X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) hypophosphatemic rickets Hypophosphatemic rickets A disorder characterized by hypophosphatemia; rickets; osteomalacia; resulting from lack of phosphate reabsorption by the kidneys and possible defects in vitamin D metabolism. Osteomalacia and Rickets (XLHR) is the most common of several hereditary disorders and is characterized by renal phosphate Phosphate Inorganic salts of phosphoric acid. Electrolytes wasting, resulting in weak or soft bones. Formerly known as “vitamin D-resistant rickets Rickets Disorders caused by interruption of bone mineralization manifesting as osteomalacia in adults and characteristic deformities in infancy and childhood due to disturbances in normal bone formation. The mineralization process may be interrupted by disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis, resulting from dietary deficiencies, or acquired, or inherited metabolic, or hormonal disturbances. Osteomalacia and Rickets,” XLHR is not currently considered true vitamin D Vitamin D A vitamin that includes both cholecalciferols and ergocalciferols, which have the common effect of preventing or curing rickets in animals. It can also be viewed as a hormone since it can be formed in skin by action of ultraviolet rays upon the precursors, 7-dehydrocholesterol and ergosterol, and acts on vitamin D receptors to regulate calcium in opposition to parathyroid hormone. Fat-soluble Vitamins and their Deficiencies resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing (related to inherited defects in the vitamin D Vitamin D A vitamin that includes both cholecalciferols and ergocalciferols, which have the common effect of preventing or curing rickets in animals. It can also be viewed as a hormone since it can be formed in skin by action of ultraviolet rays upon the precursors, 7-dehydrocholesterol and ergosterol, and acts on vitamin D receptors to regulate calcium in opposition to parathyroid hormone. Fat-soluble Vitamins and their Deficiencies metabolic pathway or calcitriol Calcitriol The physiologically active form of vitamin d. It is formed primarily in the kidney by enzymatic hydroxylation of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (calcifediol). Its production is stimulated by low blood calcium levels and parathyroid hormone. Calcitriol increases intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus, and in concert with parathyroid hormone increases bone resorption. Parathyroid Glands: Anatomy receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors). Typical clinical presentations occur during childhood and manifest as short stature, genu valgum Genu valgum Genu valgum is a deformation of the knee joint(s) that creates angulation of the lower limb(s) toward the midline in the coronal plane. Children ages 1-5 years are commonly affected. Genu Valgum or genu varum Genu varum Genu varum is a deformation of the knee joint(s) that creates angulation of the lower limb(s) away from the midline in the coronal plane. Children ages 1-5 years are commonly affected. Genu Varum, bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and dental pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways. Diagnosis is made by lab studies and confirmed by identification Identification Defense Mechanisms of the mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in the PHEX gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics. Management includes burosumab or high doses of activated vitamin D Vitamin D A vitamin that includes both cholecalciferols and ergocalciferols, which have the common effect of preventing or curing rickets in animals. It can also be viewed as a hormone since it can be formed in skin by action of ultraviolet rays upon the precursors, 7-dehydrocholesterol and ergosterol, and acts on vitamin D receptors to regulate calcium in opposition to parathyroid hormone. Fat-soluble Vitamins and their Deficiencies ( calcitriol Calcitriol The physiologically active form of vitamin d. It is formed primarily in the kidney by enzymatic hydroxylation of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (calcifediol). Its production is stimulated by low blood calcium levels and parathyroid hormone. Calcitriol increases intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus, and in concert with parathyroid hormone increases bone resorption. Parathyroid Glands: Anatomy) and phosphate Phosphate Inorganic salts of phosphoric acid. Electrolytes. Patient monitoring by a multidisciplinary team is crucial to ensure adequate growth.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) hypophosphatemic rickets Hypophosphatemic rickets A disorder characterized by hypophosphatemia; rickets; osteomalacia; resulting from lack of phosphate reabsorption by the kidneys and possible defects in vitamin D metabolism. Osteomalacia and Rickets (XLHR) is a rare genetic disorder that causes hypophosphatemia Hypophosphatemia A condition of an abnormally low level of phosphates in the blood. Bartter Syndrome and resultant clinical rickets Rickets Disorders caused by interruption of bone mineralization manifesting as osteomalacia in adults and characteristic deformities in infancy and childhood due to disturbances in normal bone formation. The mineralization process may be interrupted by disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis, resulting from dietary deficiencies, or acquired, or inherited metabolic, or hormonal disturbances. Osteomalacia and Rickets.
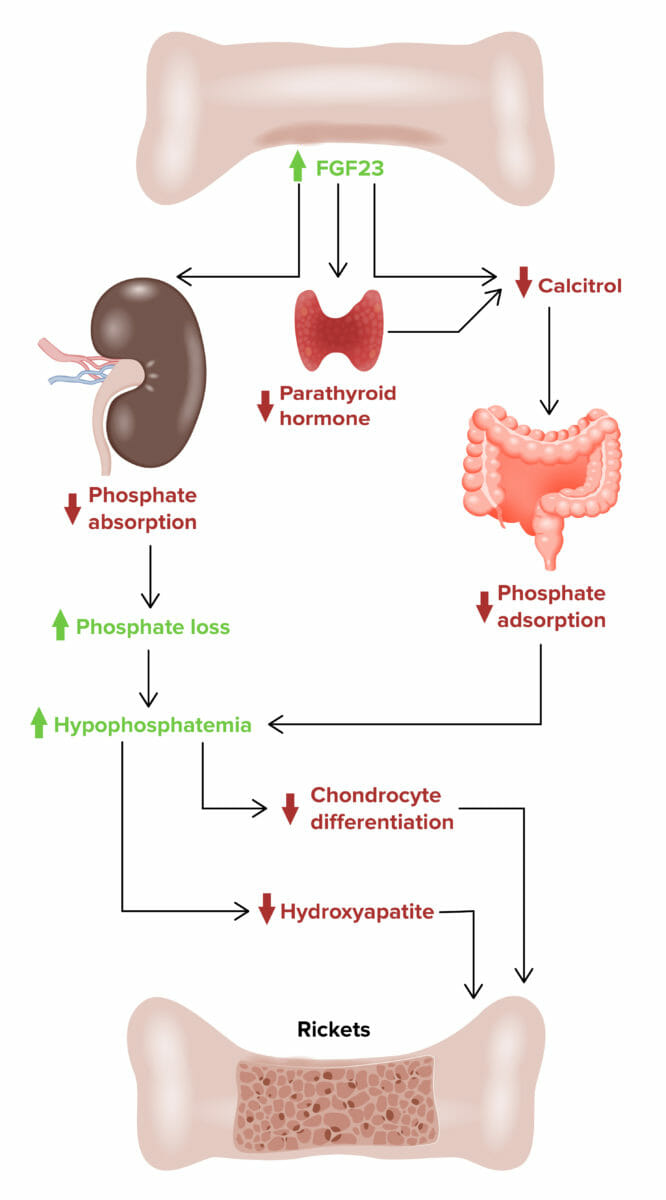
X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets:
Effect of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) on developing X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets
The clinical presentation of XLHR may vary from asymptomatic to severely symptomatic. X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) hypophosphatemic rickets Hypophosphatemic rickets A disorder characterized by hypophosphatemia; rickets; osteomalacia; resulting from lack of phosphate reabsorption by the kidneys and possible defects in vitamin D metabolism. Osteomalacia and Rickets is commonly mistaken for nutritional rickets Rickets Disorders caused by interruption of bone mineralization manifesting as osteomalacia in adults and characteristic deformities in infancy and childhood due to disturbances in normal bone formation. The mineralization process may be interrupted by disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis, resulting from dietary deficiencies, or acquired, or inherited metabolic, or hormonal disturbances. Osteomalacia and Rickets in infants, and the symptoms include:
Family history Family History Adult Health Maintenance:
Lab tests:
Genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies:
Imaging:
Radiologic evaluation should be performed to rule out physiological bowing and bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types dysplasia. Potential X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests findings may include:
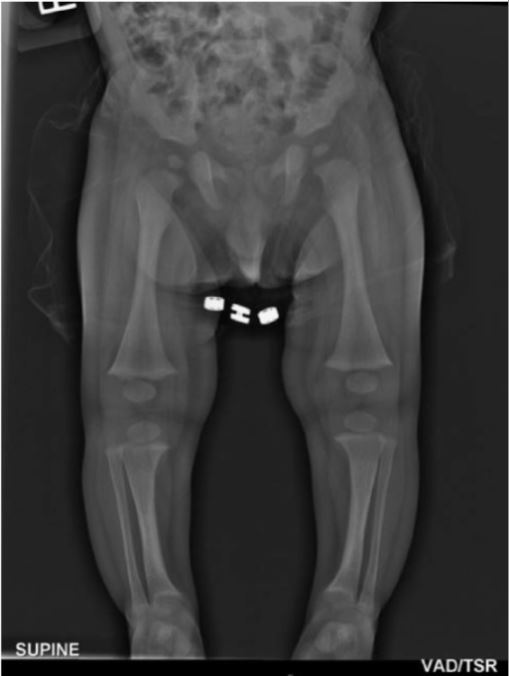
A 7-month-old infant with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets:
The long bones of the lower limbs demonstrate splaying of the metaphyses with fraying without widening of the epiphysis. Mild bowing of the tibia is also present.
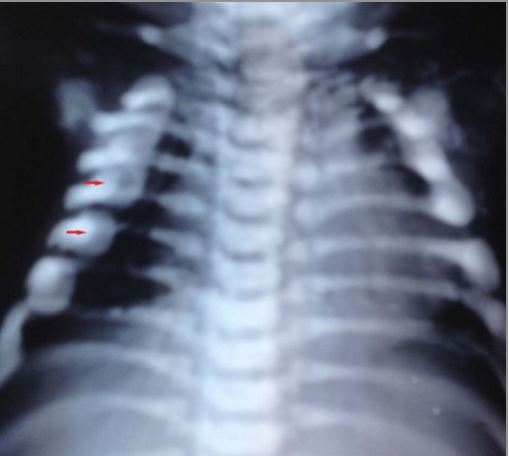
X-ray showing rachitic rosary: bead-like prominences at the costochondral junctions
Image: “Malignant infantile osteopetrosis: case report with review of literature” by Essabar L, Meskini T, Ettair S, Erreimi N, Mouane N. License: CC BY 2.0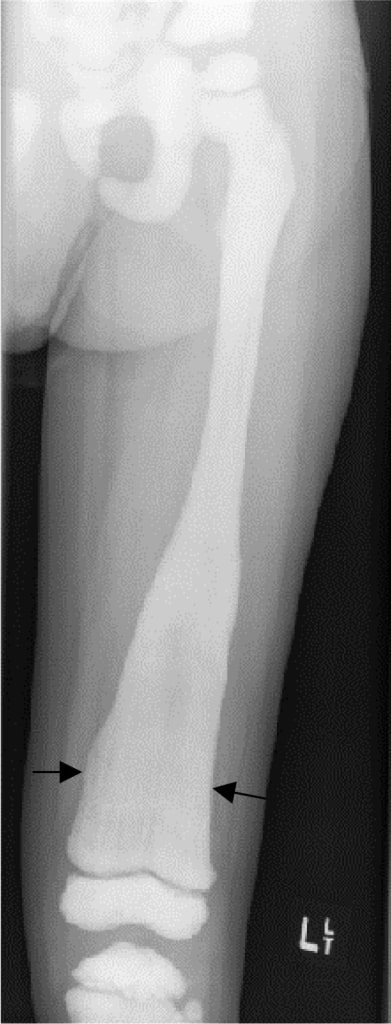
An X-ray from a 4-year-old child with distal femur Erlenmeyer flask deformity showing a flaring of the metaphysis in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets
Image: “Osteopetrosis” by Stark Z, Savarirayan R. License: CC BY 2.0The goals of treatment are to improve osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets and skeletal deformities, improve growth in infants and physical activity in children, and decrease pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways.
Some adults with XLHR may have minimal medical problems, whereas others may experience persistent discomfort or complications. Monitoring the therapy for potential complications of hyperparathyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Hyperparathyroidism is a condition associated with elevated blood levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Depending on the pathogenesis of this condition, hyperparathyroidism can be defined as primary, secondary or tertiary. Hyperparathyroidism and nephrocalcinosis is imperative.