The human spine, or vertebral column, is the most important anatomical and functional axis of the human body. It consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and 5 lumbar vertebrae and is limited cranially by the skull Skull The skull (cranium) is the skeletal structure of the head supporting the face and forming a protective cavity for the brain. The skull consists of 22 bones divided into the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) and the neurocranium. Skull: Anatomy and caudally by the sacrum. The vertebral column is the foundation for the trunk, provides an attachment for muscles and ligaments, and protects the spinal cord Spinal cord The spinal cord is the major conduction pathway connecting the brain to the body; it is part of the CNS. In cross section, the spinal cord is divided into an H-shaped area of gray matter (consisting of synapsing neuronal cell bodies) and a surrounding area of white matter (consisting of ascending and descending tracts of myelinated axons). Spinal Cord: Anatomy and nerve roots.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The vertebral column is the primary axis of the skeleton:
The vertebral column consists of 33 vertebrae placed in series and connected by intervertebral discs and ligaments.
Five different groups of vertebrae:
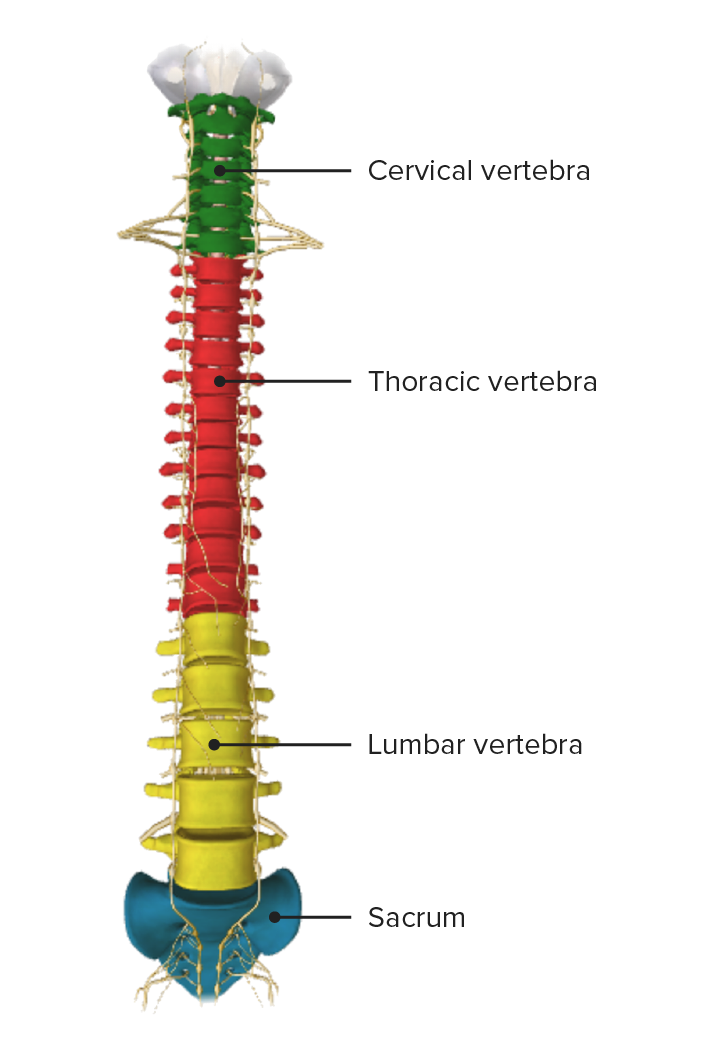
Vertebral column, anterior view
Image by BioDigital, edited by LecturioNumber of vertebrae per segment:
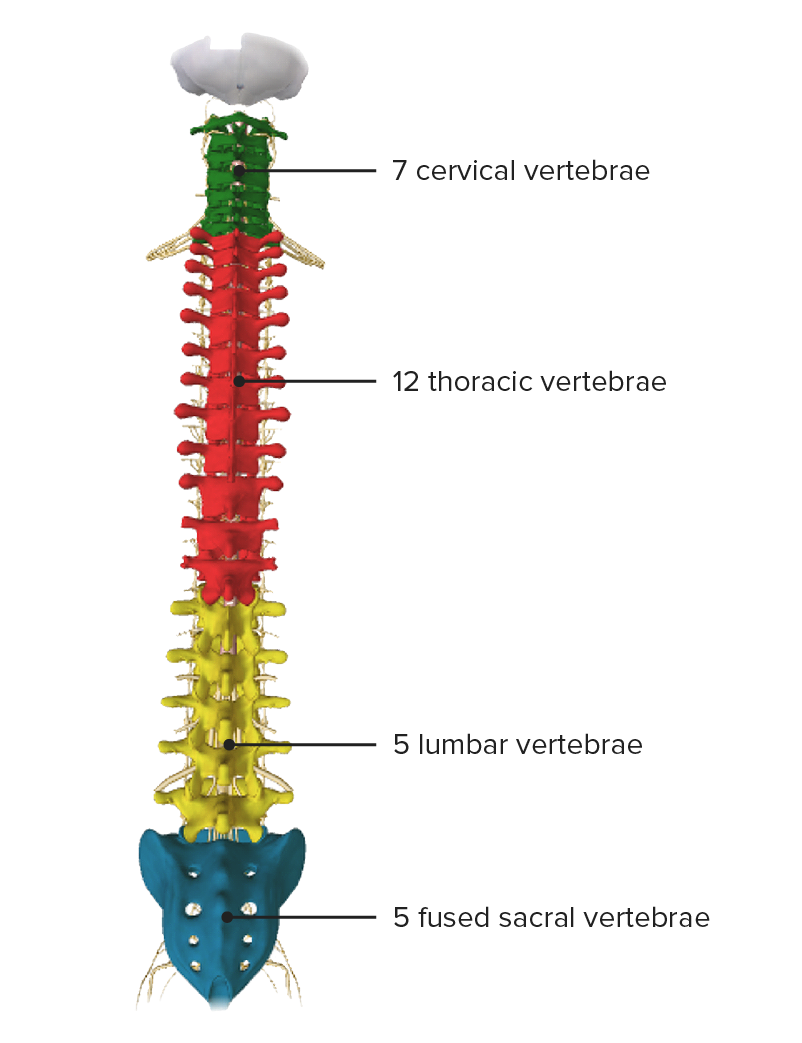
Vertebral column, posterior view
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio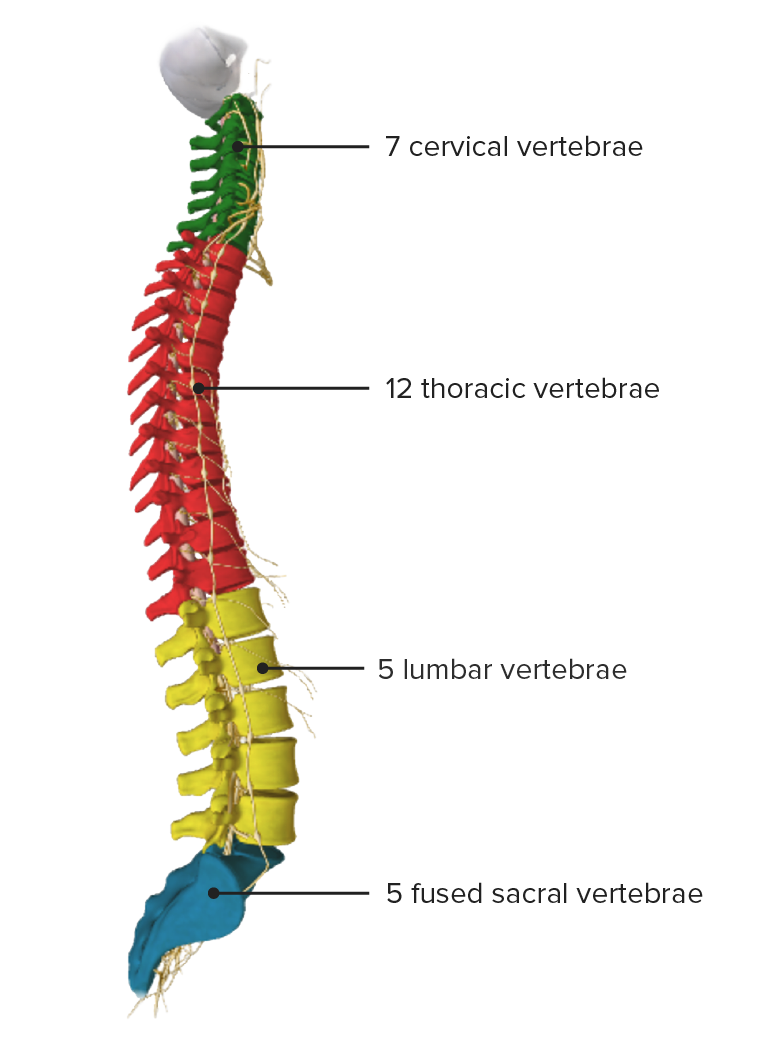
Vertebral column, lateral view
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio| Vertebrae | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Cervical |
|
| Thoracic |
|
| Lumbar |
|
| Sacrum |
|
| Coccyx |
|
| Spinal segment | Vertebrae | Curvature |
|---|---|---|
| Cervical | C1–C7 | Lordosis |
| Thoracic | T1–T12 | Kyphosis Kyphosis Deformities of the spine characterized by an exaggerated convexity of the vertebral column. The forward bending of the thoracic region usually is more than 40 degrees. This deformity sometimes is called round back or hunchback. Osteoporosis |
| Lumbar | L1–L5 | Lordosis |
| Sacral | S1 S1 Heart Sounds–S5 (fused) | Kyphosis Kyphosis Deformities of the spine characterized by an exaggerated convexity of the vertebral column. The forward bending of the thoracic region usually is more than 40 degrees. This deformity sometimes is called round back or hunchback. Osteoporosis |
| Coccygeal | 3–5 (fused) |

Spinal cord traveling through the vertebral foramen with nerve roots (in yellow) exiting through the intervertebral foramina
Image: “Articulated Vertebrae” by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.Vertebrae protect the spinal column.
Two adjacent vertebrae are often referred to as a motion segment or functional unit of the spine (e.g., C6 and C7).
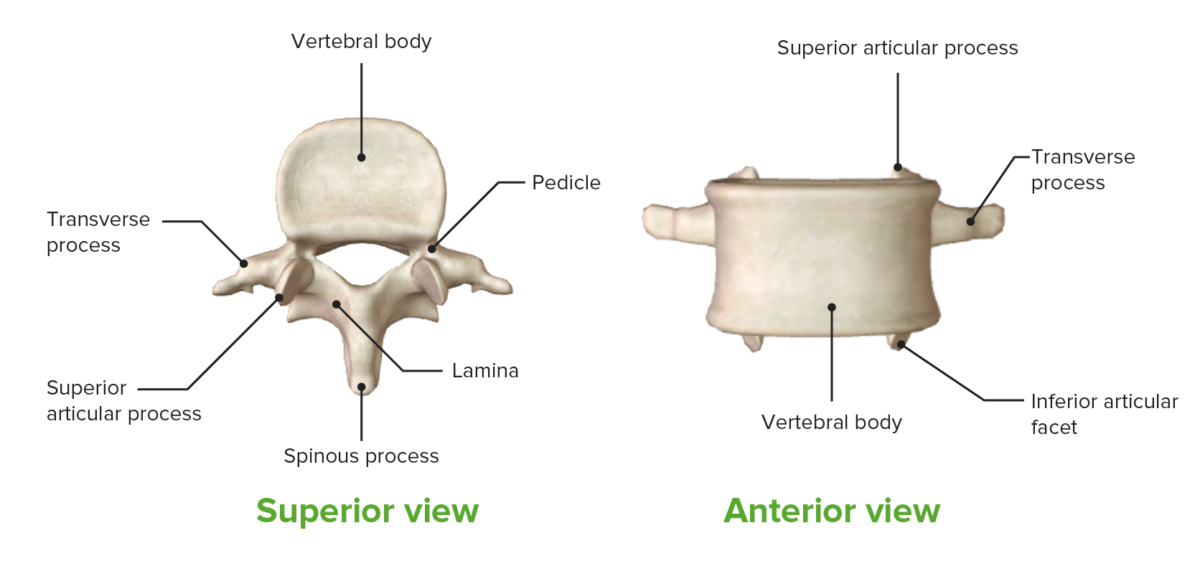
Components of vertebrae
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio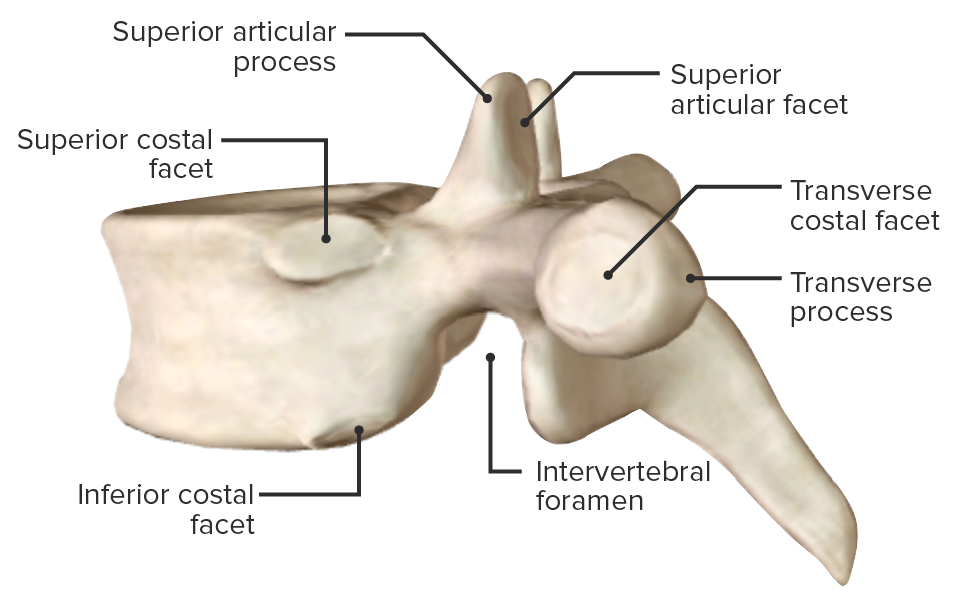
Lateral view of vertebra, highlighting the intervertebral foramen
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio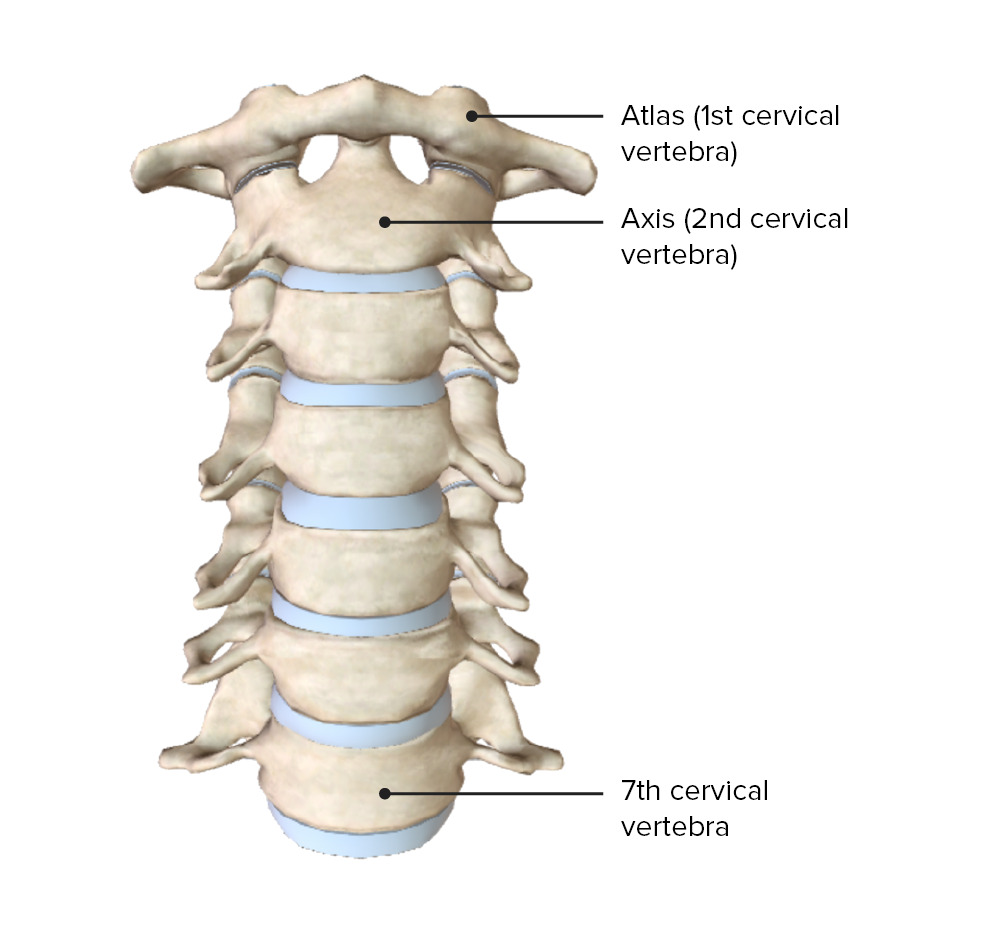
The 1st and 2nd cervical vertebrae are called the atlas and axis, respectively.
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio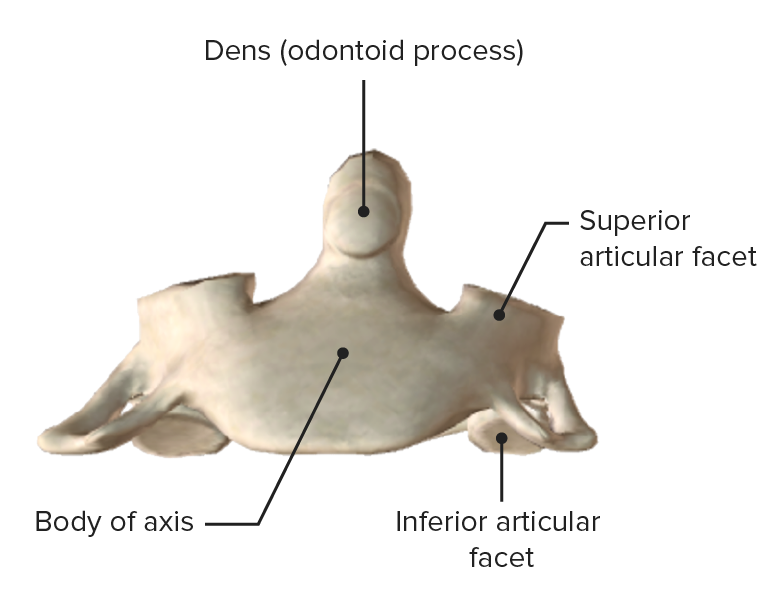
Axis, anterior view
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio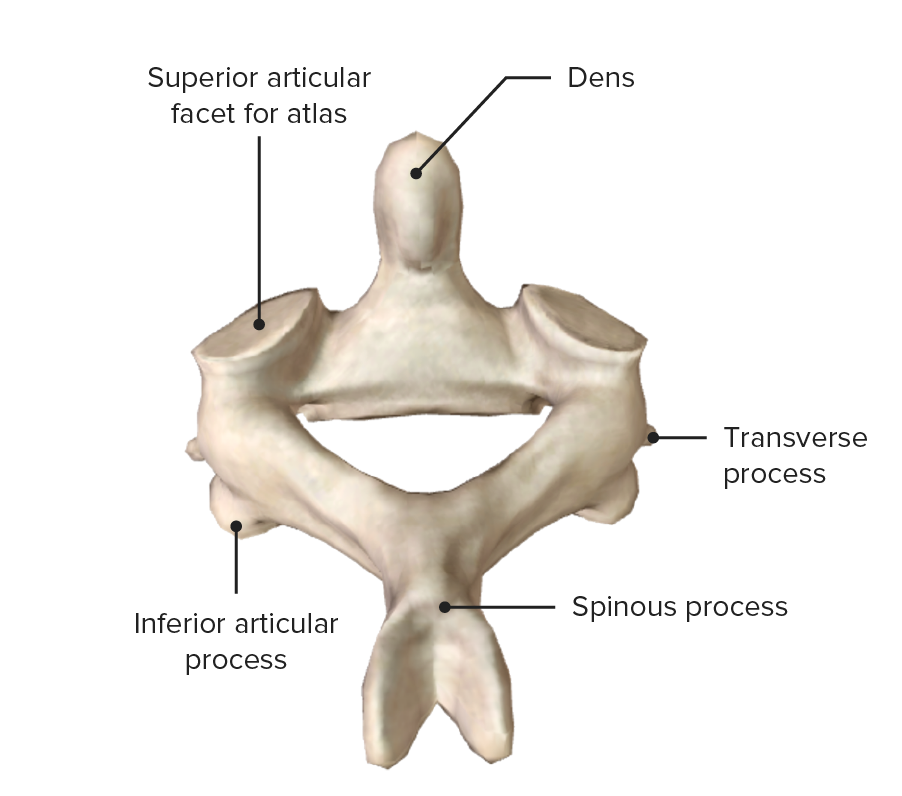
Axis (C2), posterosuperior view
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio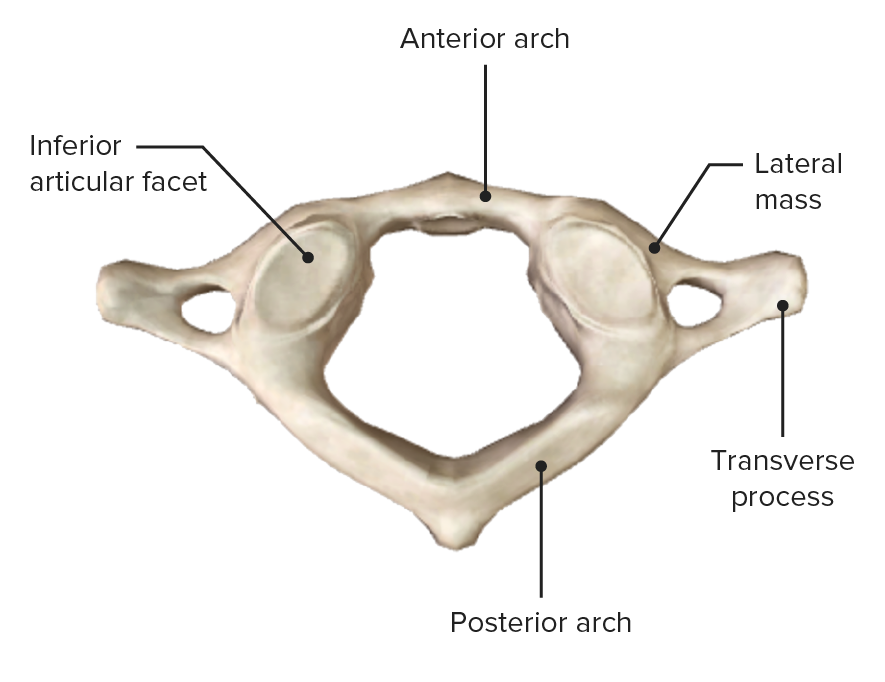
Atlas (C1), inferior view
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio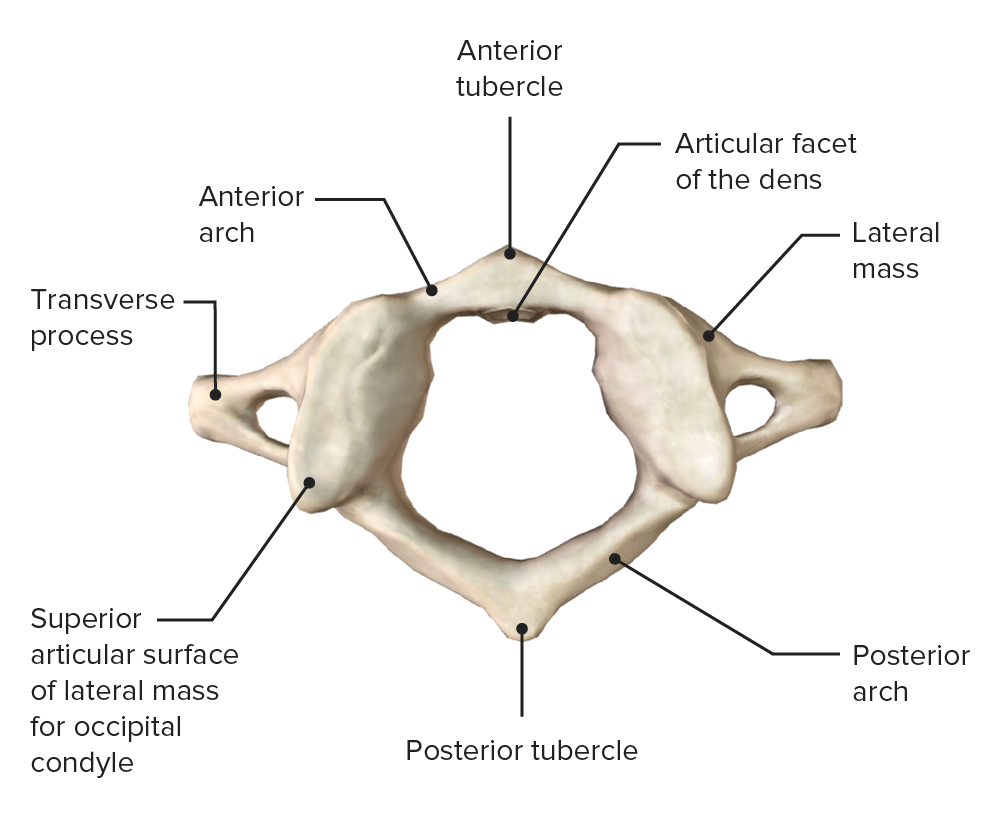
Atlas (C1), superior view
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio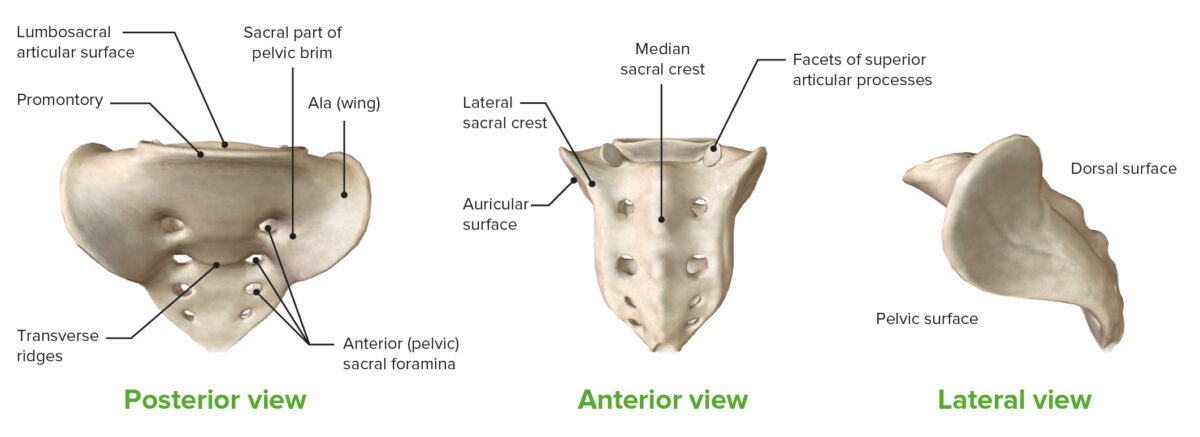
3 views of the sacrum:
The coccyx extends from the inferior portion of the sacrum.
Intervertebral discs form the primary connection between vertebrae.
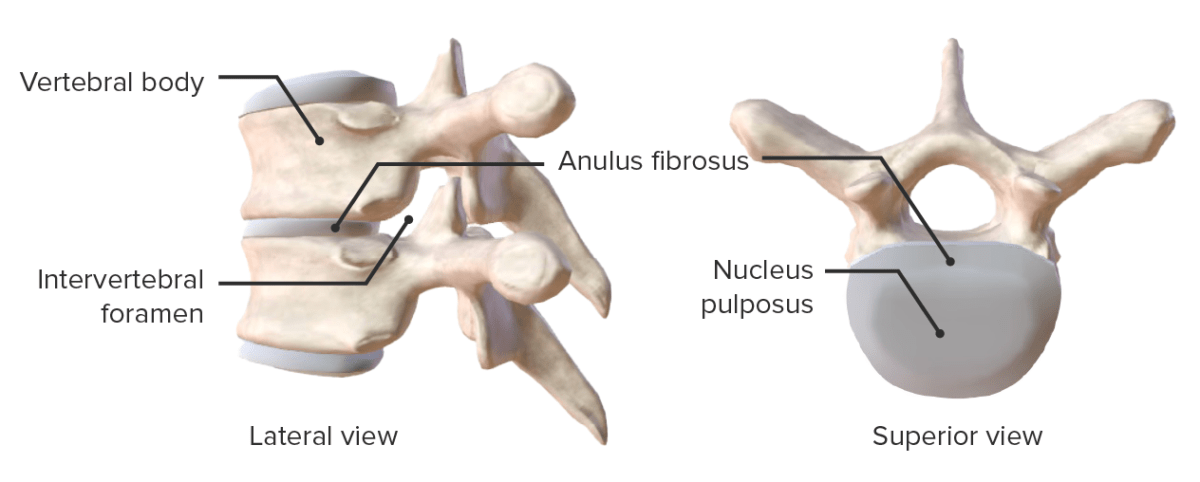
Views showing the components of the intervertebral disc
Image by Lecturio.The ligaments of the vertebral column are essential for stability of the spine:
| Ligament | Characteristics | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Anterior longitudinal ligament |
|
|
| Posterior longitudinal ligament |
|
|
| Ligamentum flavum |
|
Stabilizes the vertebral arch joint during flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs |
| Interspinous ligament |
|
Stabilizes, controls, and limits flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs, lateral flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs, and rotation Rotation Motion of an object in which either one or more points on a line are fixed. It is also the motion of a particle about a fixed point. X-rays |
| Supraspinous ligament |
|
Stabilizes, controls, and limits flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs, lateral flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs, and rotation Rotation Motion of an object in which either one or more points on a line are fixed. It is also the motion of a particle about a fixed point. X-rays |
| Intertransverse ligament | Connects the transverse processes of adjacent cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae | Limits both flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs and lateral flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs |
| Nuchal ligament |
|
Limits flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs of the cervical spine |
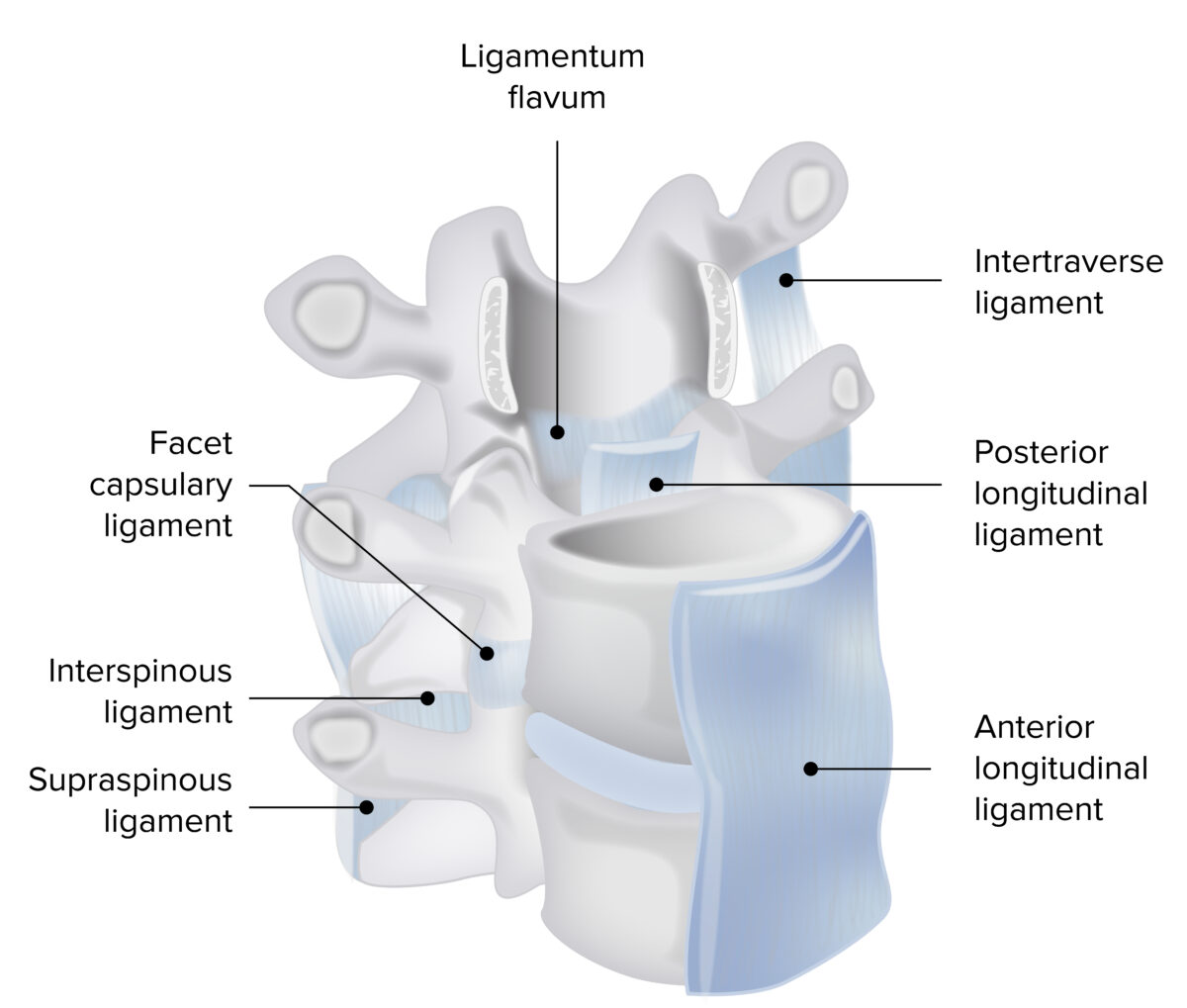
Ligaments of the vertebral column
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Joints of the spine consist of intervertebral discs and facet joints: