X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) agammaglobulinemia, also known as Bruton agammaglobulinemia or Bruton disease, is a rare, recessive genetic disorder characterized by the improper development of B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions, leading to a lack of mature B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions capable of responding to stimulation by cell-mediated immune responses or certain antigen-presenting cells Antigen-presenting cells A heterogeneous group of immunocompetent cells that mediate the cellular immune response by processing and presenting antigens to the T-cells. Traditional antigen-presenting cells include macrophages; dendritic cells; langerhans cells; and B-lymphocytes. Follicular dendritic cells are not traditional antigen-presenting cells, but because they hold antigen on their cell surface in the form of immune complexes for b-cell recognition they are considered so by some authors. Adaptive Immune Response. X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) agammaglobulinemia is more likely to be found in males than females and is due to mutations in the Bruton tyrosine Tyrosine A non-essential amino acid. In animals it is synthesized from phenylalanine. It is also the precursor of epinephrine; thyroid hormones; and melanin. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids kinase gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics on the X chromosome X chromosome The female sex chromosome, being the differential sex chromosome carried by half the male gametes and all female gametes in human and other male-heterogametic species. Basic Terms of Genetics. The result of this mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations is a complete or near-complete lack of all antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions. Presentation includes recurrent bacterial infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease after the first few months of life. Management consists of IV immunoglobulins IV immunoglobulins Immunoglobulin preparations used in intravenous infusion, containing primarily immunoglobulin g. They are used to treat a variety of diseases associated with decreased or abnormal immunoglobulin levels including pediatric aids; primary hypergammaglobulinemia; scid; cytomegalovirus infections in transplant recipients, lymphocytic leukemia, chronic; kawasaki syndrome, infection in neonates, and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. DiGeorge Syndrome and prophylactic use of antibiotics.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
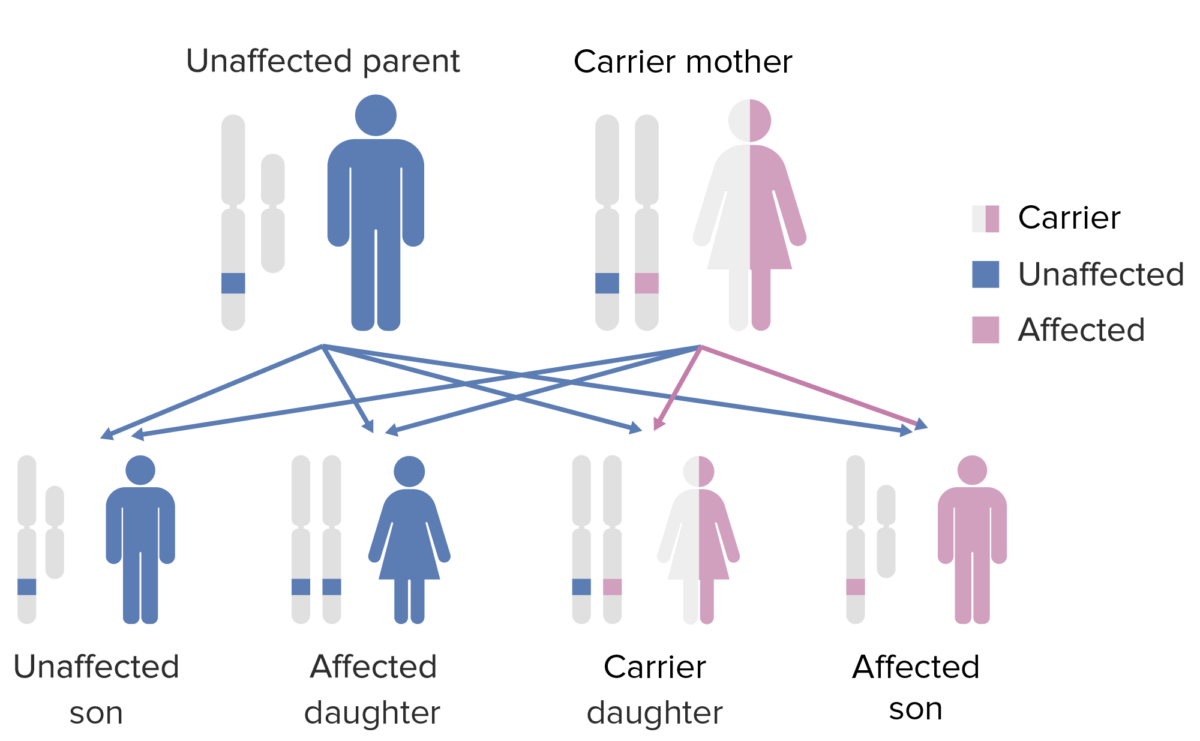
The pattern of inheritance of X-linked agammaglobulinemia:
Note that the mother must contribute the defective X gene to the male child in order for him to express this phenotype.
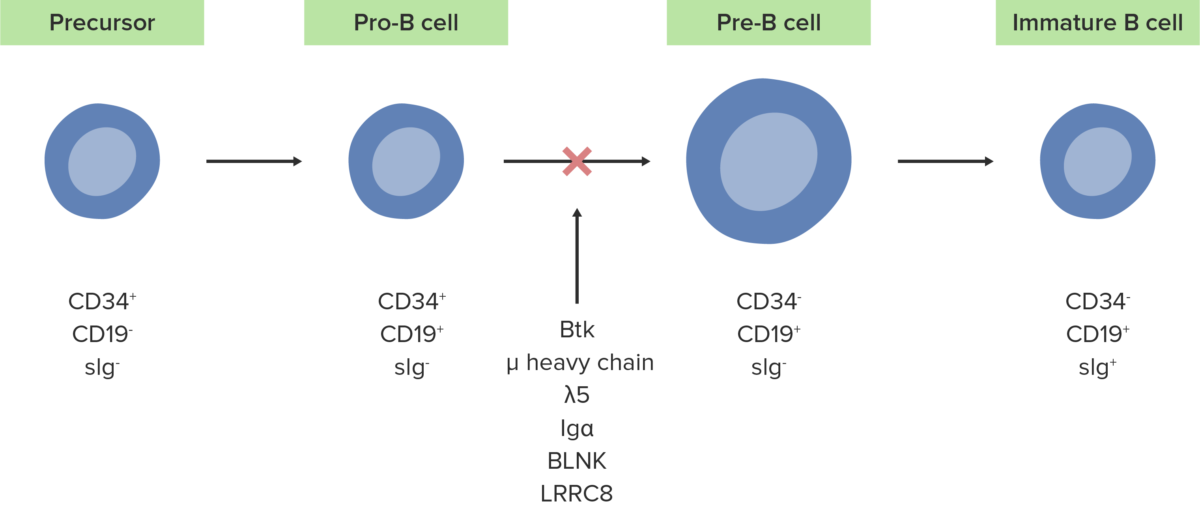
The absence or defect of the Btk enzyme inhibits the normal development of pro-B cells into pre-B cells.
Image by Lecturio.The following conditions are differential diagnoses for X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) agammaglobulinemia.