Ultrasonography is an imaging technique used in medicine for the imaging of subcutaneous body structures, blood vessels, joints, and internal organs to exclude structural pathologies. This technique is based on the utilization of ultrasound (or high-frequency, inaudible sound waves). In medical imaging, the sound waves have a frequency of 2–18 megahertz (MHz). The equipment utilizes a transducer acting as the emitter and receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors of sound waves, and a central computer processes the electrical signals to generate the image. The general advantages of this type of imaging is its low cost, availability, and safety. Some specialties that rely heavily on ultrasound examination are cardiology, nephrology, general surgery, gastroenterology, emergency medicine, and obstetrics.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
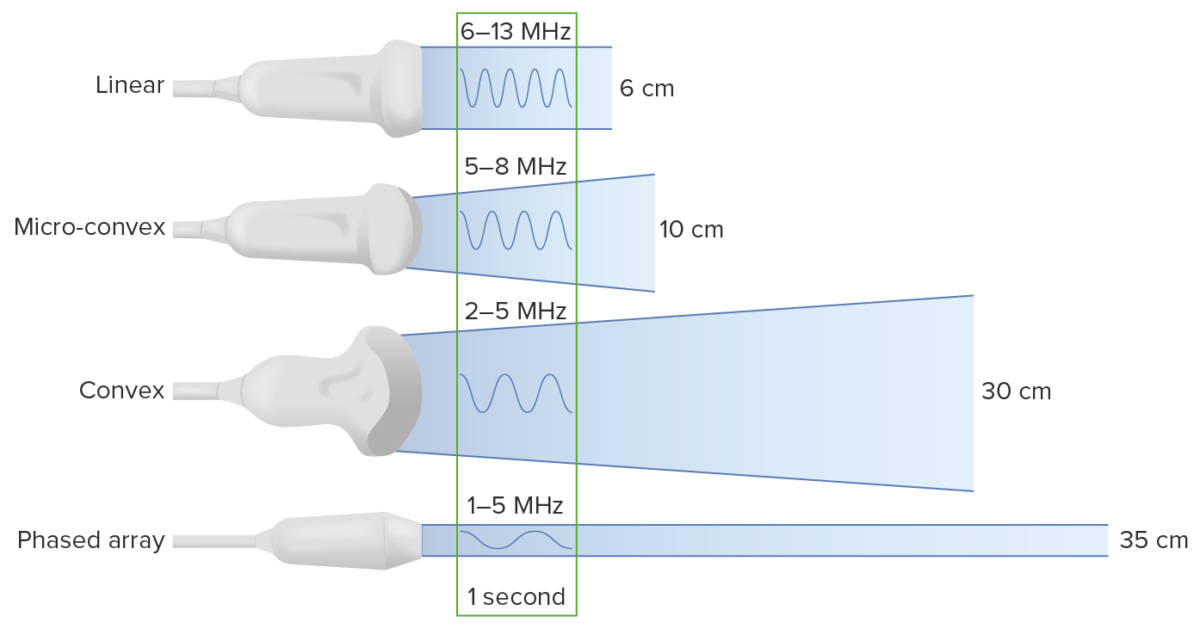
Types of transducers:
Note that decreasing the frequency increases the depth to which the ultrasound wave travels. However, this comes at the cost of image resolution.
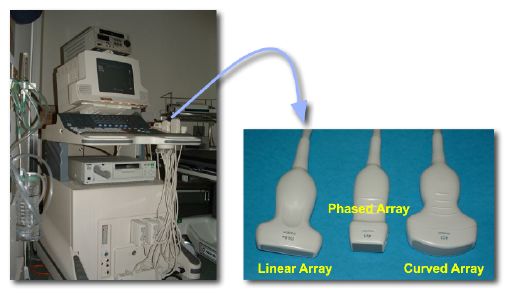
An ultrasound machine and different probes
Image: “Photos of a sonography system and typical transducers.” by Kieran Maher. License: Public DomainThe main principle behind ultrasound imaging is the transmission and reflection of sound waves through the tissues.
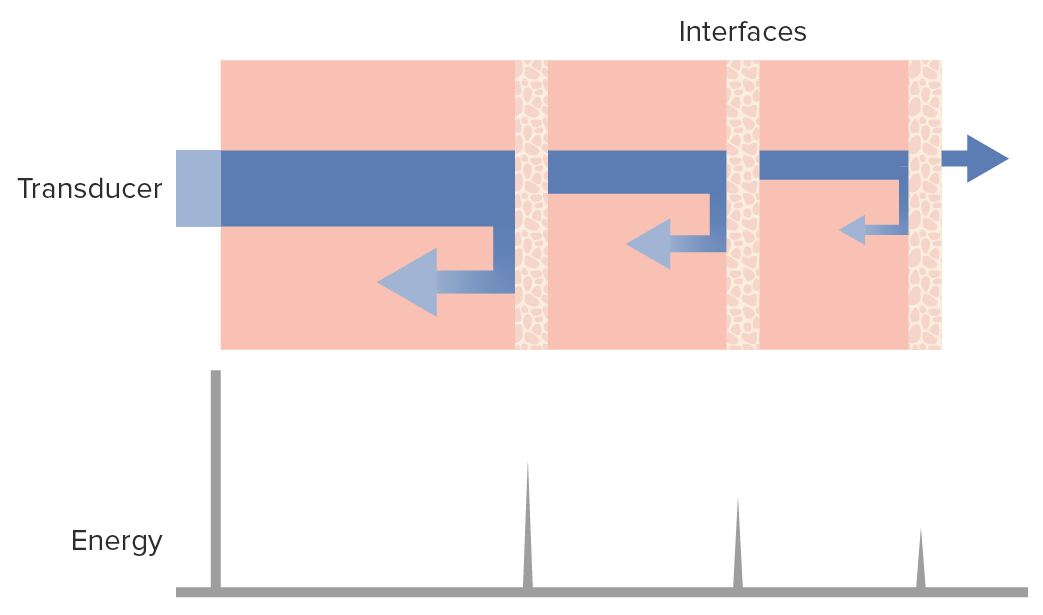
Ultrasound waves and the tissues:
The diagram shows that as the ultrasound wave beam (blue horizontal bar) penetrates the tissues, a percentage is reflected back (left arrows) toward the transducer while another continues to go deeper into the tissues (right arrow), losing some energy to the parenchyma as it goes.
Imaging planes:
Types of images:
Image definition or sharpness of the image generated can be characterized in terms of:
Image definition is also determined by how close objects are to the transducer; according to their frequencies, probes have a near and a far field of “ vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam”:
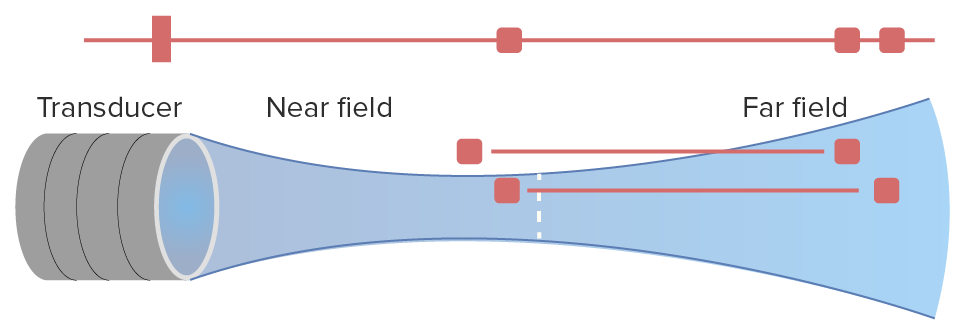
Near and far fields of a transducer in ultrasound imaging:
Note how, in the near field, the transducer has an adequate lateral definition, being able to distinguish between 2 points. On the other hand, in the far field, increasing axial definition (depth) sacrifices lateral definition.
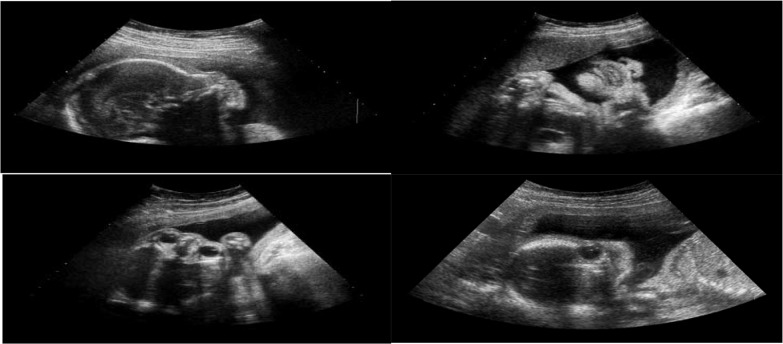
Different planes of fetal ultrasound imaging:
Top left: Sagittal plane
Top right: Coronal plane
Bottom left: Axial plane
Bottom right: Non–fetal facial standard plane (FFSP)
Doppler ultrasound (or just “Doppler”) is a widely used ultrasound method based on the principle of sound-wave compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma and dilation relative to the receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors. Doppler ultrasound is most commonly used to visualize blood flow Blood flow Blood flow refers to the movement of a certain volume of blood through the vasculature over a given unit of time (e.g., mL per minute). Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure.
The interpretation of ultrasound images is done in real time, while the examination is being performed.
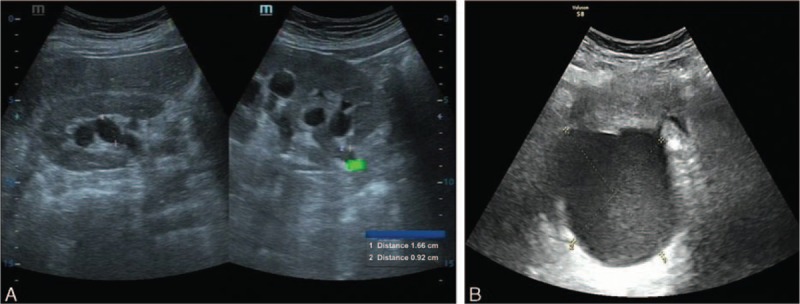
A: Urinary ultrasound showing right-sided hydronephrosis and the irregular upper section of the right ureter
B: Gynecologic ultrasound showing a cystic mass (8.8 X 7.5 X 8.6 cm) in the right rear uterus
Note that both findings are hypoechoic to anechoic because of their liquid content
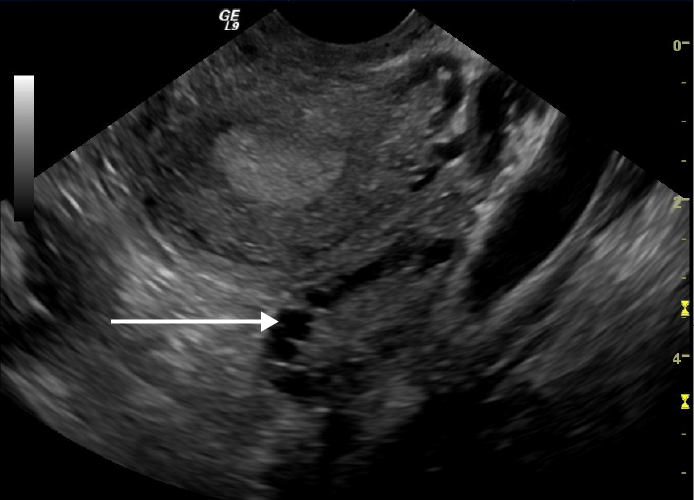
Transvaginal ultrasound showing a polycystic ovary:
Note the multiple cysts on the periphery of the ovary (white arrow)
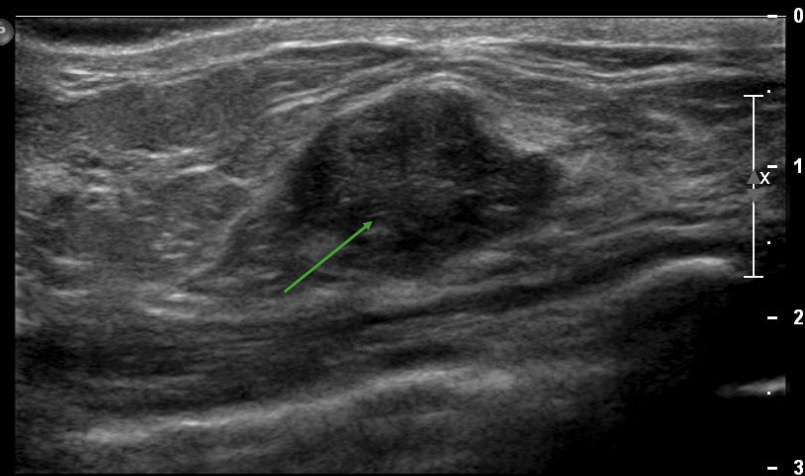
Example of a nonspecific hypoechoic structure on an ultrasound of the right breast, which could represent a malignancy, an abscess, or a benign tumor, depending on the clinical scenario
Image by Hetal Verma.
Example of a thyroid nodule containing internal calcifications, depicted as hyperechoic foci on an ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Image by Hetal Verma.By convention, in color Doppler:
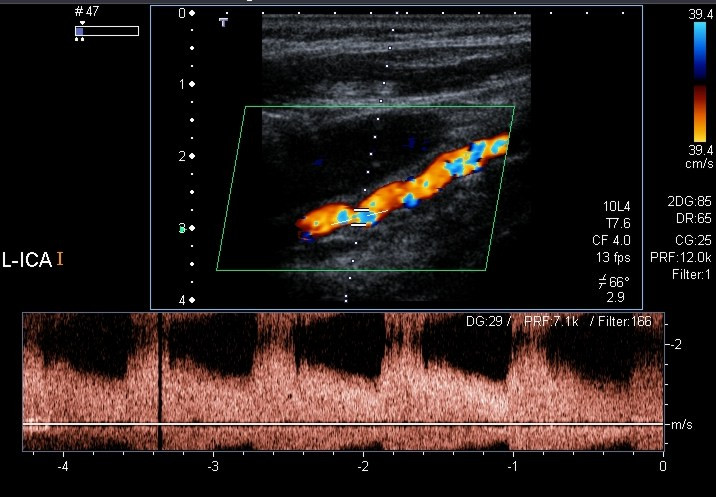
Color Doppler and spectral Doppler examination of the left internal carotid artery revealing stenoses of about 70%
Image: “Color Doppler and spectral Doppler examination of the left ICA” by Christian Arning et al. License: CC BY 2.0
Doppler ultrasound of the carotid arteries showing carotid stenosis:
A plaque can be seen obstructing < 40% of the lumen, and hyperechoic foci within the vessel wall can be seen, probably due to calcification
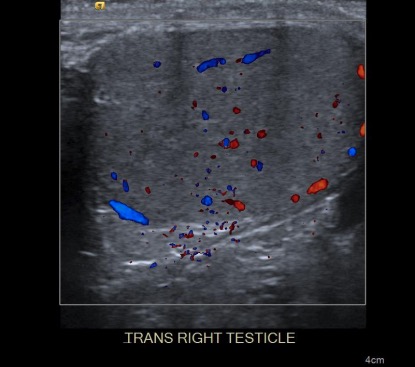
Doppler ultrasound of the right testicle:
Note the difference in color for flow coming toward the transducer (red) and flow away from the transducer (blue).
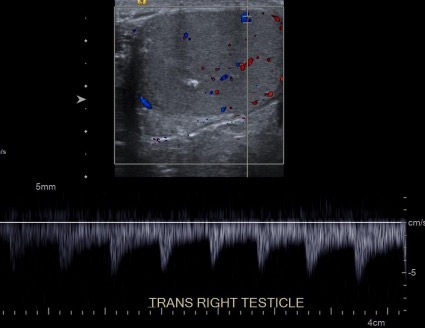
Spectral Doppler ultrasound of the right testicle:
A graph of the flow appears at the bottom of the image.
Artifacts are artificial objects produced by the equipment’s misinterpretation of sound-wave data coming back from the tissues that do not represent actual structures.
Some examples of artifacts are:
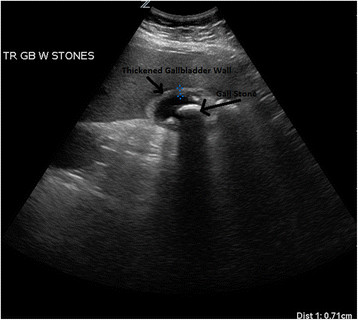
Ultrasound from a patient with acute cholecystitis:
Multiple gallstones are visualized within the gallbladder lumen with gallbladder wall thickening and pericholecystic fluid. Shadowing can be seen behind the gallstone.
| Pros | Cons CoNS Staphylococcus |
|---|---|
|
|
Indications:
There are no contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation for ultrasound imaging.
| Radiography | CT | Ultrasound | MRI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of acquisition | Ionizing radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma | Ionizing radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma | Acoustic energy | Ferromagnetic pulses |
| Relative cost | Inexpensive | Expensive | Inexpensive | Very expensive |
| Portable | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Length of exam | Seconds | < 1 minute | Seconds | Approximately 1 hour |
| Contrast | No | May be needed | May be needed | May be needed |