Vibrio is a genus of comma-shaped, gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella. It is halophilic, acid labile, and commonly isolated on thiosulfate-citrate-bile-sucrose (TCBS) agar. There are 3 clinically relevant species. Vibrio cholerae (V. cholerae) is found in brackish and marine waters. Vibrio cholerae is associated with cholera, which causes severe, secretory “rice-water” diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea. The other 2 species are Vibrio vulnificus (V. vulnificus) and Vibrio parahaemolyticus (V. parahaemolyticus), which are transmitted through raw or undercooked shellfish and are associated with wound infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, septicemia, and diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
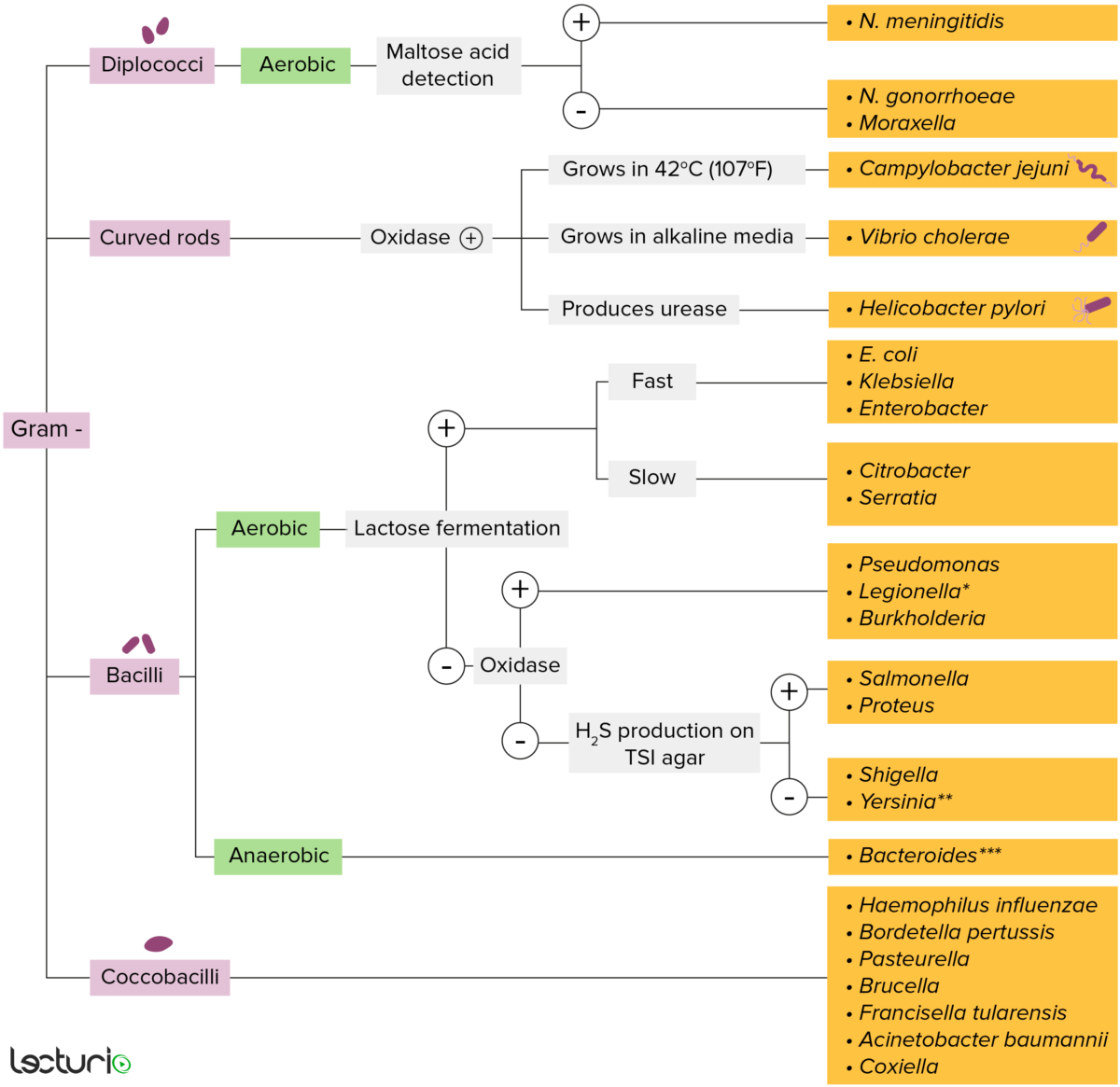
Gram-negative bacteria:
Most bacteria can be classified according to a lab procedure called Gram staining.
Bacteria with cell walls that have a thin layer of peptidoglycan do not retain the crystal violet stain utilized in Gram staining. These bacteria do, however, retain the safranin counterstain and thus appear as pinkish-red on the stain, making them gram negative. These bacteria can be further classified according to morphology (diplococci, curved rods, bacilli, and coccobacilli) and their ability to grow in the presence of oxygen (aerobic versus anaerobic). The bacteria can be more narrowly identified by growing them on specific media (triple sugar iron (TSI) agar) where their enzymes can be identified (urease, oxidase) and their ability to ferment lactose can be tested.
* Stains poorly on Gram stain
** Pleomorphic rod/coccobacillus
*** Require special transport media
V. cholerae: scanning electron micrograph
Image: “Cholera bacteria SEM” by Zeimusu. License: Public Domain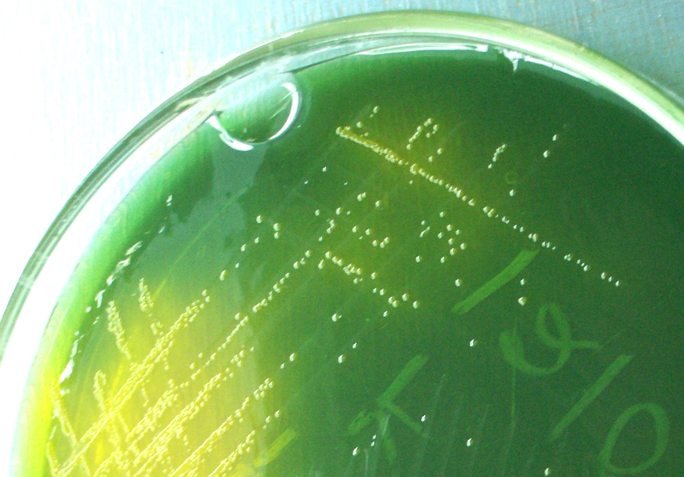
Yellow-colored (sucrose-fermenting) colonies of V. cholerae on TCBS agar
Image: “Vibrio cholerae on TCBS agar” by Microrao. License: Public DomainAbout 50% of infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease with classic V. cholerae are asymptomatic and 75% of infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease with El Tor biotype of V. cholerae are asymptomatic.
Diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea:
Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia:
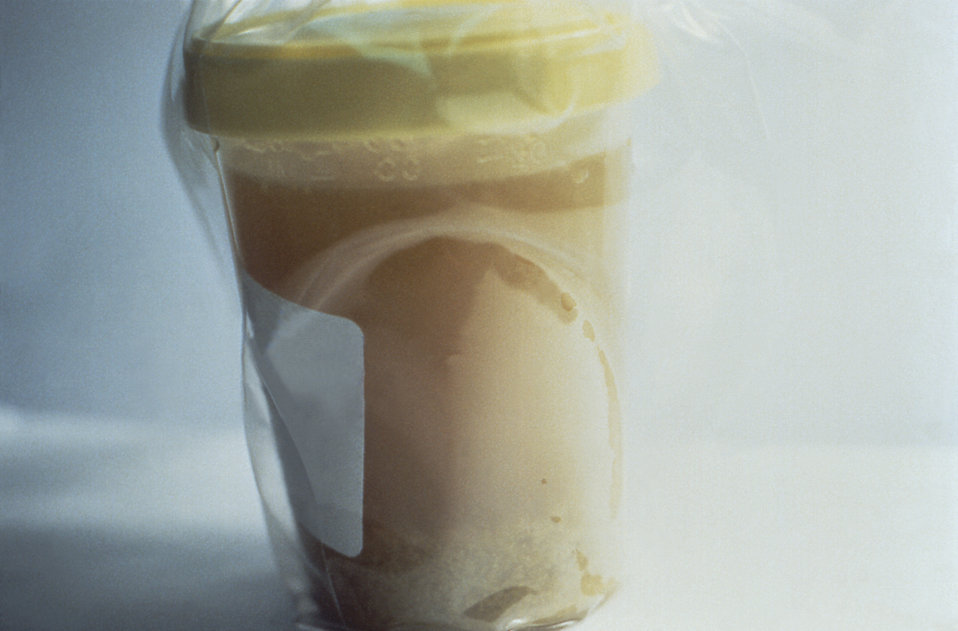

Typical cholera diarrhea that looks like “rice water”
Image: “Here, a cup of typical “rice-water” stool from a cholera patient shows flecks of mucus that have settled to the bottom” by CDC. License: Public DomainMortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status in untreated patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship is up to 50% (but < 1% with prompt electrolyte and fluid replacement).
Treatment:
Prevention: