Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS), also known as eczema-thrombocytopenia-immunodeficiency syndrome, IMD2, or immunodeficiency Immunodeficiency Chédiak-Higashi Syndrome 2, is a rare genetic mixed disorder of B- and T-cell deficiency that follows an X-linked recessive X-Linked Recessive Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy inheritance pattern. It is caused by a WAS gene mutation Gene Mutation Myotonic Dystrophies that leads to impaired actin Actin Filamentous proteins that are the main constituent of the thin filaments of muscle fibers. The filaments (known also as filamentous or f-actin) can be dissociated into their globular subunits; each subunit is composed of a single polypeptide 375 amino acids long. This is known as globular or g-actin. In conjunction with myosins, actin is responsible for the contraction and relaxation of muscle. Skeletal Muscle Contraction cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton The network of filaments, tubules, and interconnecting filamentous bridges which give shape, structure, and organization to the cytoplasm. The Cell: Cytosol and Cytoskeleton, phagocytosis Phagocytosis The engulfing and degradation of microorganisms; other cells that are dead, dying, or pathogenic; and foreign particles by phagocytic cells (phagocytes). Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation and chemotaxis Chemotaxis The movement of leukocytes in response to a chemical concentration gradient or to products formed in an immunologic reaction. Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency Type 1, impaired platelet development, and, in general, a loss of humoral and cellular responses. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome presents as a classic triad of eczema Eczema Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic, relapsing, pruritic, inflammatory skin disease that occurs more frequently in children, although adults can also be affected. The condition is often associated with elevated serum levels of IgE and a personal or family history of atopy. Skin dryness, erythema, oozing, crusting, and lichenification are present. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema), bleeding diathesis, and recurrent opportunistic infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, but also carries a high risk of development of autoimmunity Autoimmunity Autoimmunity is a pathologic immune response toward self-antigens, resulting from a combination of factors: immunologic, genetic, and environmental. The immune system is equipped with self-tolerance, allowing immune cells such as T cells and B cells to recognize self-antigens and to not mount a reaction against them. Defects in this mechanism, along with environmental triggers (such as infections) and genetic susceptibility factors (most notable of which are the HLA genes) can lead to autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity and malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax. Management includes hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Transfer of hematopoietic stem cells from bone marrow or blood between individuals within the same species (homologous transplantation) or transfer within the same individual (autologous transplantation). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has been used as an alternative to bone marrow transplantation in the treatment of a variety of neoplasms. Organ Transplantation (HSCT), immunoglobulin replacement therapy, prophylactic and therapeutic antibiotics, and systemic steroids Steroids A group of polycyclic compounds closely related biochemically to terpenes. They include cholesterol, numerous hormones, precursors of certain vitamins, bile acids, alcohols (sterols), and certain natural drugs and poisons. Steroids have a common nucleus, a fused, reduced 17-carbon atom ring system, cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene. Most steroids also have two methyl groups and an aliphatic side-chain attached to the nucleus. Benign Liver Tumors. Without HSCT, prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is poor and life expectancy Life expectancy Based on known statistical data, the number of years which any person of a given age may reasonably expected to live. Population Pyramids is shortened.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
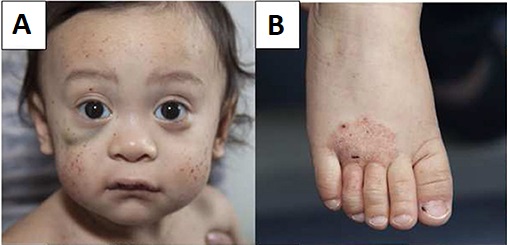
Young male patient with Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome presenting with multiple face petechiae and a hematoma under the right eye (A) and eczema of the foot (B)
Image: “Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome” by Michael H. Albert and Alexandra F. Freeman, on behalf of the Inborn Errors Working Party (IEWP) of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). License: CC BY 4.0The following conditions are differential diagnoses for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: