A VIPoma is a rare neuroendocrine tumor Tumor Inflammation arising primarily in the pancreas Pancreas The pancreas lies mostly posterior to the stomach and extends across the posterior abdominal wall from the duodenum on the right to the spleen on the left. This organ has both exocrine and endocrine tissue. Pancreas: Anatomy that releases large amounts of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide ( VIP VIP A highly basic, 28 amino acid neuropeptide released from intestinal mucosa. It has a wide range of biological actions affecting the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and respiratory systems and is neuroprotective. It binds special receptors. Gastrointestinal Neural and Hormonal Signaling). This process leads to chronic watery diarrhea Watery diarrhea Rotavirus with concomitant hypokalemia Hypokalemia Hypokalemia is defined as plasma potassium (K+) concentration < 3.5 mEq/L. Homeostatic mechanisms maintain plasma concentration between 3.5-5.2 mEq/L despite marked variation in dietary intake. Hypokalemia can be due to renal losses, GI losses, transcellular shifts, or poor dietary intake. Hypokalemia and dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration, as well as wheezing Wheezing Wheezing is an abnormal breath sound characterized by a whistling noise that can be relatively high-pitched and shrill (more common) or coarse. Wheezing is produced by the movement of air through narrowed or compressed small (intrathoracic) airways. Wheezing and flushing (known as Verner-Morrison or WDHA (chronic Watery Diarrhea, Hypokalemia, Achlorhydria) syndrome). Most tumors arise sporadically, but some are associated with MEN 1. Diagnosis is established by measuring serum VIP VIP A highly basic, 28 amino acid neuropeptide released from intestinal mucosa. It has a wide range of biological actions affecting the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and respiratory systems and is neuroprotective. It binds special receptors. Gastrointestinal Neural and Hormonal Signaling levels. Treatment consists of medical management of symptoms and complete surgical removal of the tumor Tumor Inflammation when possible.
Last updated: Jul 14, 2025
A VIPoma is a rare neuroendocrine tumor Tumor Inflammation that secretes vasoactive intestinal polypeptide ( VIP VIP A highly basic, 28 amino acid neuropeptide released from intestinal mucosa. It has a wide range of biological actions affecting the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and respiratory systems and is neuroprotective. It binds special receptors. Gastrointestinal Neural and Hormonal Signaling).
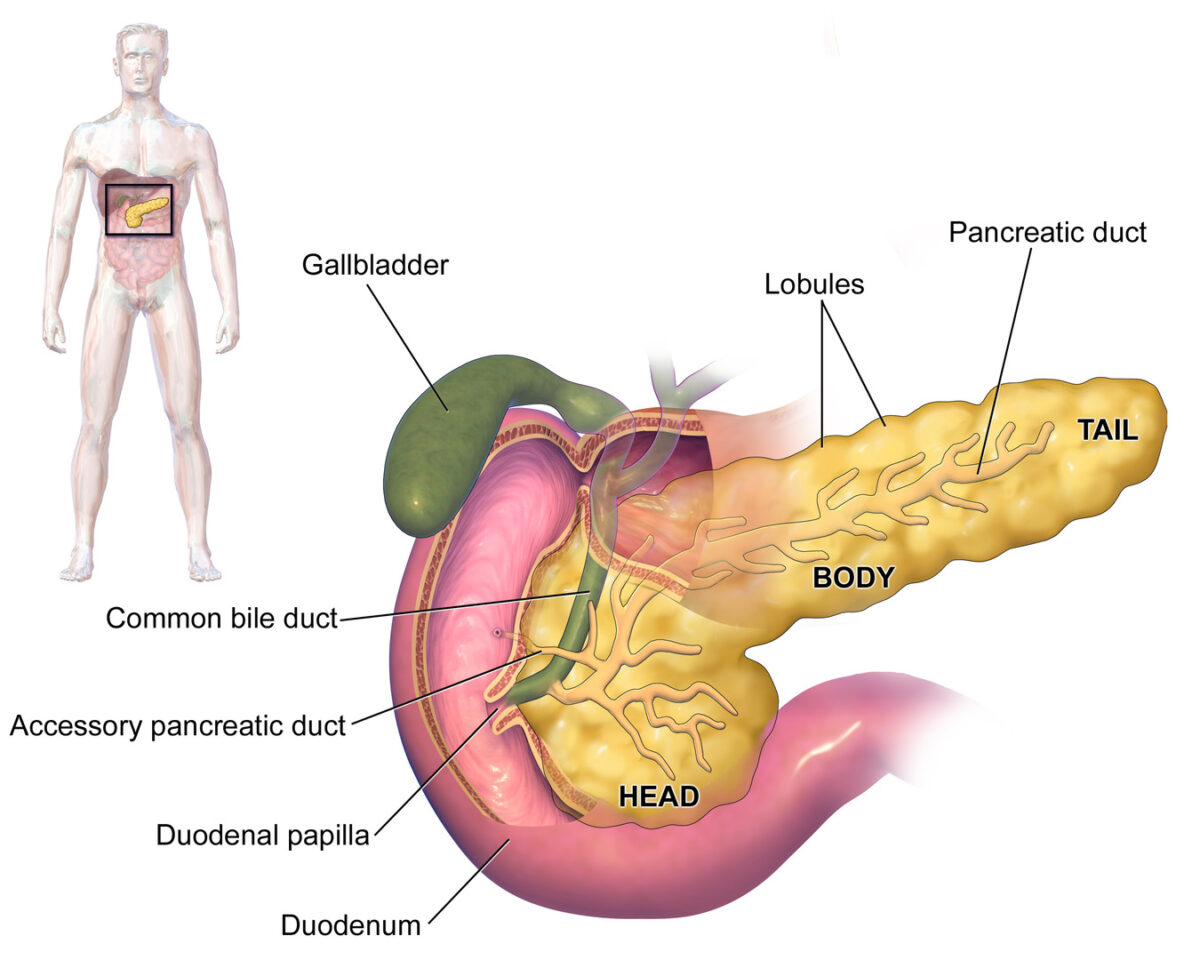
Anatomy of the pancreas
Image: “Blausen 0699 PancreasAnatomy2” by Blausen. License: CC BY 3.0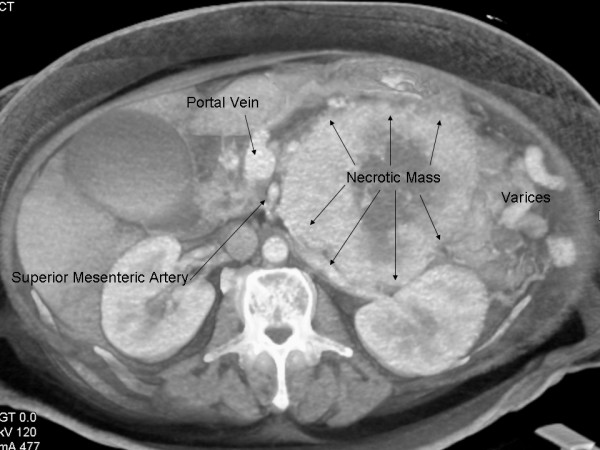
Computed tomography scan showing large necrotic pancreatic VIPoma
Image: “Multi-visceral resection of pancreatic VIPoma in a patient with sinistral portal hypertension” by Joyce DL, Hong K, Fishman EK, Wisell J, Pawlik TM. License: CC BY 2.0