Williams syndrome (WS), also known as Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS), is a genetic disease caused by a microdeletion on chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 7. Affected individuals have a characteristic elfin facies and short stature. Cognitive, developmental, and behavioral issues are common. Additionally, cardiovascular, connective tissue Connective tissue Connective tissues originate from embryonic mesenchyme and are present throughout the body except inside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of connective tissues is to provide structural support to organs. Connective tissues consist of cells and an extracellular matrix. Connective Tissue: Histology, endocrine, and renal anomalies may be present. Genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies confirms the diagnosis. Treatment is based on the clinical manifestations. Cardiovascular involvement needs to be followed closely because it is the main cause of mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status.
Last updated: Jan 24, 2025
The incidence Incidence The number of new cases of a given disease during a given period in a specified population. It also is used for the rate at which new events occur in a defined population. It is differentiated from prevalence, which refers to all cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency of Williams syndrome (WS) is 1 in 7,500–20,000 live births.
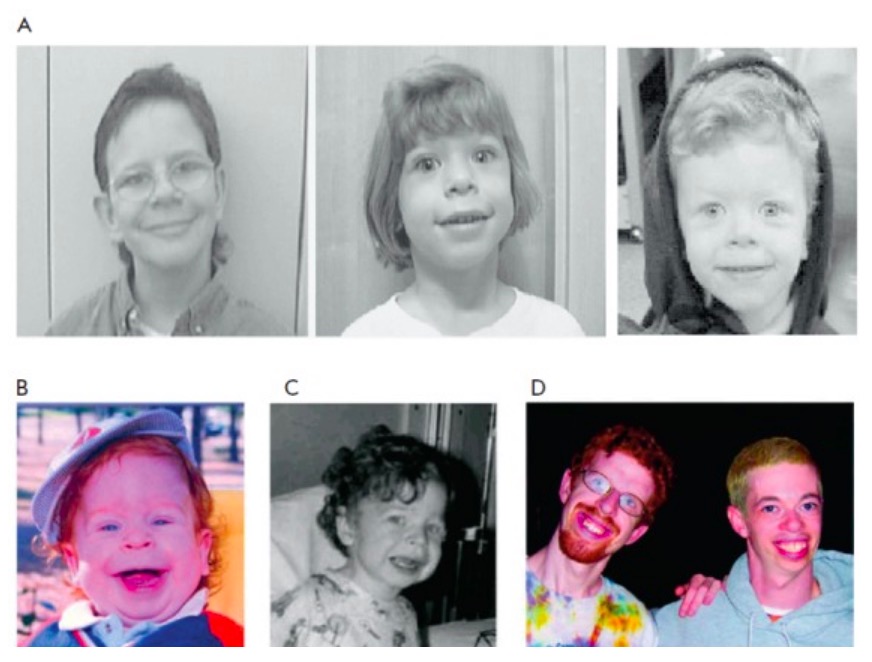
Facial features of WS
A: distinctive facial appearance of individuals with WS
B and C: a young child with WS at the age of 15 months and 3 years (note the subtle characteristic facial features, including wide mouth, chubby cheeks, long philtrum, small nose, and delicate chin)
The same patient is shown in Figs. B, C, and D (left; at 21 years of age); another individual with WS aged 28 years is shown in Fig. D on the right.
Congenital heart disease is present in 80%–90% of WS cases and is a major cause of morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status and mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with WS. The risk of sudden cardiac death Sudden cardiac death Cardiac arrest is the sudden, complete cessation of cardiac output with hemodynamic collapse. Patients present as pulseless, unresponsive, and apneic. Rhythms associated with cardiac arrest are ventricular fibrillation/tachycardia, asystole, or pulseless electrical activity. Cardiac Arrest is 25–100 times greater in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with WS.
Treatment is based on the clinical manifestations present and is aimed at improving the quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement of life and treating associated conditions.