Vaccination is the administration of a substance to induce the immune system Immune system The body's defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs to develop protection against a disease. Unlike passive immunization, which involves the administration of pre-performed antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, active immunization constitutes the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions. A vaccine is usually an antigenic, non-virulent form of a normally virulent microorganism. Vaccinations are a form of primary prevention and are the most effective form due to their safety, efficacy, low cost, and easy access. While the majority of vaccines are administered to young patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship, some vaccines are targeted to diseases that occur in middle and old age, and are therefore administered to older patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
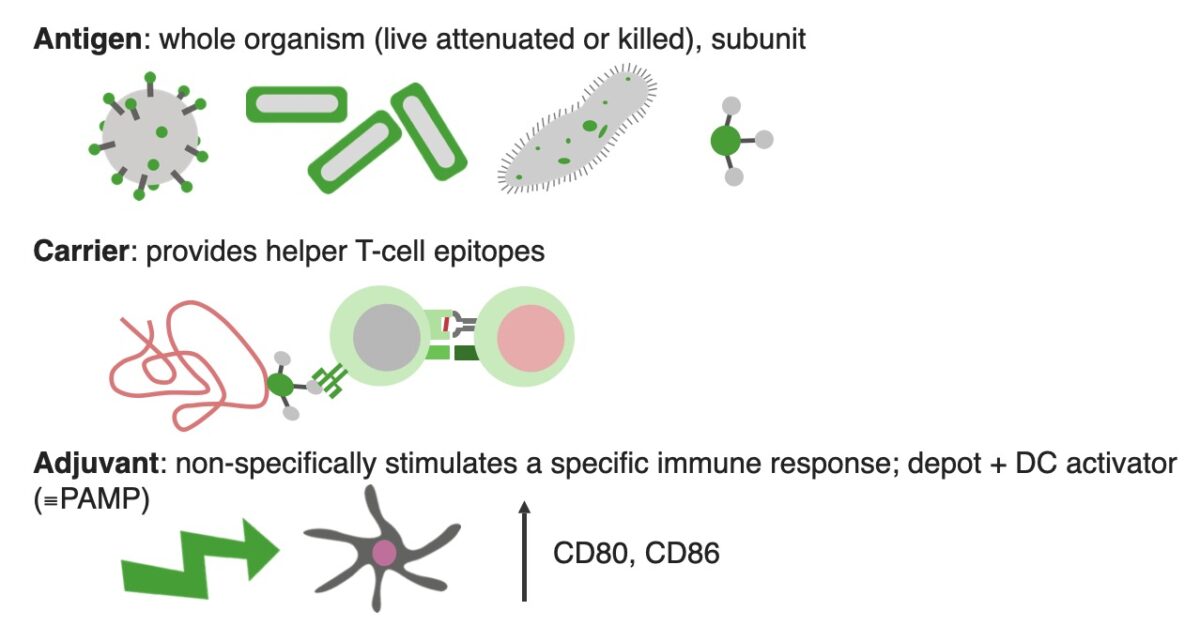
Components of a vaccine
DC activator: dendritic cell activator
PAMP: pathogen associated molecular pattern
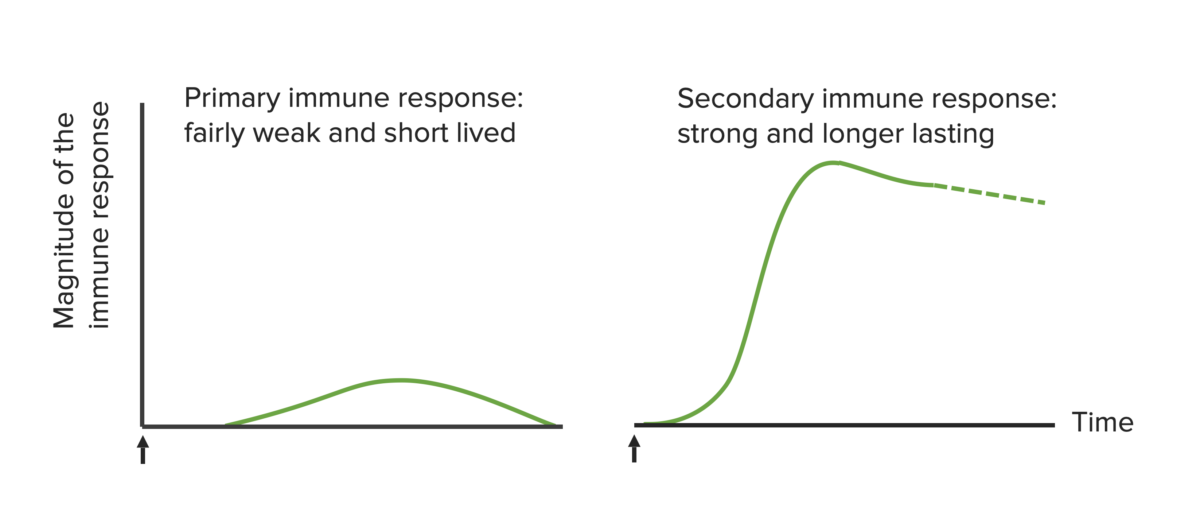
Immunological basis of active vaccination. The arrows mark the time of vaccine administration.
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Vaccine type | Description | Pros | Cons CoNS Staphylococcus | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Live attenuated |
|
Induces strong, often lifelong immunity |
|
|
| Inactivated |
|
Safer than live vaccines, easy to manufacture |
|
|
| Subunit | Includes only the antigens that best stimulate the immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs | Lower chance of adverse reactions |
|
|
| Toxoid |
|
Protects against bacterial toxins | Antitoxin levels decrease with time, may require a booster |
|
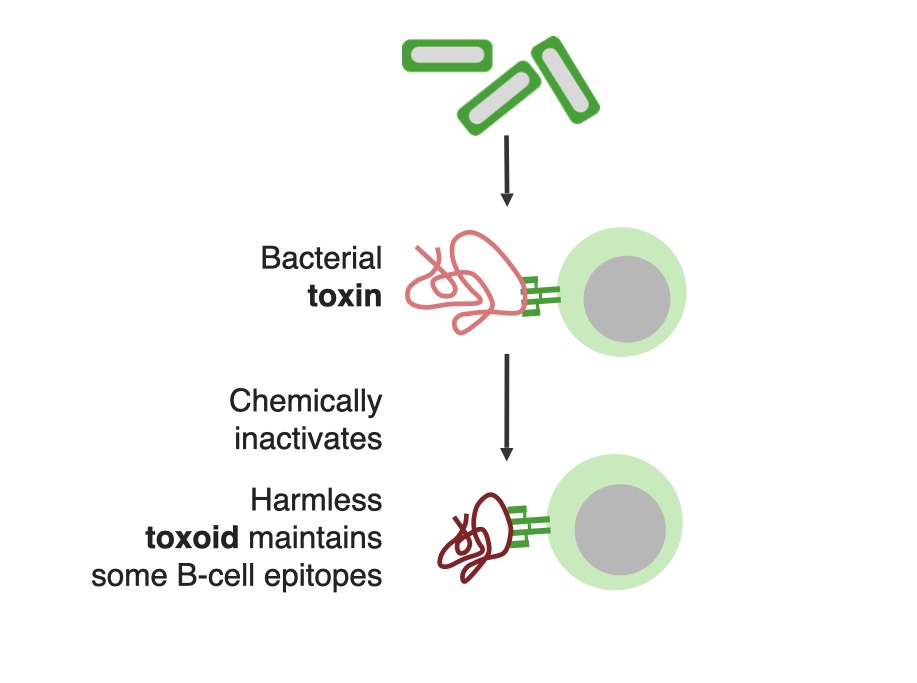
Toxoids are bacterial toxins, rendered harmless and immunogenic by chemical inactivation.
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0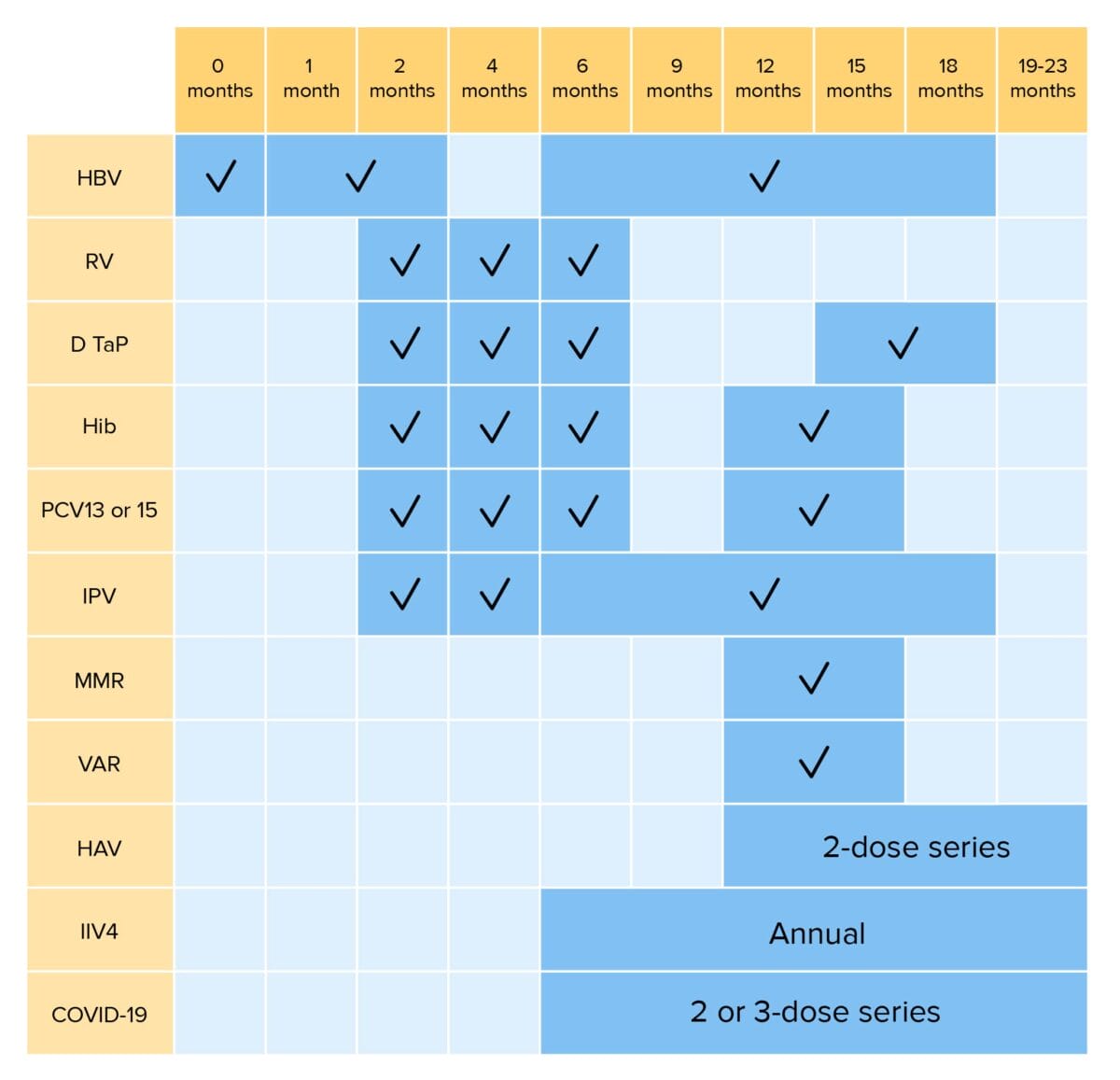
Routine vaccinations for children up to 23 months of age:
HBV: hepatitis B virus vaccination
RV: rotavirus vaccination
DTaP: diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccination
Hib: Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccination
PCV: pneumococcal conjugate vaccination
IPV: inactivated poliovirus vaccination
MMR: measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination
VAR: varicella vaccination
HAV: hepatitis A virus vaccination
IIV4: quadrivalent inactivated influenza vaccination
COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination (bivalent)
*RV1 is a 2-dose series; RV5 is a 3-dose series
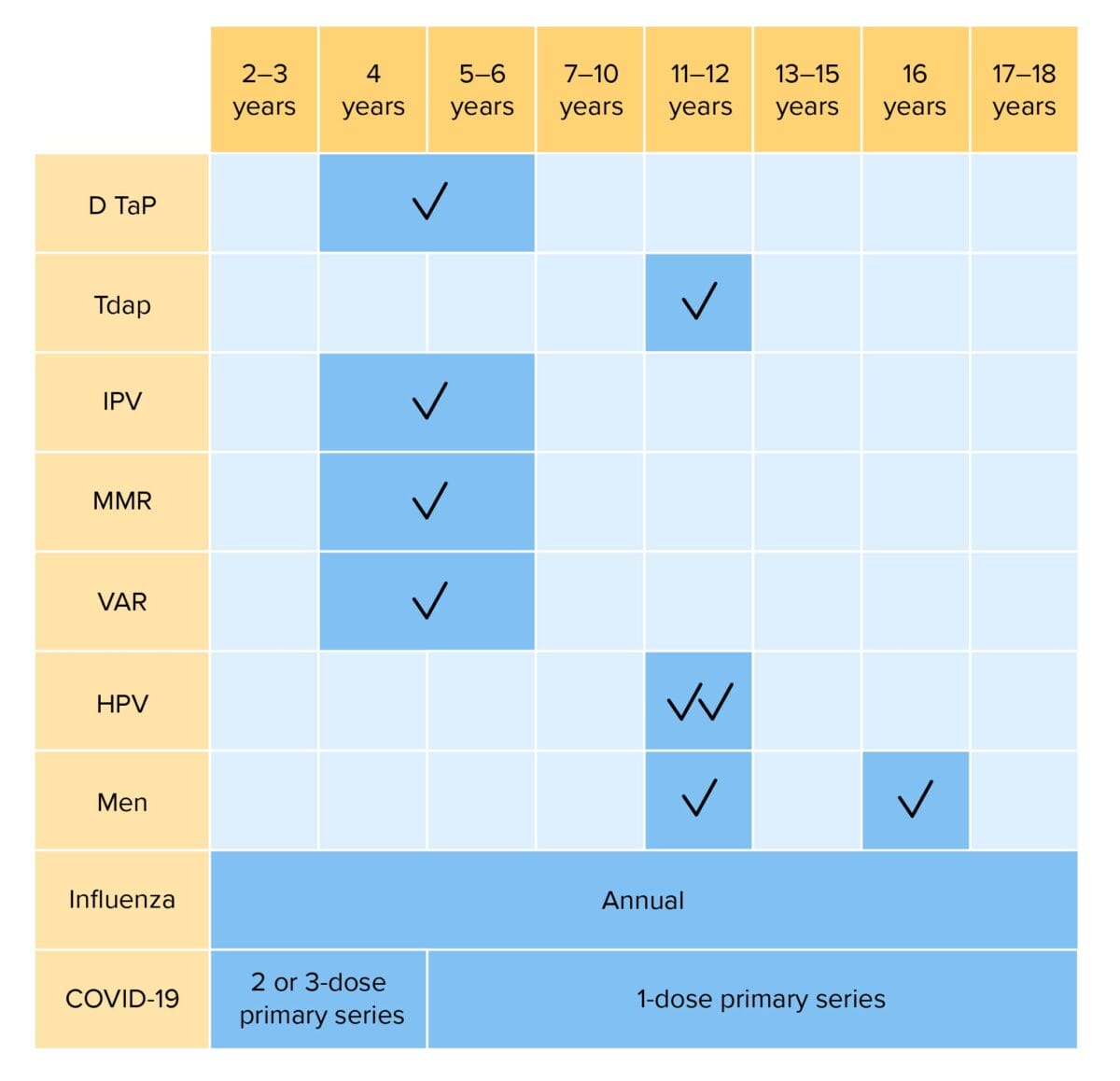
Routine vaccinations for children 2–18 years of age:
DTaP: diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis vaccination
Tdap: tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccination
Hib: Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccination
IPV: inactivated poliovirus vaccination
MMR: measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination
VAR: varicella vaccination
HPV: human papillomavirus vaccination
Men: meningococcal vaccination
COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination (bivalent)
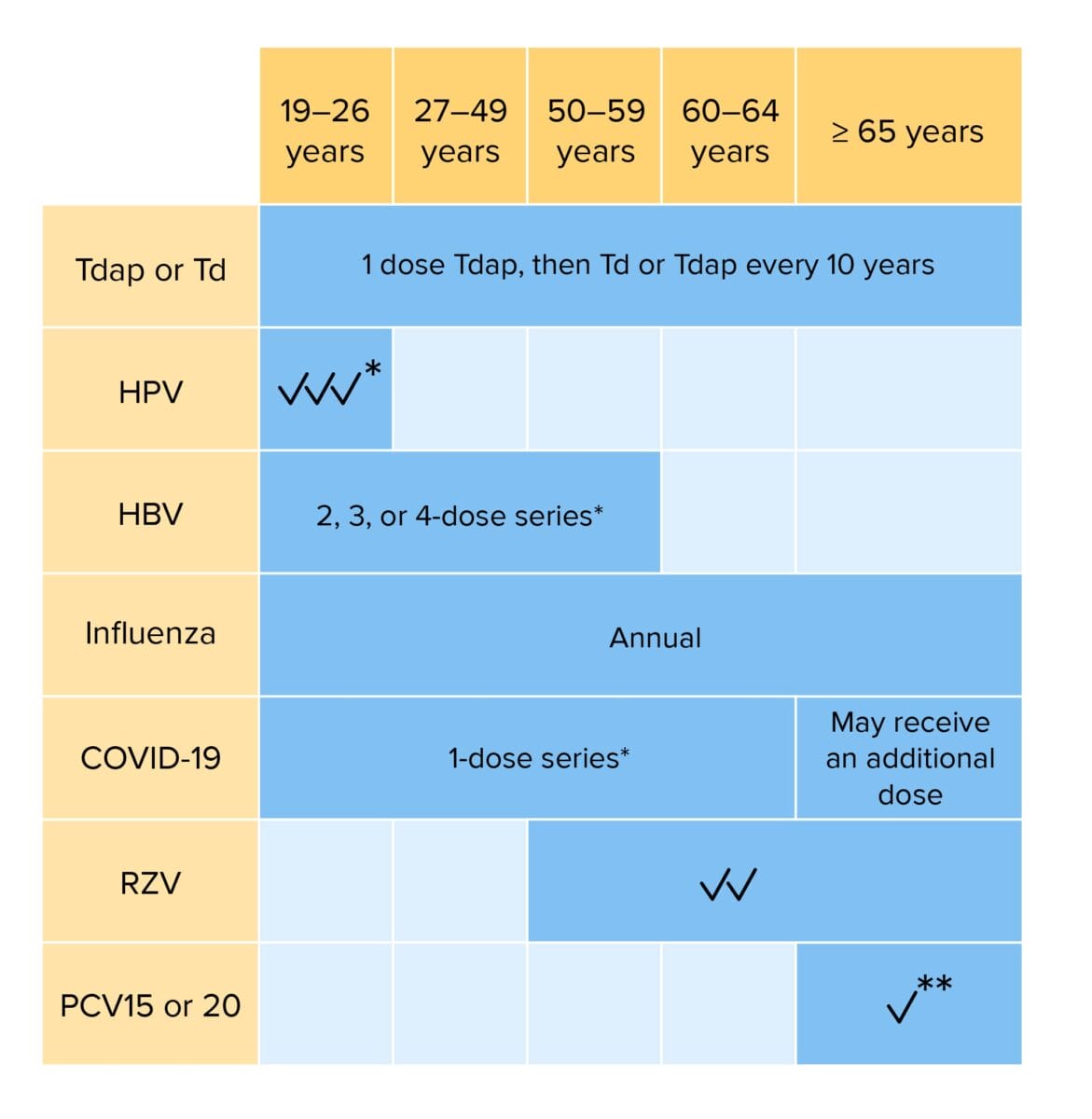
Routine vaccination for adults:
Individuals with risk factors may require additional vaccinations or alterations in dosing schedule.
Tdap: tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccination
Td: tetanus and diphtheria vaccination
HPV: human papillomavirus vaccination
HBV: hepatitis B virus vaccination
COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination (bivalent)
RZV: recombinant zoster vaccination
PCV: pneumococcal conjugate vaccination
*If not previously vaccinated
**If PCV15 is given, should be followed PPSV23 (pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination)
| Live | Viral | Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus (member of the family Adenoviridae) is a nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA virus. Adenovirus is transmitted in a variety of ways, and it can have various presentations based on the site of entry. Presentation can include febrile pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, acute respiratory disease, atypical pneumonia, and gastroenteritis. Adenovirus, sabin Sabin A live vaccine containing attenuated poliovirus, types I, II, and III, grown in monkey kidney cell tissue culture, used for routine immunization of children against polio. This vaccine induces long-lasting intestinal and humoral immunity. Killed vaccine induces only humoral immunity. Oral poliovirus vaccine should not be administered to immunocompromised individuals or their household contacts. Poliovirus/Poliomyelitis polio, varicella, yellow fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, smallpox Smallpox An acute, highly contagious, often fatal infectious disease caused by an orthopoxvirus characterized by a biphasic febrile course and distinctive progressive skin eruptions. Vaccination has succeeded in eradicating smallpox worldwide. Orthopoxvirus, influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza (intranasal), MMR MMR A DNA repair pathway involved in correction of errors introduced during DNA replication when an incorrect base, which cannot form hydrogen bonds with the corresponding base in the parent strand, is incorporated into the daughter strand. Excinucleases recognize the base pair mismatch and cause a segment of polynucleotide chain to be excised from the daughter strand, thereby removing the mismatched base. Lynch syndrome, oral rotavirus Rotavirus A genus of Reoviridae, causing acute gastroenteritis in birds and mammals, including humans. Transmission is horizontal and by environmental contamination. Seven species (rotaviruses A through G) are recognized. Rotavirus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial | BCG BCG An active immunizing agent and a viable avirulent attenuated strain of Mycobacterium bovis, which confers immunity to mycobacterial infections. It is used also in immunotherapy of neoplasms due to its stimulation of antibodies and non-specific immunity. Cancer Immunotherapy, oral typhoid Typhoid Typhoid (or enteric) fever is a severe, systemic bacterial infection classically caused by the facultative intracellular and Gram-negative bacilli Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi (S. Typhimurium, formerly S. typhi). S. paratyphi serotypes A, B, or C can cause a similar syndrome. Enteric Fever (Typhoid Fever) | ||
| Killed | Full | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology | Salk Salk A suspension of formalin-inactivated poliovirus grown in monkey kidney cell tissue culture and used to prevent poliomyelitis. Poliovirus/Poliomyelitis polio, rabies Rabies Acute viral CNS infection affecting mammals, including humans. It is caused by rabies virus and usually spread by contamination with virus-laden saliva of bites inflicted by rabid animals. Important animal vectors include the dog, cat, bat, fox, raccoon, skunk, and wolf. Rabies Virus, hepatitis A Hepatitis A Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV), a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. HAV causes an acute, highly contagious hepatitis with unspecific prodromal symptoms such as fever and malaise followed by jaundice and elevated liver transaminases. Hepatitis A Virus, influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza (injection) |
| Subunit | Protein-based | Subunit: hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus (HBsAg), HPV HPV Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a nonenveloped, circular, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the Papillomaviridae family. Humans are the only reservoir, and transmission occurs through close skin-to-skin or sexual contact. Human papillomaviruses infect basal epithelial cells and can affect cell-regulatory proteins to result in cell proliferation. Papillomavirus (HPV) (types 6, 11, 16, and 18), acellular pertussis Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a potentially life-threatening highly contagious bacterial infection of the respiratory tract caused by Bordetella pertussis. The disease has 3 clinical stages, the second and third of which are characterized by an intense paroxysmal cough, an inspiratory whoop, and post-tussive vomiting. Pertussis (Whooping Cough) (aP) | |
| Polysaccharide based |
|
||
The following mnemonic can help you remember the viral and bacterial live vaccine types: Attention Teachers! Please Vaccinate Small, Beautiful Young Infants with MMR MMR A DNA repair pathway involved in correction of errors introduced during DNA replication when an incorrect base, which cannot form hydrogen bonds with the corresponding base in the parent strand, is incorporated into the daughter strand. Excinucleases recognize the base pair mismatch and cause a segment of polynucleotide chain to be excised from the daughter strand, thereby removing the mismatched base. Lynch syndrome Regularly!
Attention: Adenovirus
Teachers: Typhoid
Please: Sabin Sabin A live vaccine containing attenuated poliovirus, types I, II, and III, grown in monkey kidney cell tissue culture, used for routine immunization of children against polio. This vaccine induces long-lasting intestinal and humoral immunity. Killed vaccine induces only humoral immunity. Oral poliovirus vaccine should not be administered to immunocompromised individuals or their household contacts. Poliovirus/Poliomyelitis Polio
Vaccinate: Varicella
Small: Smallpox
Beautiful: BCG
Young: Yellow fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever
Infants: Influenza (intranasal)
MMR MMR A DNA repair pathway involved in correction of errors introduced during DNA replication when an incorrect base, which cannot form hydrogen bonds with the corresponding base in the parent strand, is incorporated into the daughter strand. Excinucleases recognize the base pair mismatch and cause a segment of polynucleotide chain to be excised from the daughter strand, thereby removing the mismatched base. Lynch syndrome
Regularly: Rotavirus