The ventricular system is an extension Extension Examination of the Upper Limbs of the subarachnoid space Subarachnoid space The space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater, filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It contains large blood vessels that supply the brain and spinal cord. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage into the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification consisting of a series of interconnecting spaces and channels Channels The Cell: Cell Membrane. Four chambers are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): the paired lateral ventricles, the unpaired 3rd ventricle, and the unpaired 4th ventricle. Connections between the structures occur via the interventricular foramen of Monro and the cerebral aqueduct (sylvian aqueduct). The foramen of Magendie and the foramen of Luschka, are additional channels Channels The Cell: Cell Membrane present in the 4th ventricle.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The ventricular system consists of 4 ventricles with an aqueduct connecting the 3rd and 4th ventricles. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows through the ventricles before entering the subarachnoid space Subarachnoid space The space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater, filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It contains large blood vessels that supply the brain and spinal cord. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage of the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification and spinal cord Spinal cord The spinal cord is the major conduction pathway connecting the brain to the body; it is part of the CNS. In cross section, the spinal cord is divided into an H-shaped area of gray matter (consisting of synapsing neuronal cell bodies) and a surrounding area of white matter (consisting of ascending and descending tracts of myelinated axons). Spinal Cord: Anatomy from the 4th ventricle:
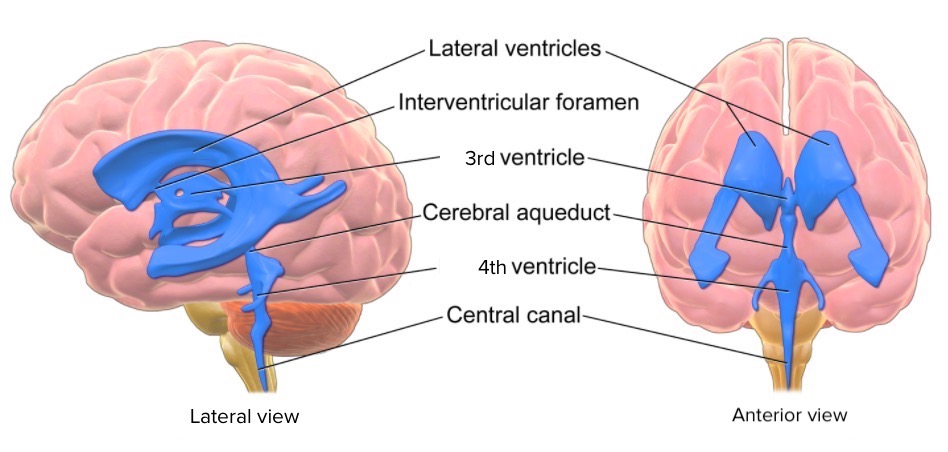
Ventricles of the brain
Image: “Ventricles of the brain” by Bruce Blaus. License: CC BY 3.0, edited by Lecturio.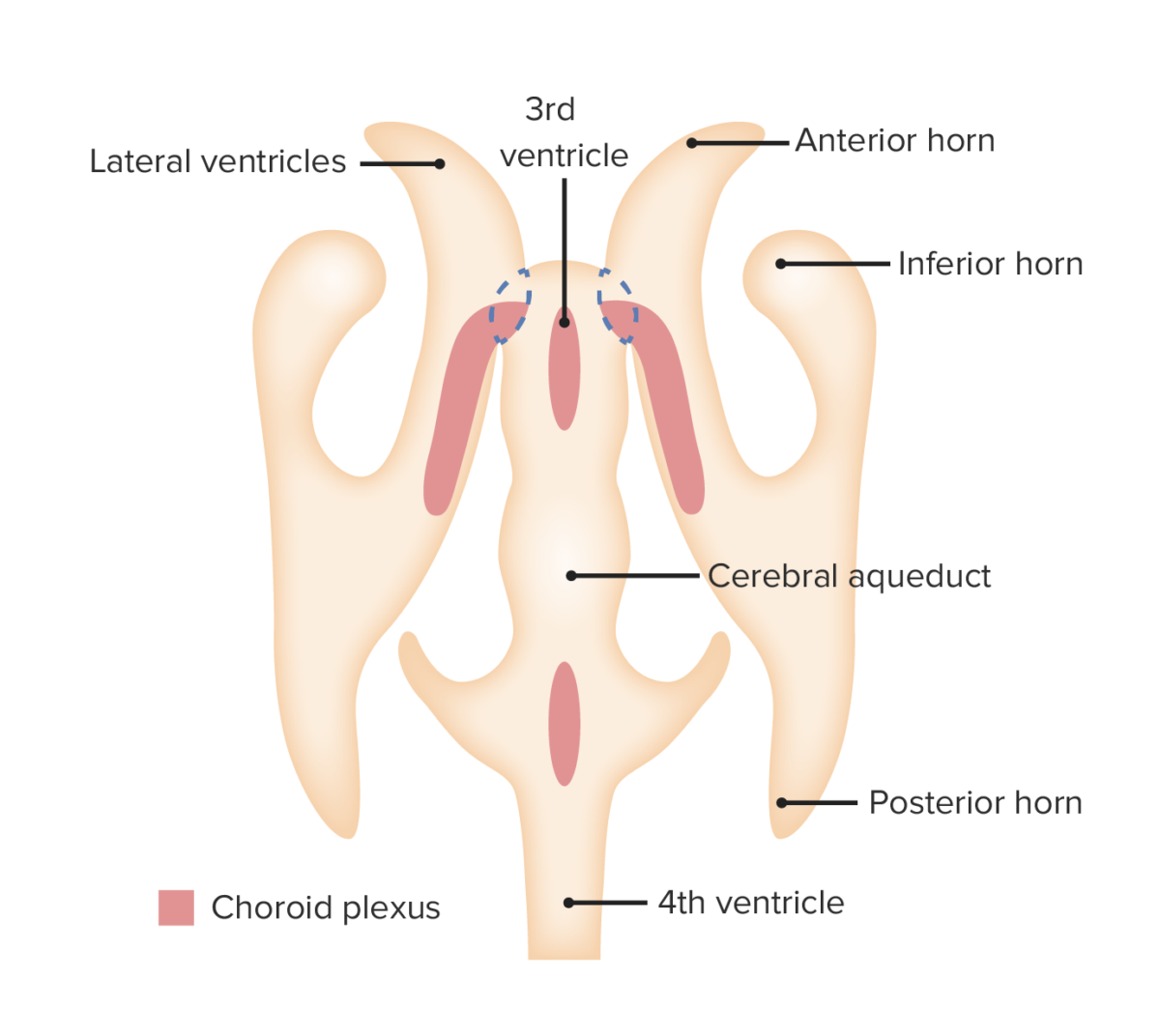
Choroid plexus development: The choroid plexus is located throughout the ventricular system and is responsible for the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid.
Image by Lecturio.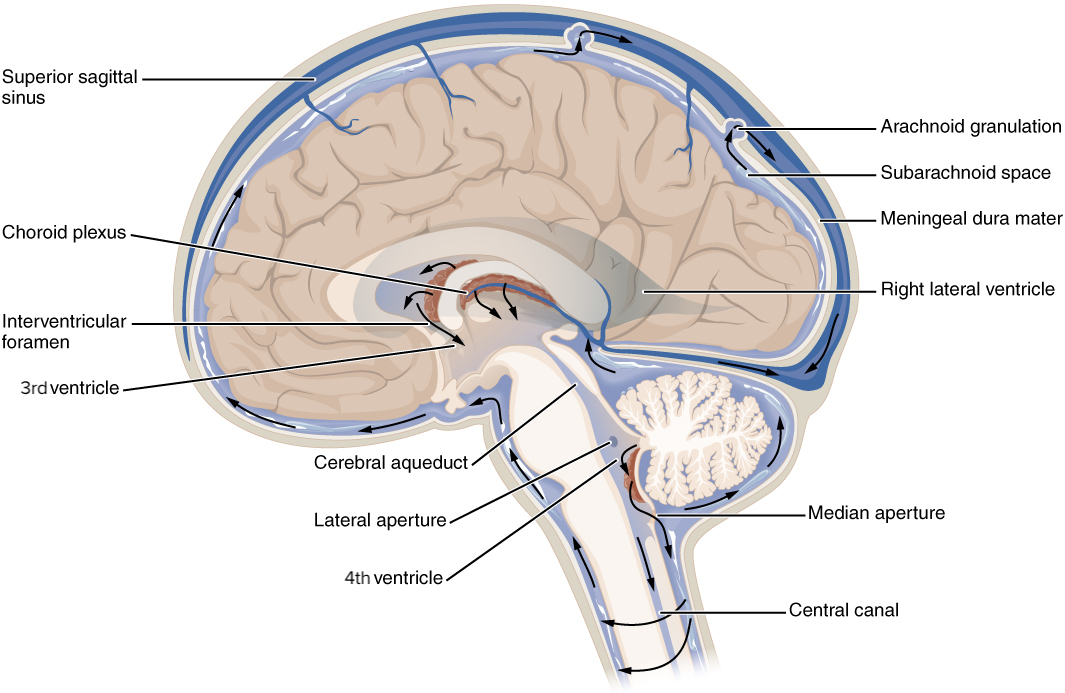
Circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF):
Note the emergence of CSF from the choroid plexus into the ventricles. Cerebrospinal fluid is reabsorbed by arachnoid granulations into the venous circulation.