Urinary incontinence (UI) is the involuntary leakage of urine. It is common, is undertreated, can limit participation in activities, and can impact an individual’s quality of life. In older adults, urinary incontinence can increase overall morbidity and mortality. The 5 types of UI include stress, urge, mixed, overflow, and functional. The etiology of urinary incontinence is often multifactorial. Risk factors for women include prior vaginal deliveries, obesity, and menopause; the leading risk factor for men is previous prostate surgery. Diagnosis is based on clinical history. Testing is individualized to exclude a potentially reversible cause or an underlying medical condition such as infection or malignancy. Management is directed to the type of incontinence and the cause. Treatment most commonly involves lifestyle modification and pelvic floor muscle exercises; some patients may need pharmacologic or surgical treatment. Treatment effectiveness is measured by self-assessment tools.
Last updated: Aug 6, 2025
Urinary incontinence is loss of bladder Bladder A musculomembranous sac along the urinary tract. Urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters, and is held there until urination. Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess control, leading to involuntary loss of urine or uncontrolled urine leakage, which presents a hygienic or social problem to the individual and impacts quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement of life.
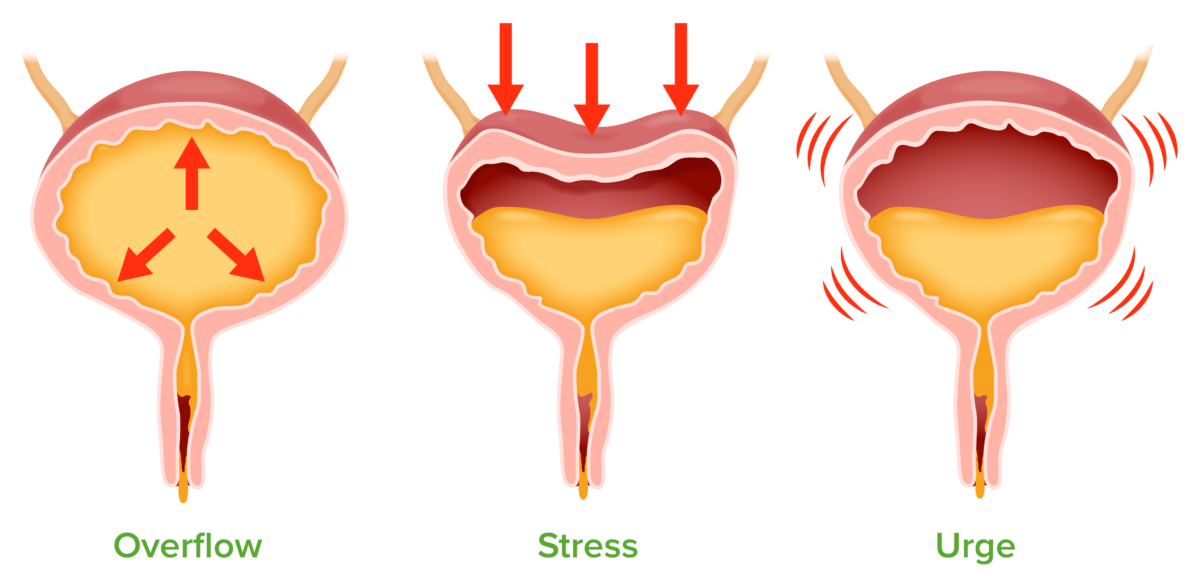
Urinary incontinence:
Overflow: urinary overdistension caused by bladder outlet obstruction or impaired detrusor contractility
Stress: leakage of urine with increased intraabdominal pressure due to urinary outlet incompetence
Urge: overactivity of the detrusor muscle
Focus the history on symptoms consistent with incontinence based on the type of circumstance:
Management of urinary incontinence is dependent on several factors:
Surgical intervention is considered when other methods of management fail.