Vasculitides are a group of conditions characterized by vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage, and damage to the organs supplied by the affected vessels. The affected arteries Arteries Arteries are tubular collections of cells that transport oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart to the tissues of the body. The blood passes through the arteries in order of decreasing luminal diameter, starting in the largest artery (the aorta) and ending in the small arterioles. Arteries are classified into 3 types: large elastic arteries, medium muscular arteries, and small arteries and arterioles. Arteries: Histology are of different sizes and locations and vary by the type of vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Vasculitides can be a primary condition or secondary to another underlying disease. There is no clearly known pathophysiology. The diagnosis should be considered in any individual with palpable purpura, pulmonary infiltrates, ischemic events, and multisystem disease Multisystem disease Mitochondrial Myopathies. Prompt recognition and therapy of the vasculitides are imperative, as they are often serious and sometimes fatal diseases. Management includes immunosuppressive, antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B, and/or antiinflammatory agents.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Vasculitides are diseases of the blood vessels, with inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of vessel walls leading to bleeding, ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage, and necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage of distal tissue and organs.
The following classification is adapted from the 2012 International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides:
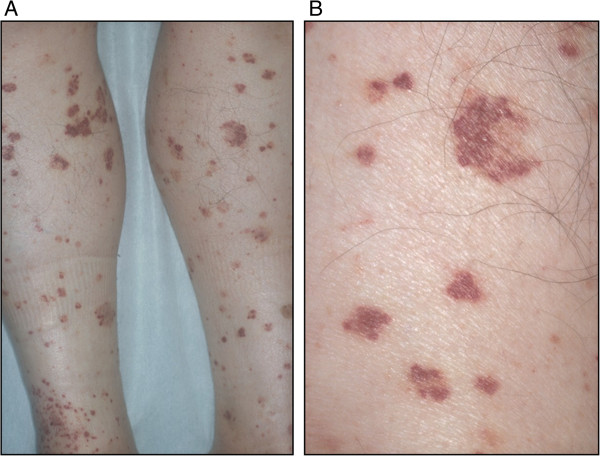
Purpura:
A: Diffuse small palpable purpura on the lower extremities
B: Magnified view
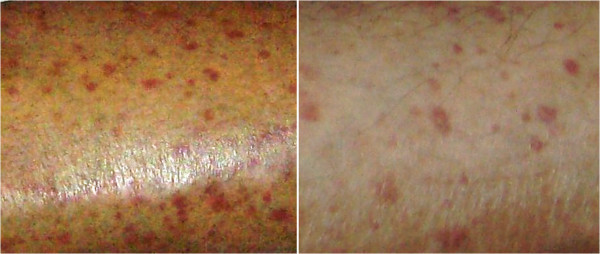
Purpuric skin rash in an individual with cryoglobulinemic vasculitis secondary to a connective tissue disease.
Image: “Purpuric skin rash” by Gheita TA et al. License: CC BY 4.0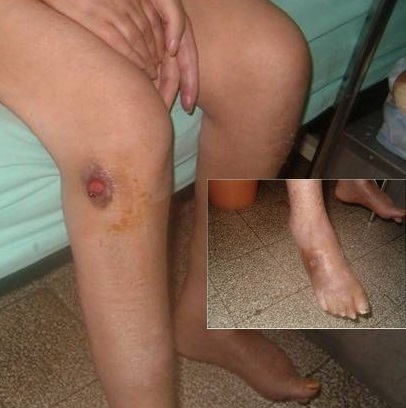
Multiple ulcerations in an individual with microscopic polyangiitis
Image: “Multiple ulcerations in a patient with microscopic polyangiitis” by Khammassi N et al. License: CC BY 2.0Initial lab evaluation in suspected vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus includes:
Additional testing may include:
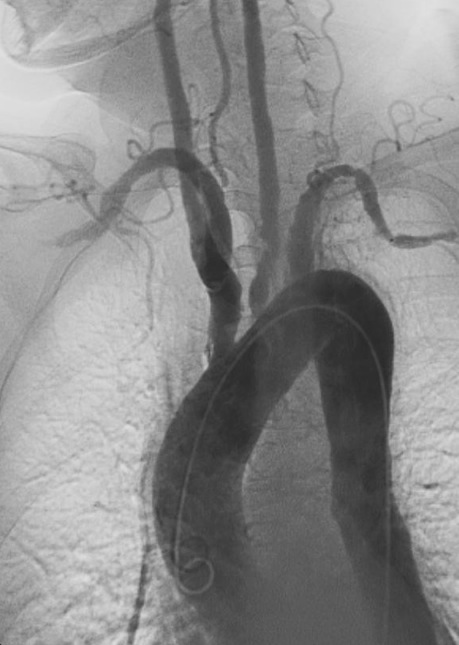
Angiography of Takayasu arteritis:
Note the stenosis and poststenotic dilations in main branches of the aortic arch.
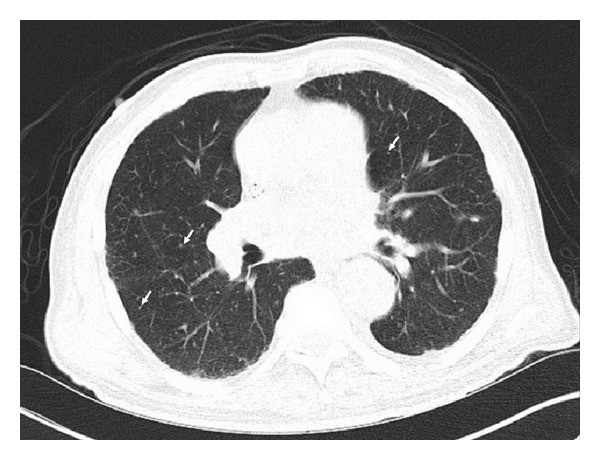
CT scan with diffuse tiny bilateral pulmonary nodules (arrows) secondary to granulomatous disease, particularly with large calcified granulomas with mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy.
This individual was positive for ANCA and diagnosed with microscopic polyangiitis. Image: “CT scan with diffuse tiny bilateral pulmonary nodules” by Iruku P et al. License: CC BY 3.0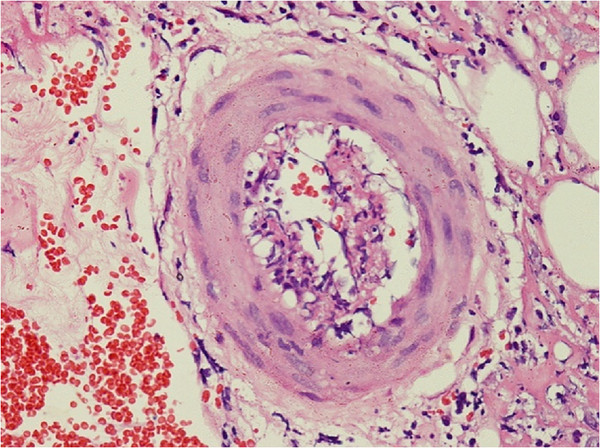
Skin biopsy shows perivascular lymphocytic and neutrophilic infiltration with fibrinoid necrosis of vessel wall and leukocytoclastic and red cell extravasations in an individual with polyarteritis nodosa.
Image: “Skin biopsy shows perivascular lymphocytic and neutrophilic infiltration” by Rodrigo D et al. License: CC BY 2.0