Cell: Organelles. Symptoms are present from the time of birth and include hypotonia Hypotonia Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, poor feeding, seizures Seizures A seizure is abnormal electrical activity of the neurons in the cerebral cortex that can manifest in numerous ways depending on the region of the brain affected. Seizures consist of a sudden imbalance that occurs between the excitatory and inhibitory signals in cortical neurons, creating a net excitation. The 2 major classes of seizures are focal and generalized. Seizures, and certain distinctive physical features, notably facial characteristics and skeletal malformations. There is no cure for ZWS. The average survival rate is less than 1 year.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Clinical manifestations of ZWS are present at birth.
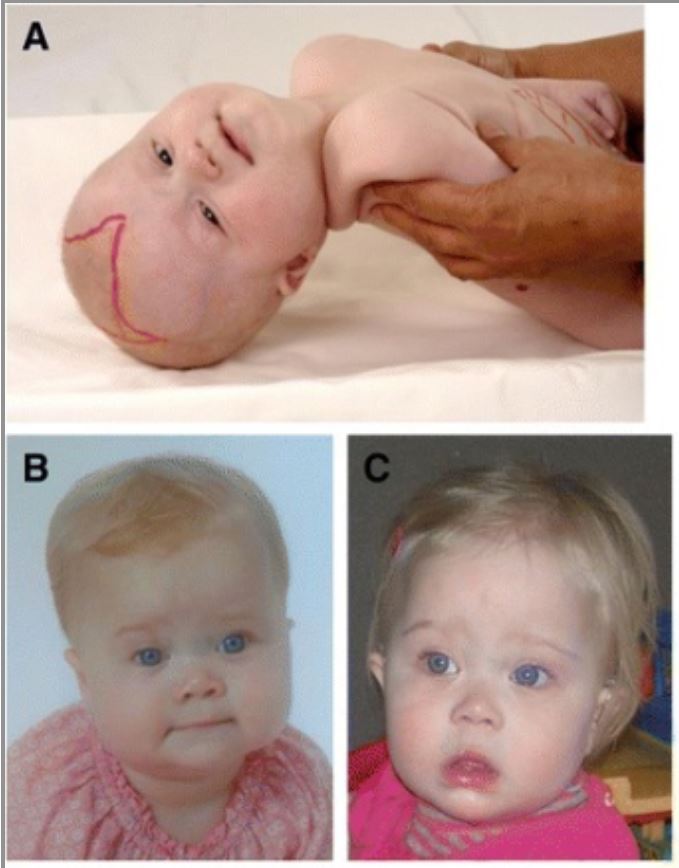
Craniofacial dysmorphic features in patients with Zellweger spectrum disorder (ZSD)
A 6-month-old girl (A) with typical craniofacial dysmorphia, epicanthal folds, high forehead, broad nasal bridge, hypoplastic supraorbital ridges, and large anterior fontanel (drawn). Images (B) and (C) show a girl with ZSD at the age of 9 months (B) and 14 months (C). Facial dysmorphism in this girl is less pronounced.
There is no cure and no effective treatment for ZWS. Treatment is supportive at best.
Death typically occurs within 1 year of birth (usually < 6 months), typically due to respiratory failure Respiratory failure Respiratory failure is a syndrome that develops when the respiratory system is unable to maintain oxygenation and/or ventilation. Respiratory failure may be acute or chronic and is classified as hypoxemic, hypercapnic, or a combination of the two. Respiratory Failure.
Zellweger syndrome is part of a clinical continuum of peroxisome biogenesis disorders known as Zellweger spectrum disorder (ZSD). All of the following conditions also have autosomal recessive inheritance Autosomal recessive inheritance Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance, and are diagnosed and managed similar to ZWS:
The differential diagnosis for ZWS is vast. Clinical features, biochemical testing, imaging, and ultimately genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies help to differentiate and provide a diagnosis. The following are disorders that should be considered in any neonate Neonate An infant during the first 28 days after birth. Physical Examination of the Newborn that presents with profound hypotonia Hypotonia Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: