The vulva is the external genitalia of the female and includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule Vestibule An oval, bony chamber of the inner ear, part of the bony labyrinth. It is continuous with bony cochlea anteriorly, and semicircular canals posteriorly. The vestibule contains two communicating sacs (utricle and saccule) of the balancing apparatus. The oval window on its lateral wall is occupied by the base of the stapes of the middle ear. Ear: Anatomy, vestibular bulb, and greater vestibular glands. The vagina is the female genital canal, extending from the vulva externally to the cervix Cervix The uterus, cervix, and fallopian tubes are part of the internal female reproductive system. The most inferior portion of the uterus is the cervix, which connects the uterine cavity to the vagina. Externally, the cervix is lined by stratified squamous cells; however, the cervical canal is lined by columnar epithelium. Uterus, Cervix, and Fallopian Tubes: Anatomy uteri internally. The structures have sexual, reproductive, and urinary functions and a rich blood supply, mainly arising from the internal iliac artery.
Last updated: Nov 19, 2024
Male development is triggered by the presence of certain hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types; female development is triggered primarily by the absence of hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types.
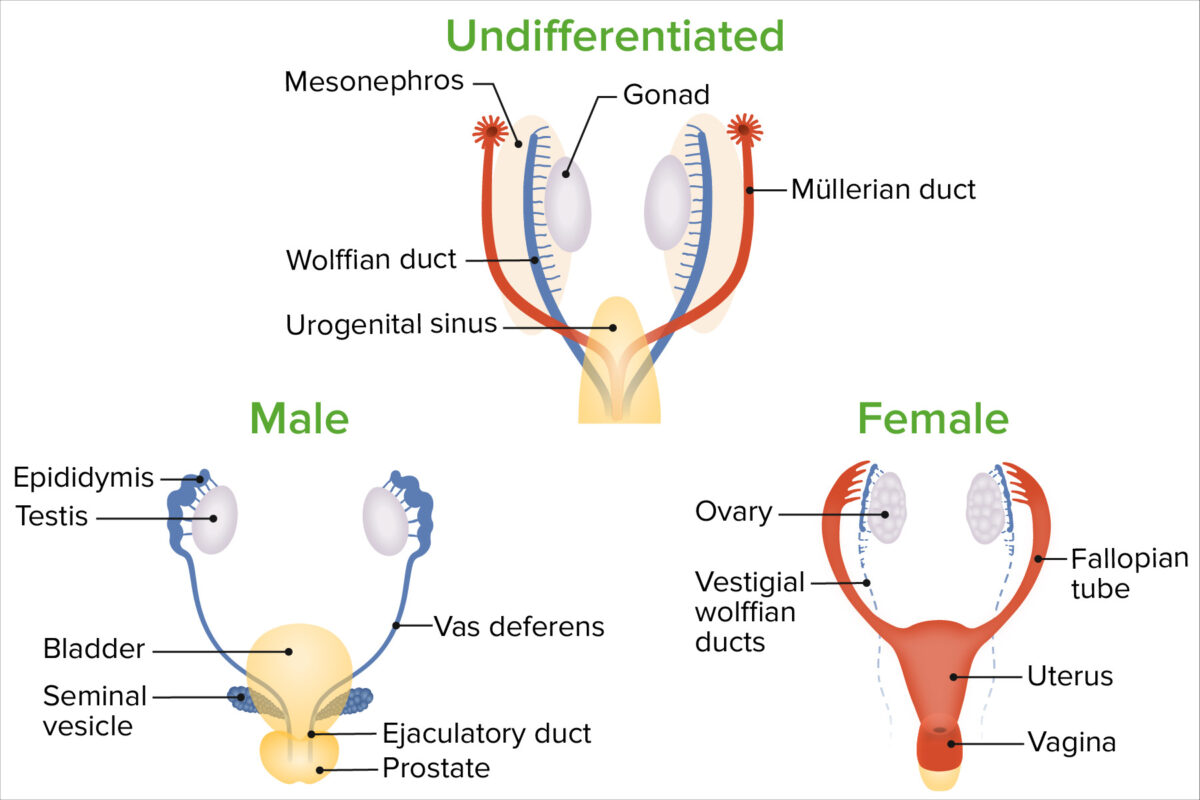
Sex differentiation
Image by Lecturio.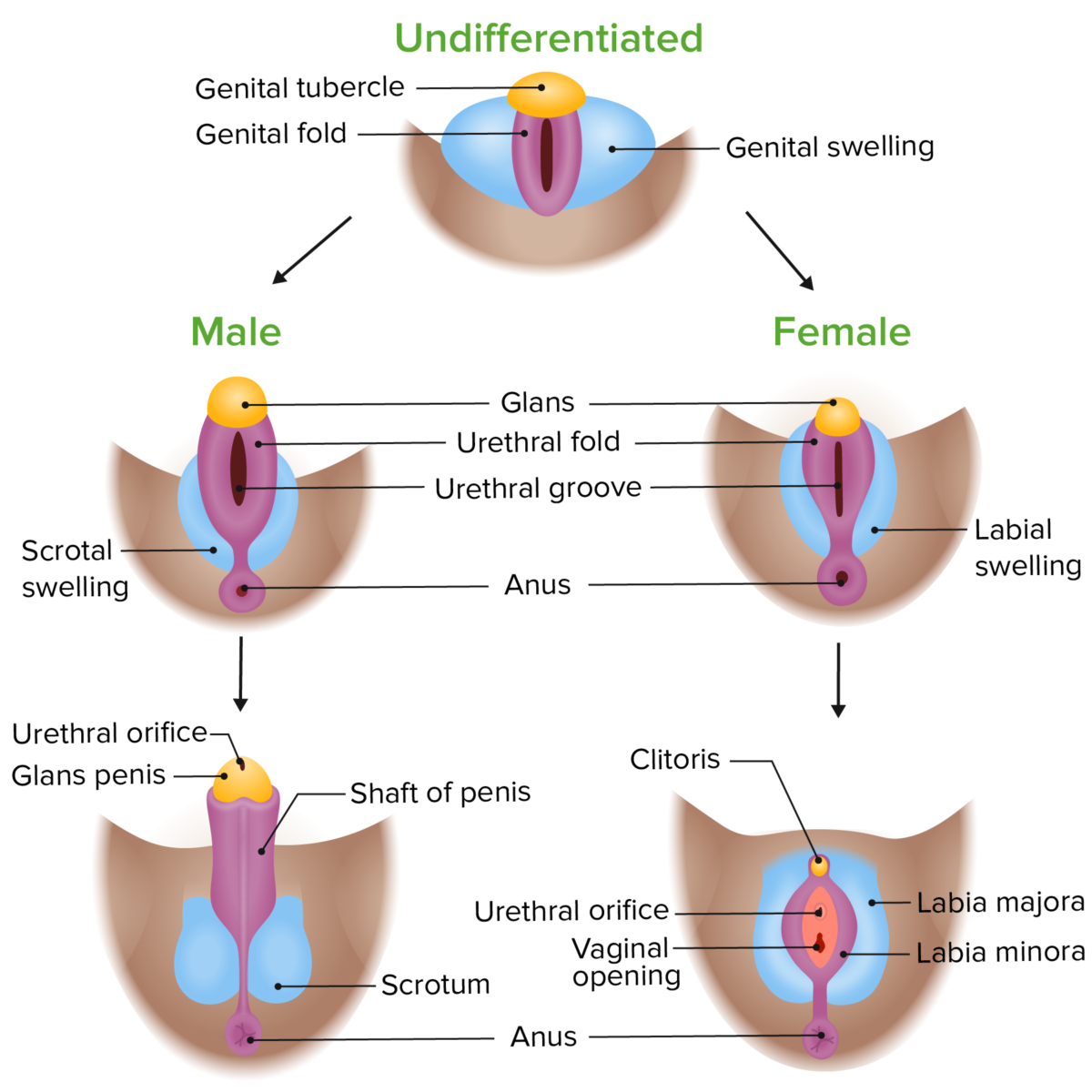
Phenotypic differentiation of the external genitalia in male and female embryos
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0The vagina is the external entrance to the female reproductive tract.
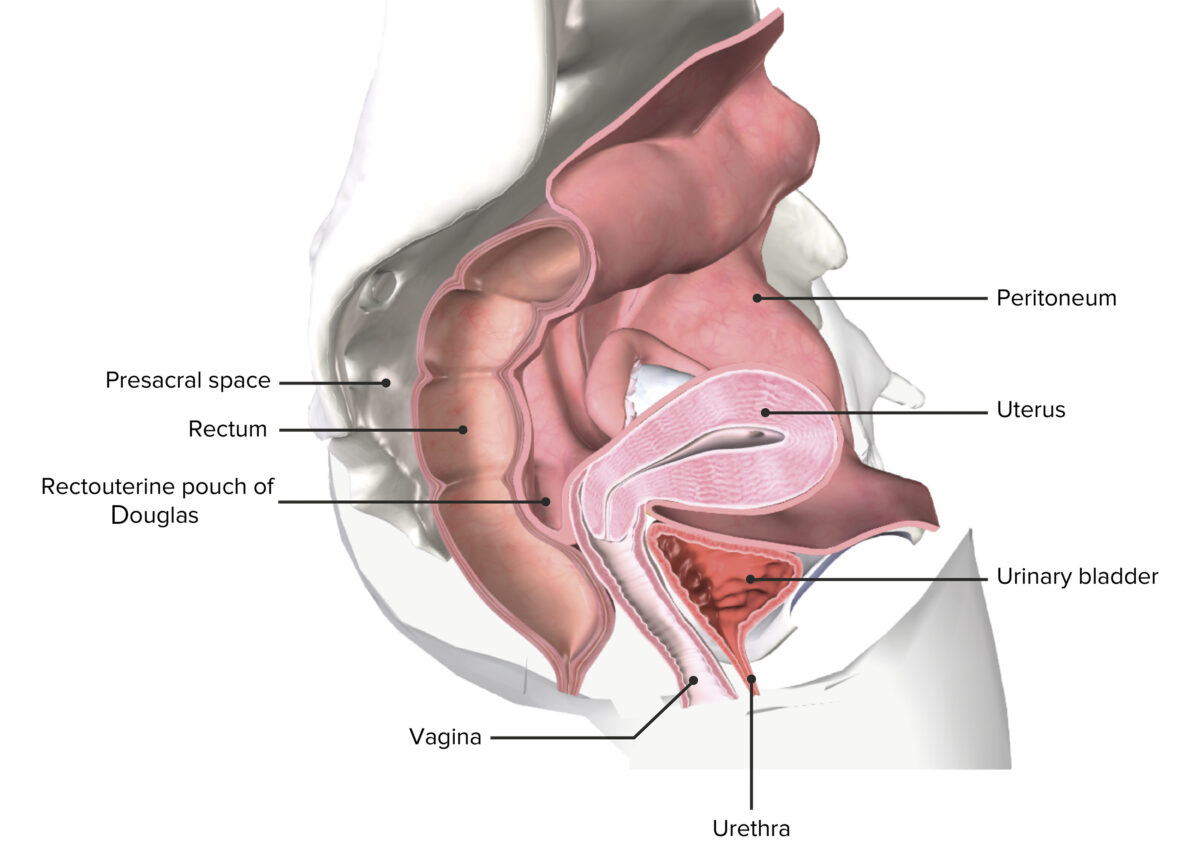
A sectioned female pelvis depicting the uterus in situ
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio
A normal hymen
Image by Lecturio.The vulva refers to the external female genitalia and occupies most of the perineum.
The perineum refers to the external surface, including the vulva, and the shallow “space” beneath.
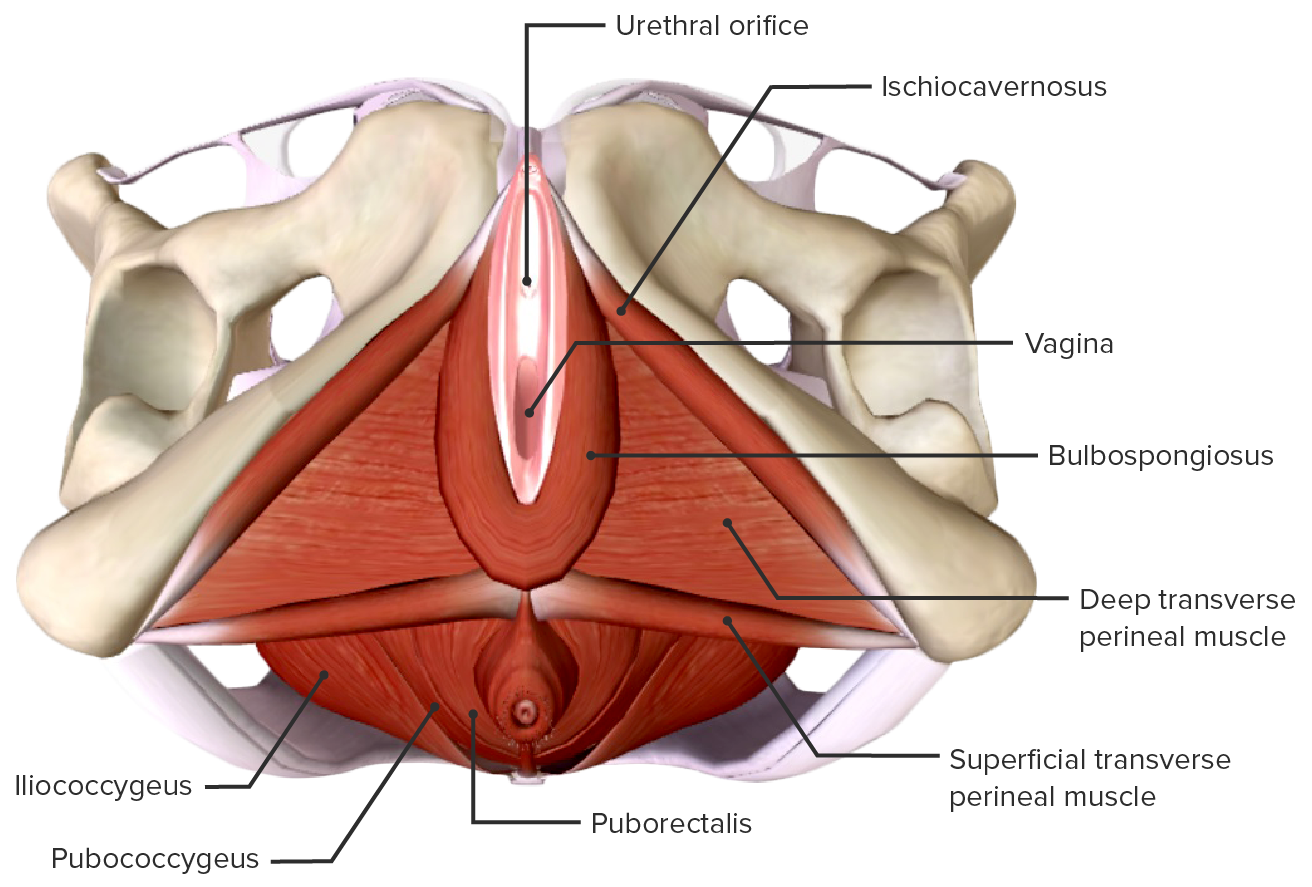
Muscular anatomy of the perineum
Image by Lecturio.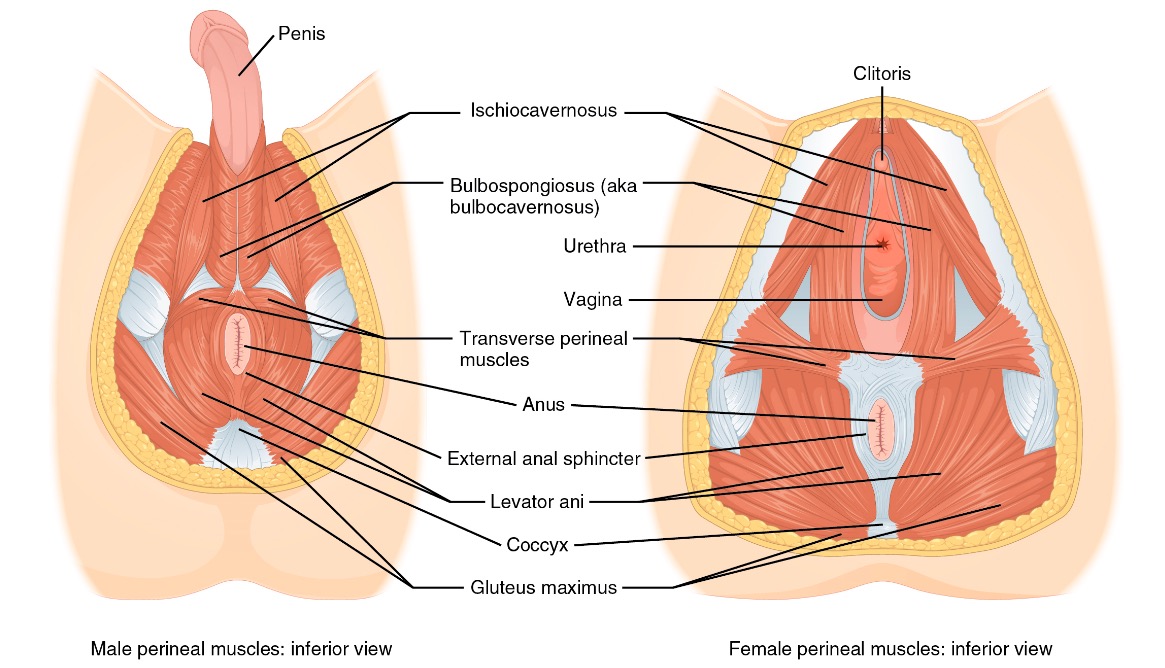
Comparison of the male and female perineal muscles
Image: “Male and female perineum muscles” by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY 4.0The pelvic diaphragm Diaphragm The diaphragm is a large, dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The diaphragm consists of muscle fibers and a large central tendon, which is divided into right and left parts. As the primary muscle of inspiration, the diaphragm contributes 75% of the total inspiratory muscle force. Diaphragm: Anatomy provides structure to the pelvic cavity and surrounding structures. In addition, 3 primary levels of vaginal support Levels of Vaginal Support Pelvic Organ Prolapse are all connected through endopelvic fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis.
The pelvic diaphragm Diaphragm The diaphragm is a large, dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The diaphragm consists of muscle fibers and a large central tendon, which is divided into right and left parts. As the primary muscle of inspiration, the diaphragm contributes 75% of the total inspiratory muscle force. Diaphragm: Anatomy is the deepest layer of the pelvic floor.
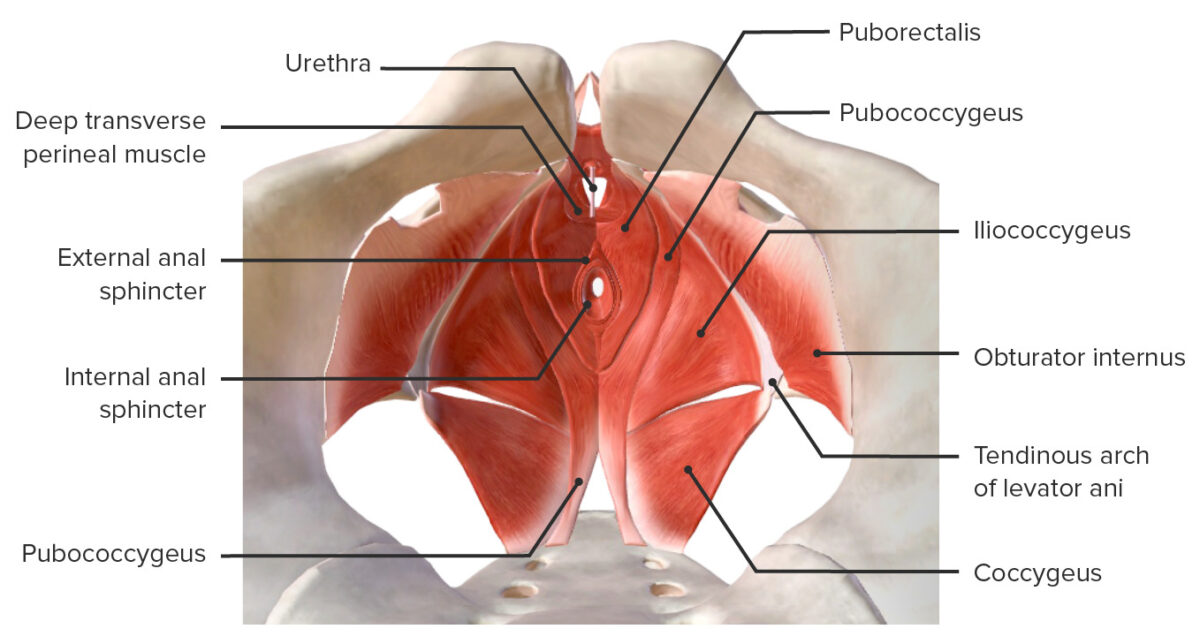
Muscles of the pelvic floor
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio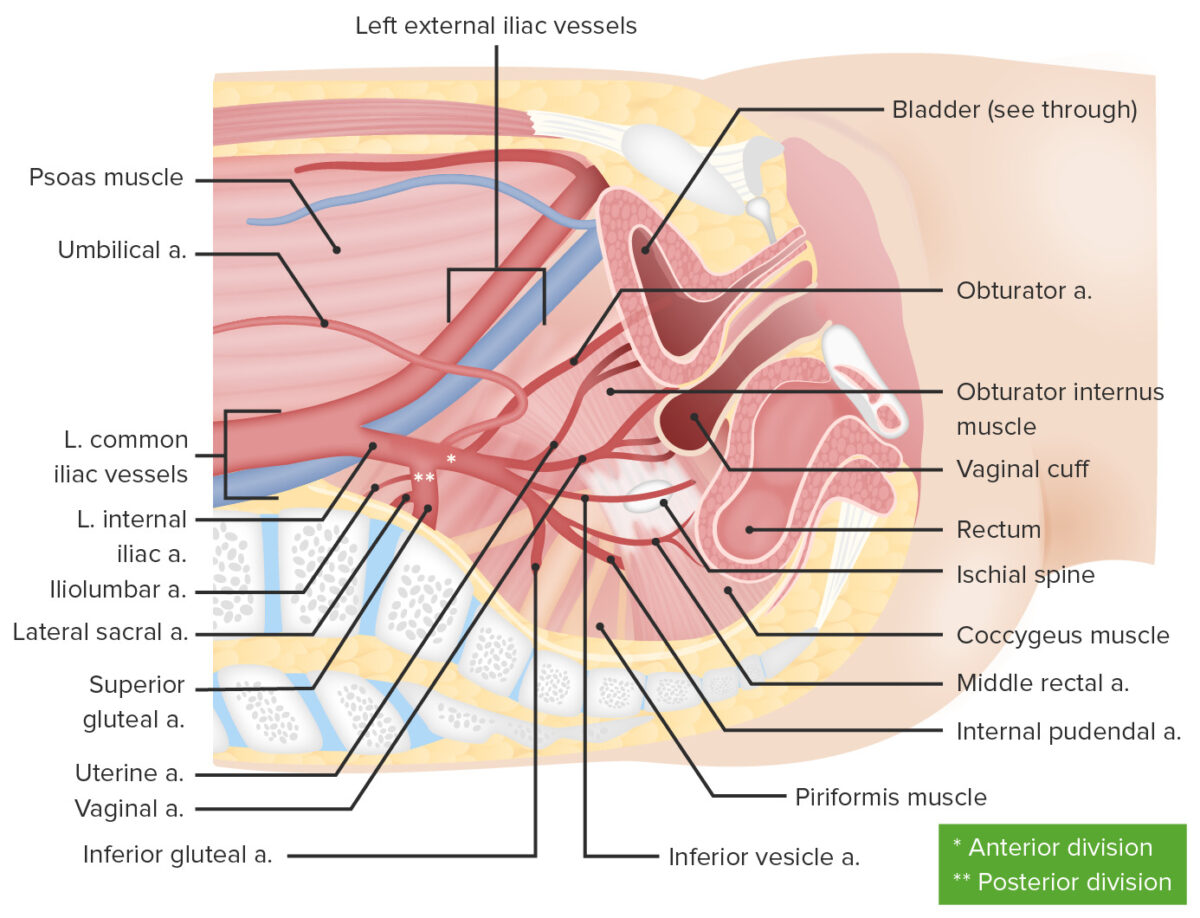
Blood supply for the female reproductive system
Image by Lecturio.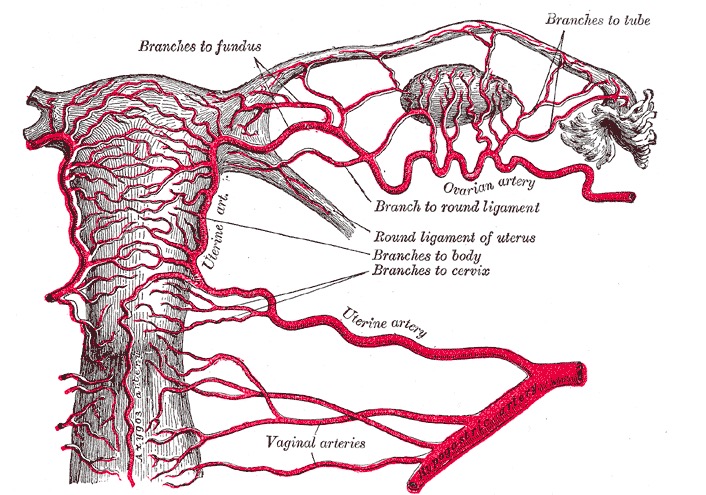
Arterial supply to the uterus and upper vagina
Image: “Arterial supply to the uterus and upper vagina” by Henry Gray. License: Public DomainThe vagina is a fibromuscular tube lined by mucosa made up of 3 layers:
1. Outer adventitia:
2. Middle muscularis layer:
3. Inner mucosal layer: