Uterine leiomyomas (or uterine fibroids Uterine Fibroids Gynecological Imaging) are benign Benign Fibroadenoma tumors arising from smooth muscle cells in the uterine myometrium. Leiomyosarcomas, however, are malignant tumors, arising de novo (not from fibroids Fibroids A benign tumor derived from smooth muscle tissue, also known as a fibroid tumor. They rarely occur outside of the uterus and the gastrointestinal tract but can occur in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, probably arising from the smooth muscle of small blood vessels in these tissues. Infertility). With a lifetime risk of > 70% for both African American and Caucasian women, fibroids Fibroids A benign tumor derived from smooth muscle tissue, also known as a fibroid tumor. They rarely occur outside of the uterus and the gastrointestinal tract but can occur in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, probably arising from the smooth muscle of small blood vessels in these tissues. Infertility are common. Conversely, leiomyosarcomas are rare. Leiomyosarcomas may present similarly to uterine fibroids Uterine Fibroids Gynecological Imaging making preoperative diagnosis challenging. Both conditions present with abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and/or bulk symptoms. A fibroid is identified as a hypoechoic Hypoechoic A structure that produces a low-amplitude echo (darker grays) Ultrasound (Sonography), well-circumscribed, round mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast on pelvic ultrasound. A leiomyosarcoma is usually diagnosed on a postoperative specimen. Depending on patient symptoms and preference, treatment for leiomyoma Leiomyoma A benign tumor derived from smooth muscle tissue, also known as a fibroid tumor. They rarely occur outside of the uterus and the gastrointestinal tract but can occur in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, probably arising from the smooth muscle of small blood vessels in these tissues. Infertility may include surgical resection or medical options to reduce bleeding and/or bulk. Management of leiomyosarcoma, which carries a poor prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas, may include adjuvant Adjuvant Substances that augment, stimulate, activate, potentiate, or modulate the immune response at either the cellular or humoral level. The classical agents (freund's adjuvant, bcg, corynebacterium parvum, et al.) contain bacterial antigens. Some are endogenous (e.g., histamine, interferon, transfer factor, tuftsin, interleukin-1). Their mode of action is either non-specific, resulting in increased immune responsiveness to a wide variety of antigens, or antigen-specific, i.e., affecting a restricted type of immune response to a narrow group of antigens. The therapeutic efficacy of many biological response modifiers is related to their antigen-specific immunoadjuvanticity. Vaccination chemotherapy Chemotherapy Osteosarcoma based on stage.
Last updated: Jun 27, 2025
Leiomyomas are benign Benign Fibroadenoma, smooth muscle tumors arising from the uterine myometrium, whereas leiomyosarcomas are aggressive, malignant tumors of the myometrium.
Predisposing factors:
Classification:
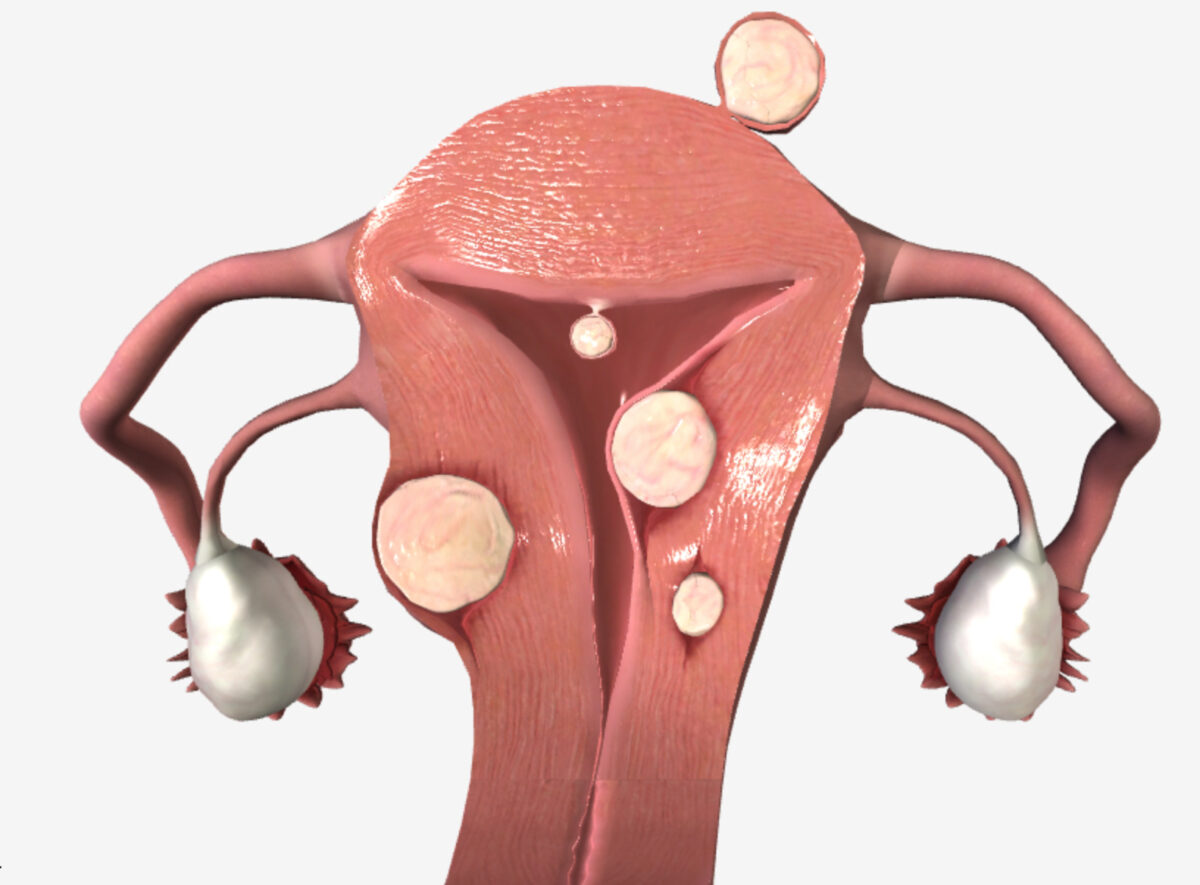
Uterine fibroids (location):
Subserosal fibroid (beneath the serosa), submucosal fibroid (under the endometrium), intramural fibroid (in the myometrial wall), pedunculated fibroid (growing off the uterine corpus on a stalk)
Patterns:
Differentiated from leiomyomas by the degree of:
Predisposing factors:
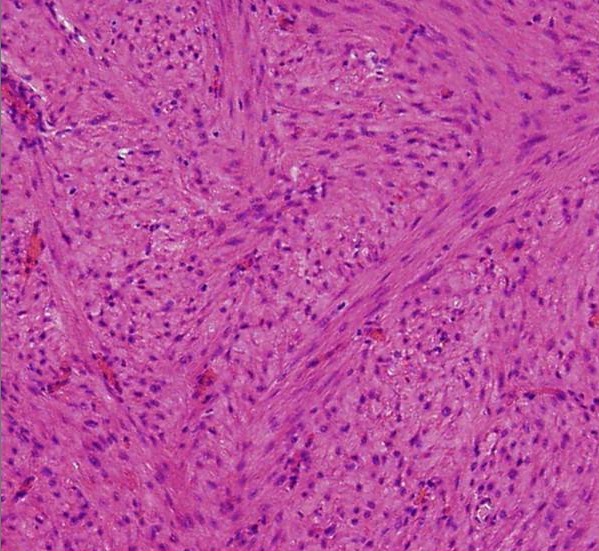
Histology of a leiomyoma:
Proliferation of spindle-shaped cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and fibers (H&E); no evidence of mitotic figures or atypia seen
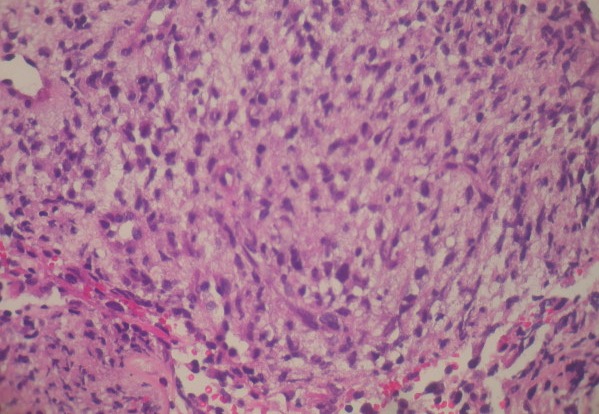
Histology of a leiomyosarcoma:
Neoplastic spindle cell proliferation arranged in interlacing bundles and fascicles (H&E)
Presentations of leiomyoma Leiomyoma A benign tumor derived from smooth muscle tissue, also known as a fibroid tumor. They rarely occur outside of the uterus and the gastrointestinal tract but can occur in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, probably arising from the smooth muscle of small blood vessels in these tissues. Infertility and leiomyosarcoma can be clinically indistinguishable.
Both leiomyoma Leiomyoma A benign tumor derived from smooth muscle tissue, also known as a fibroid tumor. They rarely occur outside of the uterus and the gastrointestinal tract but can occur in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, probably arising from the smooth muscle of small blood vessels in these tissues. Infertility and leiomyosarcoma may be asymptomatic.
Workup for leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas are the same, but there are no tests or findings with high positive predictive value Positive predictive value The positive predictive value is the percentage of people with a positive test result who actually have the disease among all people with a positive result, regardless of whether or not they have the disease. Epidemiological Values of Diagnostic Tests for sarcomas.
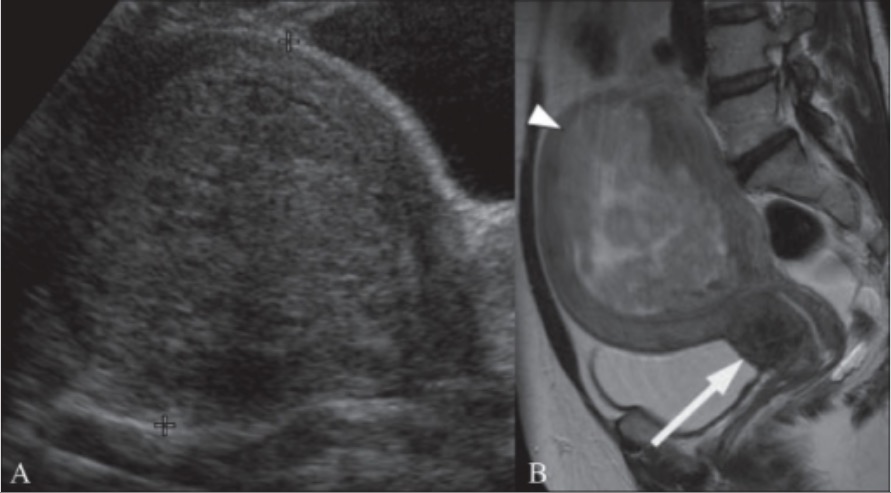
A 49-year-old woman with a history of menorrhagia:
A: Transabdominal ultrasound image showing a bulky uterus with 10 cm submucosal fibroid (between cursors)
B: Sagittal T2 weighted MRI in the same patient shows the submucosal fibroid (arrowhead) is heterogeneous, indicating degeneration. Also shown is a 2.5 cm cervical fibroid (arrow).
General management:
To treat bleeding symptoms (1st-line medical management):
To treat bulk or pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways symptoms (1st line) or bleeding symptoms (2nd line):
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone Gonadotropin-releasing hormone A decapeptide that stimulates the synthesis and secretion of both pituitary gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone. Gnrh is produced by neurons in the septum preoptic area of the hypothalamus and released into the pituitary portal blood, leading to stimulation of gonadotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland. Puberty (GNRH) analogs:
Leiomyosarcomas are usually only diagnosed following surgery for presumed fibroids Fibroids A benign tumor derived from smooth muscle tissue, also known as a fibroid tumor. They rarely occur outside of the uterus and the gastrointestinal tract but can occur in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, probably arising from the smooth muscle of small blood vessels in these tissues. Infertility. Management decisions are typically made after an initial procedure:
Prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual’s condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas:
The differential diagnoses of uterine mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast and/or pelvic pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways include: