Urticaria is raised, well-circumscribed areas (wheals) of edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema ( swelling Swelling Inflammation) and erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion ( redness Redness Inflammation) involving the dermis Dermis A layer of vascularized connective tissue underneath the epidermis. The surface of the dermis contains innervated papillae. Embedded in or beneath the dermis are sweat glands; hair follicles; and sebaceous glands. Skin: Structure and Functions and epidermis Epidermis The external, nonvascular layer of the skin. It is made up, from within outward, of five layers of epithelium: (1) basal layer (stratum basale epidermidis); (2) spinous layer (stratum spinosum epidermidis); (3) granular layer (stratum granulosum epidermidis); (4) clear layer (stratum lucidum epidermidis); and (5) horny layer (stratum corneum epidermidis). Skin: Structure and Functions with associated pruritus Pruritus An intense itching sensation that produces the urge to rub or scratch the skin to obtain relief. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) (itch). Urticaria is not a single disease but rather is a reaction pattern representing cutaneous mast cell Mast cell Granulated cells that are found in almost all tissues, most abundantly in the skin and the gastrointestinal tract. Like the basophils, mast cells contain large amounts of histamine and heparin. Unlike basophils, mast cells normally remain in the tissues and do not circulate in the blood. Mast cells, derived from the bone marrow stem cells, are regulated by the stem cell factor. Angioedema degranulation resulting in the release of histamine and other vasoactive substances from mast cells Mast cells Granulated cells that are found in almost all tissues, most abundantly in the skin and the gastrointestinal tract. Like the basophils, mast cells contain large amounts of histamine and heparin. Unlike basophils, mast cells normally remain in the tissues and do not circulate in the blood. Mast cells, derived from the bone marrow stem cells, are regulated by the stem cell factor. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation and basophils Basophils Granular leukocytes characterized by a relatively pale-staining, lobate nucleus and cytoplasm containing coarse dark-staining granules of variable size and stainable by basic dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation in the dermis Dermis A layer of vascularized connective tissue underneath the epidermis. The surface of the dermis contains innervated papillae. Embedded in or beneath the dermis are sweat glands; hair follicles; and sebaceous glands. Skin: Structure and Functions resulting in extravasation of plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products into the dermis Dermis A layer of vascularized connective tissue underneath the epidermis. The surface of the dermis contains innervated papillae. Embedded in or beneath the dermis are sweat glands; hair follicles; and sebaceous glands. Skin: Structure and Functions. Urticaria can be caused by myriad inciting events, such as allergic reactions Allergic Reactions Type I hypersensitivity reaction against plasma proteins in donor blood Transfusion Reactions, infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, exposure, and many others. The diagnosis is made clinically. H1-antagonists are used as 1st-line treatment.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Urticaria is a vascular reaction of the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions noted as a transient appearance of slightly elevated plaques (wheals) that are redder or paler than adjacent skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions and often accompanied by significant itching.
IgE-mediated urticarias (type I hypersensitivity, release of histamine from mast cells Mast cells Granulated cells that are found in almost all tissues, most abundantly in the skin and the gastrointestinal tract. Like the basophils, mast cells contain large amounts of histamine and heparin. Unlike basophils, mast cells normally remain in the tissues and do not circulate in the blood. Mast cells, derived from the bone marrow stem cells, are regulated by the stem cell factor. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation) are often due to exposure to certain allergens:
Non–IgE-mediated urticaria (histamine release secondary to):
Physical urticarias:
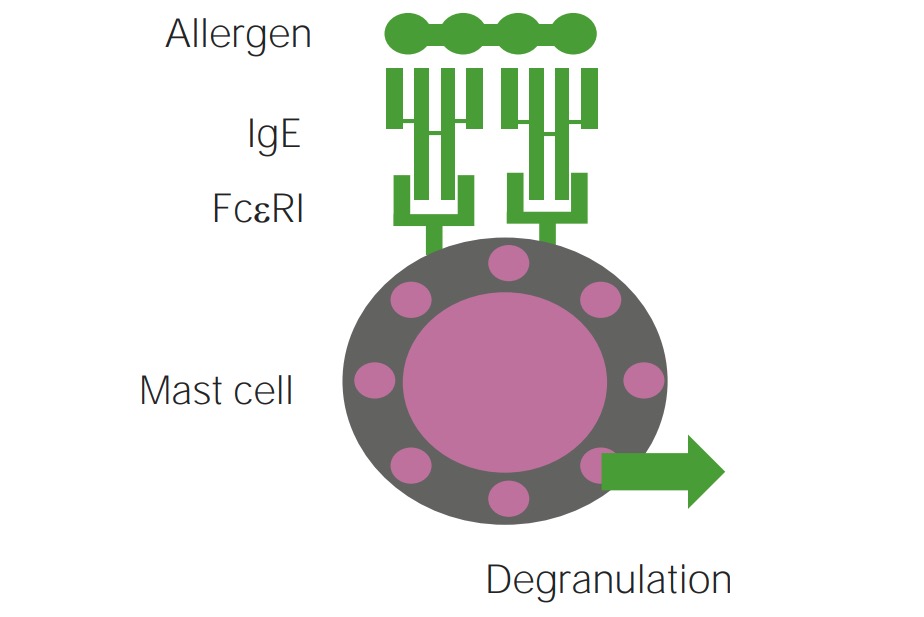
Mechanism of type 1 hypersensitivity reaction involved in IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation
Image by Lecturio.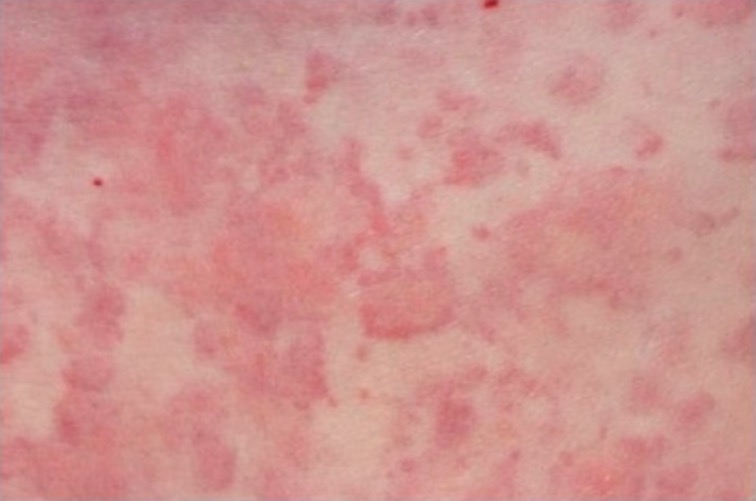
Urticarial rash
Image: “Urticarial rash at presentation” by Regional Immunology Service, Royal Hospitals, The Belfast Trust, Grosvenor Road, Belfast BT12 6BN. License: CC BY 2.0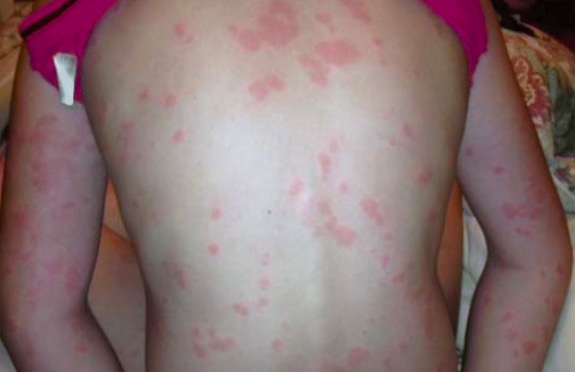
Urticarial rash
Image: “Chronic spontaneous urticaria” by University of Toronto, Medicine, Toronto, ON Canada. License: CC BY 4.0Challenge tests can be used to elicit symptoms of physical urticaria.
If associated with anaphylaxis Anaphylaxis An acute hypersensitivity reaction due to exposure to a previously encountered antigen. The reaction may include rapidly progressing urticaria, respiratory distress, vascular collapse, systemic shock, and death. Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction: