The myeloid lineage produces a diverse group of blood cells (leukocytes) involved in the defense of the body against foreign substances or infectious agents. Monocytes Monocytes Large, phagocytic mononuclear leukocytes produced in the vertebrate bone marrow and released into the blood; contain a large, oval or somewhat indented nucleus surrounded by voluminous cytoplasm and numerous organelles. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation, neutrophils Neutrophils Granular leukocytes having a nucleus with three to five lobes connected by slender threads of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing fine inconspicuous granules and stainable by neutral dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation, eosinophils Eosinophils Granular leukocytes with a nucleus that usually has two lobes connected by a slender thread of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing coarse, round granules that are uniform in size and stainable by eosin. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation, basophils Basophils Granular leukocytes characterized by a relatively pale-staining, lobate nucleus and cytoplasm containing coarse dark-staining granules of variable size and stainable by basic dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation, and mast cells Mast cells Granulated cells that are found in almost all tissues, most abundantly in the skin and the gastrointestinal tract. Like the basophils, mast cells contain large amounts of histamine and heparin. Unlike basophils, mast cells normally remain in the tissues and do not circulate in the blood. Mast cells, derived from the bone marrow stem cells, are regulated by the stem cell factor. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation all arise from the common myeloid progenitor (CMP), which develops from bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis stem cells. However, leukocytes have different functions. Neutrophils Neutrophils Granular leukocytes having a nucleus with three to five lobes connected by slender threads of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing fine inconspicuous granules and stainable by neutral dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation kill invading bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology and fungi Fungi A kingdom of eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms that live parasitically as saprobes, including mushrooms; yeasts; smuts, molds, etc. They reproduce either sexually or asexually, and have life cycles that range from simple to complex. Filamentous fungi, commonly known as molds, refer to those that grow as multicellular colonies. Mycology, eosinophils Eosinophils Granular leukocytes with a nucleus that usually has two lobes connected by a slender thread of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing coarse, round granules that are uniform in size and stainable by eosin. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation increase in parasitic infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, basophils Basophils Granular leukocytes characterized by a relatively pale-staining, lobate nucleus and cytoplasm containing coarse dark-staining granules of variable size and stainable by basic dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation and mast cells Mast cells Granulated cells that are found in almost all tissues, most abundantly in the skin and the gastrointestinal tract. Like the basophils, mast cells contain large amounts of histamine and heparin. Unlike basophils, mast cells normally remain in the tissues and do not circulate in the blood. Mast cells, derived from the bone marrow stem cells, are regulated by the stem cell factor. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation are key to allergic response as sources of histamine, and monocytes Monocytes Large, phagocytic mononuclear leukocytes produced in the vertebrate bone marrow and released into the blood; contain a large, oval or somewhat indented nucleus surrounded by voluminous cytoplasm and numerous organelles. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation are released from bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis to become macrophages Macrophages The relatively long-lived phagocytic cell of mammalian tissues that are derived from blood monocytes. Main types are peritoneal macrophages; alveolar macrophages; histiocytes; kupffer cells of the liver; and osteoclasts. They may further differentiate within chronic inflammatory lesions to epithelioid cells or may fuse to form foreign body giant cells or langhans giant cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation in the tissues. The development in the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis is regulated by different cytokines Cytokines Non-antibody proteins secreted by inflammatory leukocytes and some non-leukocytic cells, that act as intercellular mediators. They differ from classical hormones in that they are produced by a number of tissue or cell types rather than by specialized glands. They generally act locally in a paracrine or autocrine rather than endocrine manner. Adaptive Immune Response.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
White myeloid cells are leukocytes developed from the common myeloid progenitor (CMP), which is derived from hematopoietic stem cells Hematopoietic stem cells Progenitor cells from which all blood cells derived. They are found primarily in the bone marrow and also in small numbers in the peripheral blood. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis (HSCs) of the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis.
| Type | Nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles | Granules | Characteristics and functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monocyte (3%–7% of differential count) | Kidney shaped (indented or C shaped) | None | Characteristics:
Functions:
|
| Type | Nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles | Granules | Characteristics and functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil (50%–70% of differential count) | Multilobed (3–5 lobes) |
|
Lifespan:
Target and function:
|
| Eosinophil (1%–3% of differential count) | Bilobed |
|
Lifespan:
Target and function:
|
| Basophil (0.5%–1% of differential count) | Bilobed or trilobed |
|
Lifespan:
Target and function:
|
| Mast cell Mast cell Granulated cells that are found in almost all tissues, most abundantly in the skin and the gastrointestinal tract. Like the basophils, mast cells contain large amounts of histamine and heparin. Unlike basophils, mast cells normally remain in the tissues and do not circulate in the blood. Mast cells, derived from the bone marrow stem cells, are regulated by the stem cell factor. Angioedema | Round (margins obscured by packed granules) | Purple to red |
|
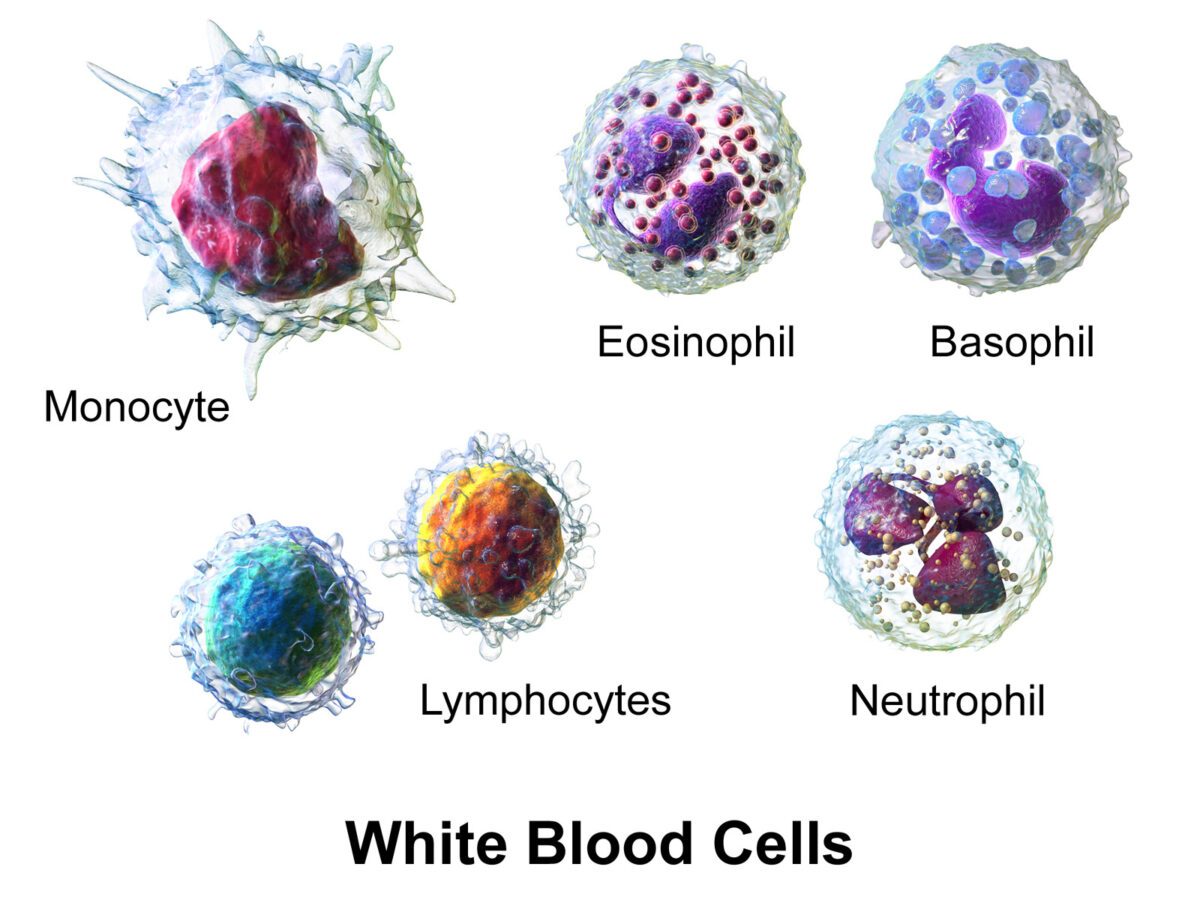
White blood cells (WBCs), or leukocytes, in the blood:
Granulocytes include basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils; agranulocytes include lymphocytes and monocytes.
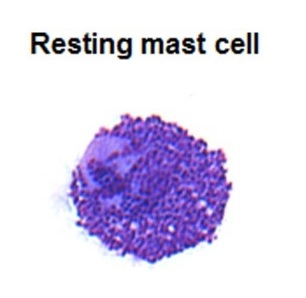
Mast cell: typically oval in shape, with cytoplasm filled with basophilic granules
Image: “May–Grünwald/Giemsa stain of a resting human intestinal mast cell” by Benhamou M et al. License: CC BY 3.0, cropped by Lecturio.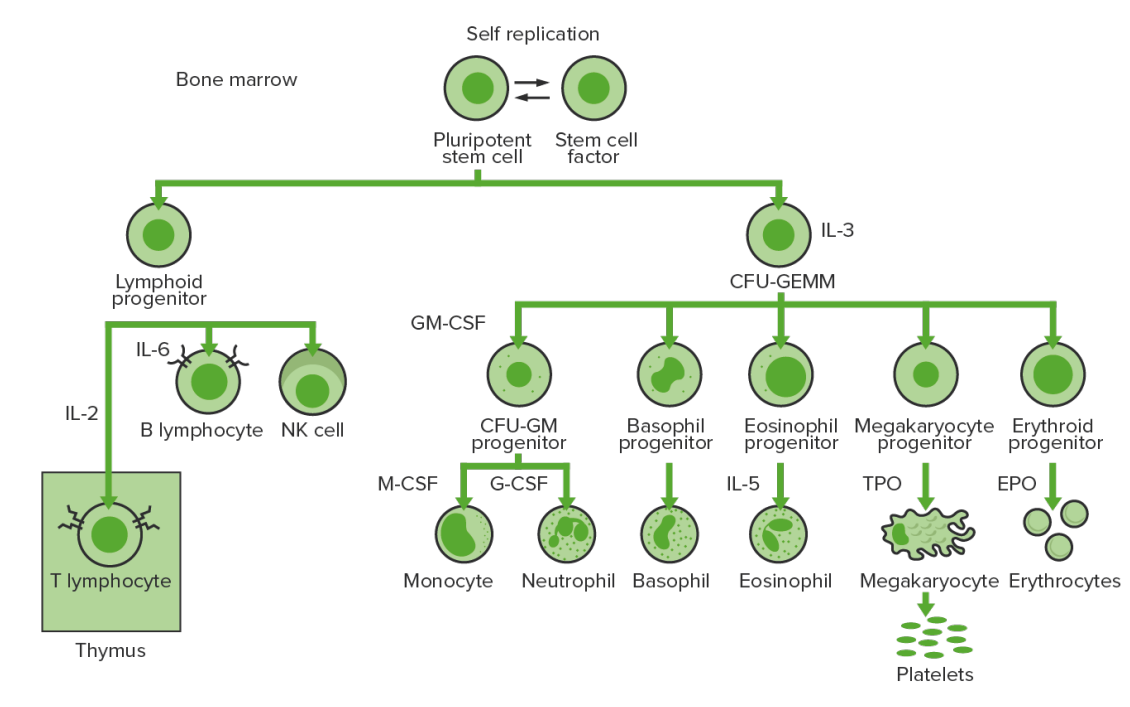
Bone marrow hematopoiesis: proliferation and differentiation of the formed elements of blood.
IL-3: interleukin-3
CFU-GEMM: colony-forming unit–granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte, megakaryocyte
IL-2: interleukin-2
IL-6: interleukin-6
CFU-GM: colony-forming unit–granulocyte-macrophage
GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
M-CSF: macrophage colony-stimulating factor
G-CSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
IL-5: interleukin-5
NK: natural killer
TPO: thrombopoietin
EPO: erythropoietin
| Cytokines Cytokines Non-antibody proteins secreted by inflammatory leukocytes and some non-leukocytic cells, that act as intercellular mediators. They differ from classical hormones in that they are produced by a number of tissue or cell types rather than by specialized glands. They generally act locally in a paracrine or autocrine rather than endocrine manner. Adaptive Immune Response/growth factors | Activities | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Stem cell factor Stem cell factor A hematopoietic growth factor and the ligand of the cell surface c-kit protein (proto-oncogene proteins c-kit). It is expressed during embryogenesis and is a growth factor for a number of cell types including the mast cells and the melanocytes in addition to the hematopoietic stem cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis (SCF) | Stimulates all hematopoietic progenitor cells | Bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis stromal cells |
| Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) | Stimulates myeloid progenitor cells Myeloid progenitor cells Stem cells derived from hematopoietic stem cells. Derived from these myeloid progenitor cells are the megakaryocytes; erythroid cells; myeloid cells; and some dendritic cells. Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Endothelial cells, T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified – cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions |
| Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) | Stimulates neutrophil precursor cells | Endothelial cells, macrophages Macrophages The relatively long-lived phagocytic cell of mammalian tissues that are derived from blood monocytes. Main types are peritoneal macrophages; alveolar macrophages; histiocytes; kupffer cells of the liver; and osteoclasts. They may further differentiate within chronic inflammatory lesions to epithelioid cells or may fuse to form foreign body giant cells or langhans giant cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation |
| Monocyte colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) | Stimulates monocyte precursor cells | Endothelial cells, macrophages Macrophages The relatively long-lived phagocytic cell of mammalian tissues that are derived from blood monocytes. Main types are peritoneal macrophages; alveolar macrophages; histiocytes; kupffer cells of the liver; and osteoclasts. They may further differentiate within chronic inflammatory lesions to epithelioid cells or may fuse to form foreign body giant cells or langhans giant cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation |
| Interleukin-1 Interleukin-1 A soluble factor produced by monocytes; macrophages, and other cells which activates T-lymphocytes and potentiates their response to mitogens or antigens. Interleukin-1 is a general term refers to either of the two distinct proteins, interleukin-1alpha and interleukin-1beta. The biological effects of il-1 include the ability to replace macrophage requirements for t-cell activation. Interleukins (IL-1) | Regulation of cytokine secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies of many leukocytes | Macrophages Macrophages The relatively long-lived phagocytic cell of mammalian tissues that are derived from blood monocytes. Main types are peritoneal macrophages; alveolar macrophages; histiocytes; kupffer cells of the liver; and osteoclasts. They may further differentiate within chronic inflammatory lesions to epithelioid cells or may fuse to form foreign body giant cells or langhans giant cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation, T helper cells |
| Interleukin-3 Interleukin-3 A multilineage cell growth factor secreted by lymphocytes; epithelial cells; and astrocytes which stimulates clonal proliferation and differentiation of various types of blood and tissue cells. Platelets: Histology (IL-3) | Mitogen for all granulocyte and megakaryocyte Megakaryocyte Very large bone marrow cells which release mature blood platelets. Platelets: Histology/erythrocyte progenitor cells | T helper cells |
| Interleukin-4 Interleukin-4 A soluble factor produced by activated T-lymphocytes that induces the expression of mhc class II genes and fc receptors on B-lymphocytes and causes their proliferation and differentiation. It also acts on T-lymphocytes, mast cells, and several other hematopoietic lineage cells. Interleukins (IL-4) | Development of basophils Basophils Granular leukocytes characterized by a relatively pale-staining, lobate nucleus and cytoplasm containing coarse dark-staining granules of variable size and stainable by basic dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation and mast cells Mast cells Granulated cells that are found in almost all tissues, most abundantly in the skin and the gastrointestinal tract. Like the basophils, mast cells contain large amounts of histamine and heparin. Unlike basophils, mast cells normally remain in the tissues and do not circulate in the blood. Mast cells, derived from the bone marrow stem cells, are regulated by the stem cell factor. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation, and activation of B-lymphocyte | T helper cells |
| Interleukin-5 Interleukin-5 A cytokine that promotes differentiation and activation of eosinophils. It also triggers activated B-lymphocytes to differentiate into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Interleukins (IL-5) | Development and activation of eosinophils Eosinophils Granular leukocytes with a nucleus that usually has two lobes connected by a slender thread of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing coarse, round granules that are uniform in size and stainable by eosin. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation | T helper cells |
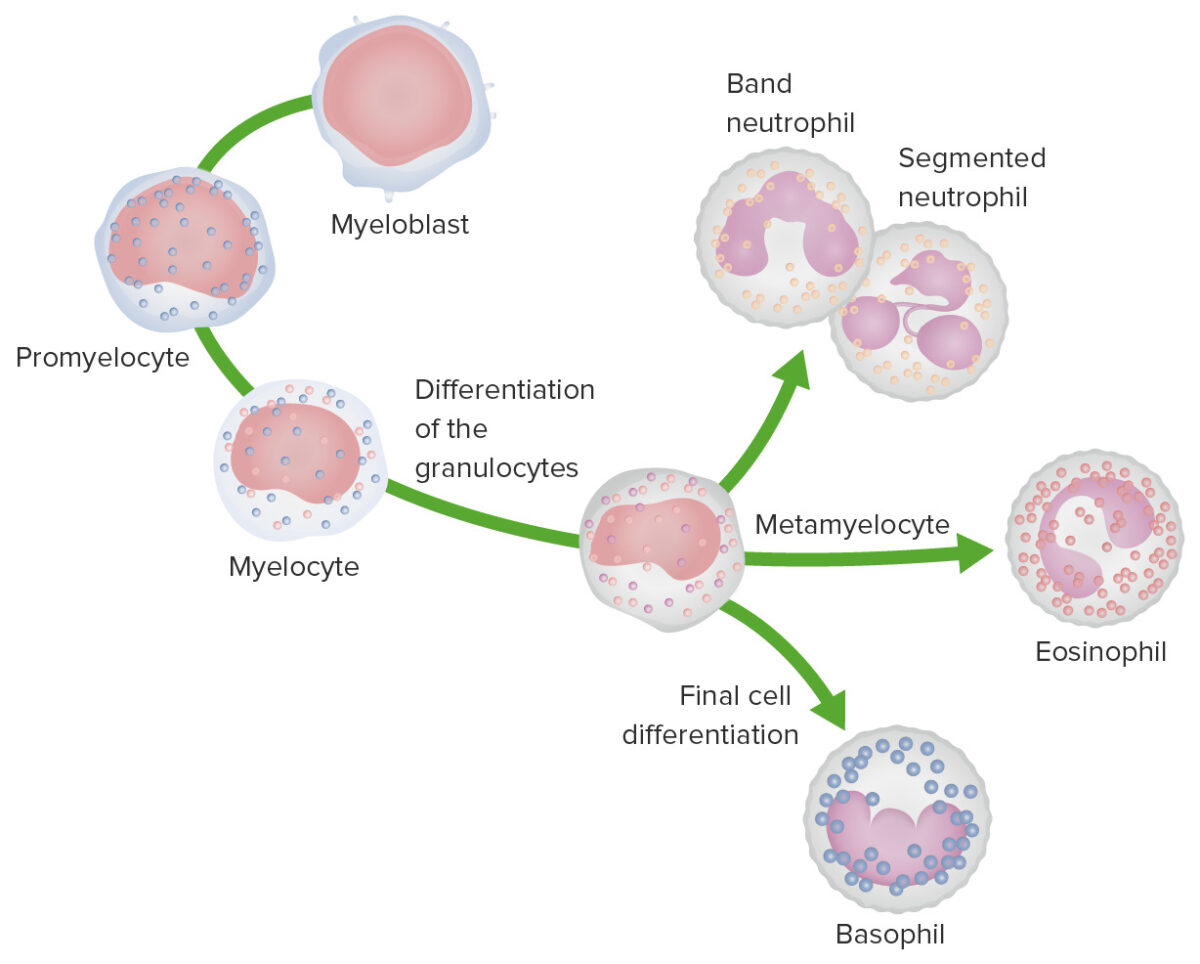
Granulopoiesis: Images depict the stages of granulocyte development.
In the most immature stage, the myeloblast is characterized by a large nucleus with faint nucleoli and a nongranular, basophilic cytoplasm.
During the promyelocyte stage, the cell enlarges and azurophilic granules appear in the cytoplasm.
In the myelocyte stage, cell division ceases and specific granules appear in the cytoplasm.
During the metamyelocyte stage, the size of the cell decreases and nuclear morphology changes; the nucleus begins to indent. For neutrophils, the nucleus forms a horseshoe shape as a band cell and is multilobulated in the mature neutrophil.
For eosinophils, the nucleus becomes bilobed and the cytoplasm has eosinophilic granules.
For basophils, the nucleus is bilobed and the cell has basic granules.
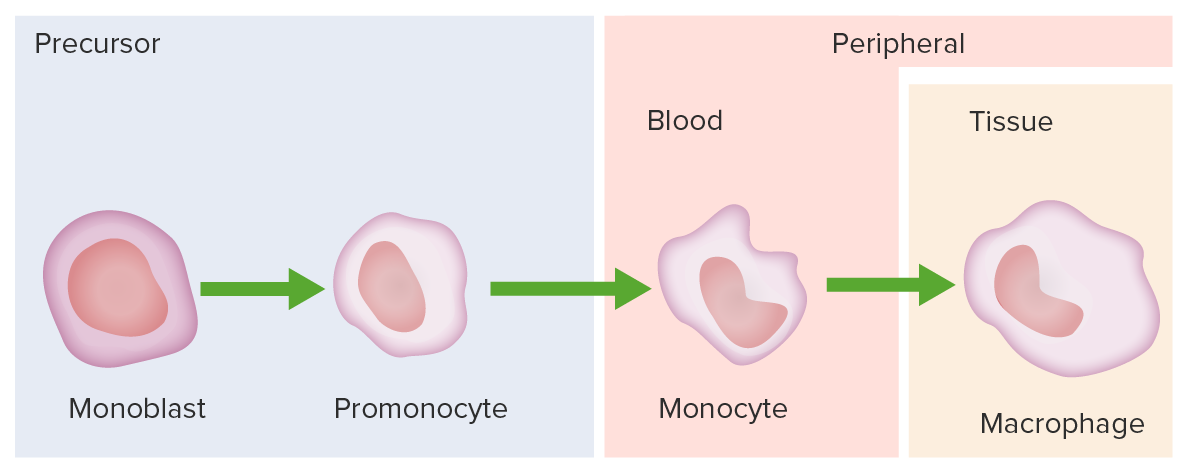
Monocyte development starts from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and progresses through stages to the colony-forming unit granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM):
The 1st monocyte precursor is the monoblast, which has a round or oval nucleus.
The promonocyte follows and has a convoluted nucleus.
The monocyte arises with an indented nucleus and is released from the bone marrow to become a macrophage in the tissues.