Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease is an autosomal dominant genetic condition resulting from a deletion or mutation in the VHL gene. Individuals diagnosed with VHL disease have tumors and cysts in various parts of their bodies and may present with hemangioblastomas, renal cell carcinoma (RCC), pheochromocytoma, endolymphatic sac tumors of the middle ear, pancreatic tumors, and papillary cystadenomas of the epididymis or the broad ligament. The diagnosis is by genetic testing, laboratory evaluation of BUN, laboratory evaluation for the presence of catecholamines in the blood or urine, fundoscopic exam of the eye to detect hemangioblastoma of the retina, and CT/MRI to detect any other tumors. Management of the disease includes surgical removal of tumors.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease is an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance disorder characterized by hemangioblastomas of the retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy and CNS; cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change involving the kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy, pancreas Pancreas The pancreas lies mostly posterior to the stomach and extends across the posterior abdominal wall from the duodenum on the right to the spleen on the left. This organ has both exocrine and endocrine tissue. Pancreas: Anatomy, and epididymis Epididymis The convoluted cordlike structure attached to the posterior of the testis. Epididymis consists of the head (caput), the body (corpus), and the tail (cauda). A network of ducts leaving the testis joins into a common epididymal tubule proper which provides the transport, storage, and maturation of spermatozoa. Testicles: Anatomy; renal cell carcinoma Renal cell carcinoma Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a tumor that arises from the lining of the renal tubular system within the renal cortex. Renal cell carcinoma is responsible for 80%-85% of all primary renal neoplasms. Most RCCs arise sporadically, but smoking, hypertension, and obesity are linked to its development. Renal Cell Carcinoma ( RCC RCC Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a tumor that arises from the lining of the renal tubular system within the renal cortex. Renal cell carcinoma is responsible for 80%-85% of all primary renal neoplasms. Most RCCs arise sporadically, but smoking, hypertension, and obesity are linked to its development. Renal Cell Carcinoma); pheochromocytomas; and pancreatic islet cell Islet cell Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (PanNETs) tumors.
The presentation varies depending on the size and location of the tumor Tumor Inflammation. Family history Family History Adult Health Maintenance is a key piece of information, as the majority of cases are inherited. Physical examination is usually nonrevealing, with the exception of affected individuals who present with neurologic abnormalities in the setting of hemangioblastomas.
HIPPEL:
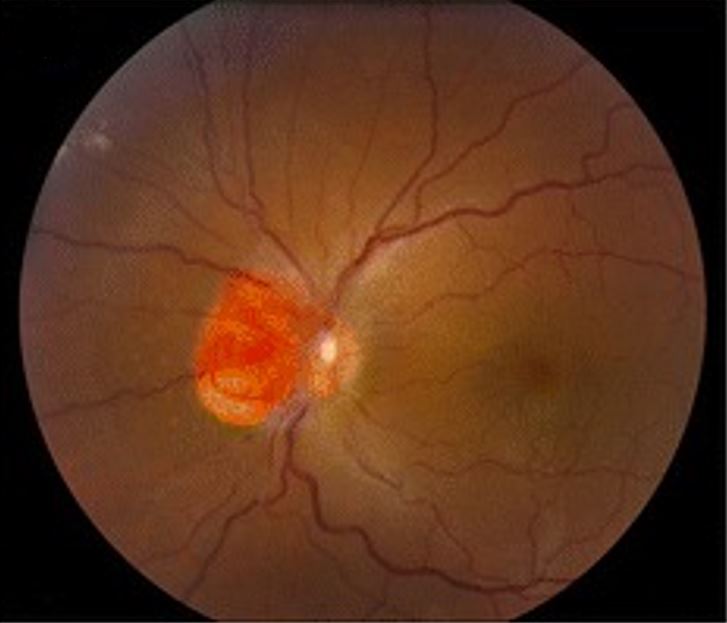
Hemangioblastoma involving the optic nerve, as seen in von Hippel-Lindau disease
Image: “Clinical photographs of the eye from the patient with von Hippel-Lindau disease” by Chen S, Chew EY, Chan CC. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.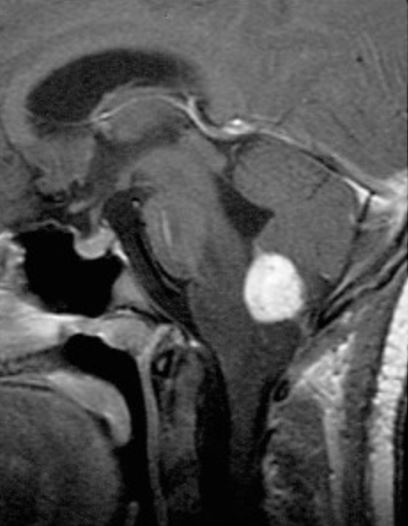
Sagittal, contrasted, T1-weighted MRI shows contrast enhancing medullary hemangioblastoma
Image: “Radiographic images of hemangioblastomas” by Schunemann V, Huntoon K, Lonser RR. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.Treatment of VHL disease is tailored depending on the location and size of the lesions, symptoms of the individual, and the extent of the disease.
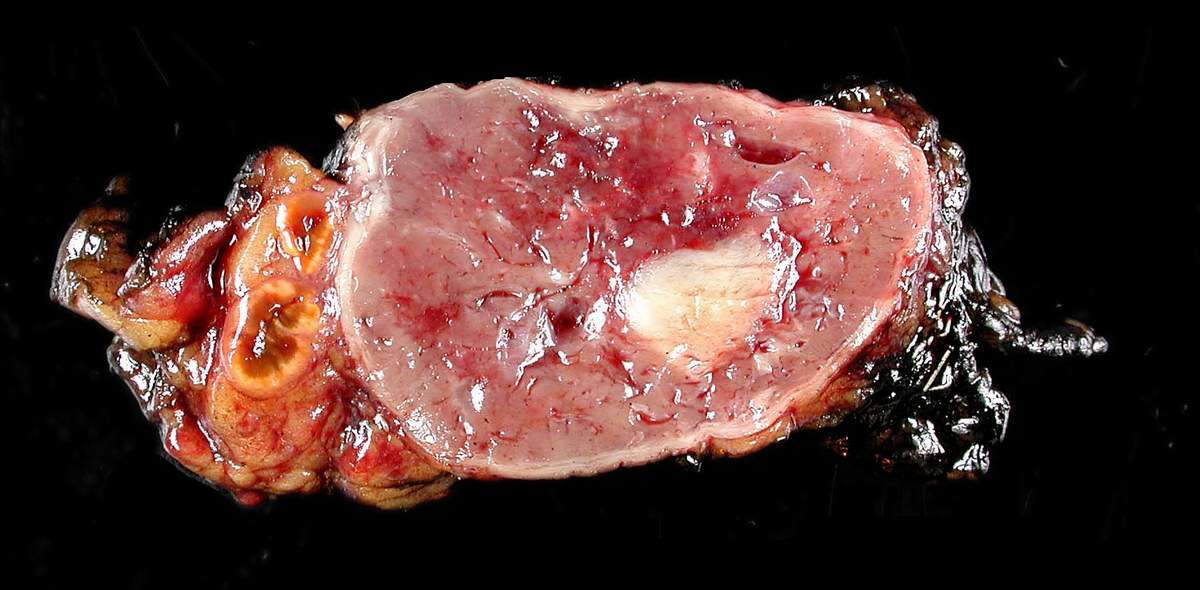
Surgically removed pheochromocytoma
Image: “Adrenal paraganglioma clinical Pheochromocytoma” by Michael Feldman. License: CC BY 2.0