Type III hypersensitivity, also known as immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity, occurs when antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions and antigens form immune complexes Immune complexes The complex formed by the binding of antigen and antibody molecules. The deposition of large antigen-antibody complexes leading to tissue damage causes immune complex diseases. C3 Deficiency (ICs) in circulation Circulation The movement of the blood as it is pumped through the cardiovascular system. ABCDE Assessment and deposit in susceptible tissues. The complement system Complement system Serum glycoproteins participating in the host defense mechanism of complement activation that creates the complement membrane attack complex. Included are glycoproteins in the various pathways of complement activation (classical complement pathway; alternative complement pathway; and lectin complement pathway). Innate Immunity: Barriers, Complement, and Cytokines triggers the immune response, leading to leukocyte recruitment Recruitment Skeletal Muscle Contraction and tissue injury. There is no single clinical syndrome for this hypersensitivity. Symptoms reflect the impairment of multiple organ systems based on sites of IC IC Inhaled Anesthetics deposition. Diagnostic workup depends largely on the history and includes laboratory tests, imaging, and biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma of the affected organ. Treatment consists of removal or avoidance of offending agents and, in severe conditions, glucocorticoids Glucocorticoids Glucocorticoids are a class within the corticosteroid family. Glucocorticoids are chemically and functionally similar to endogenous cortisol. There are a wide array of indications, which primarily benefit from the antiinflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of this class of drugs. Glucocorticoids or immunosuppressive therapy.
Last updated: Nov 23, 2024
Immune complex formation: IC IC Inhaled Anesthetics formed by the binding of Ag AG Metabolic Acidosis and Ab
Immune complex deposition
Immune complex deposition depends on:
Immune complex inflammatory reaction
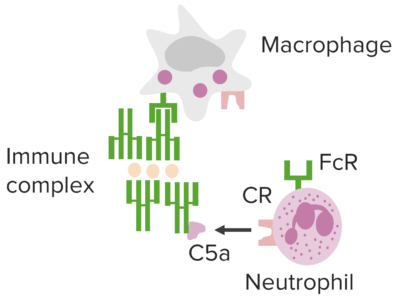
Immune complex–mediated pathways underlying type III hypersensitivity.
Image by Lecturio.Manifestations are affected by the route of entry, site(s) of IC IC Inhaled Anesthetics deposition, and persistence of antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination(s).
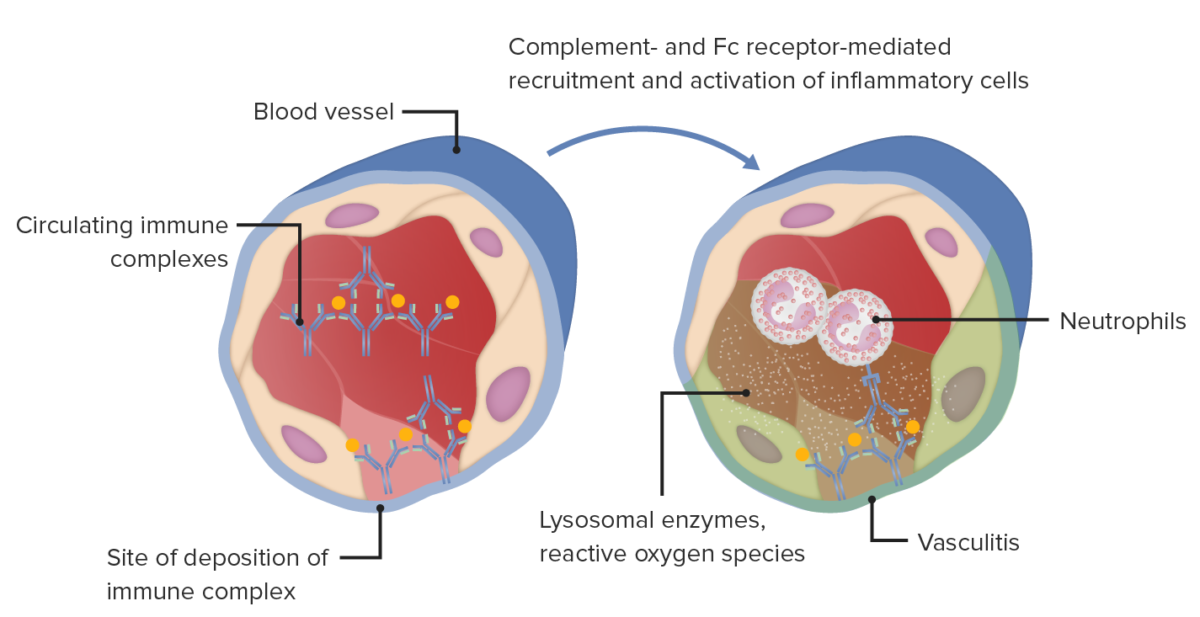
Type III hypersensitivity immune complex mediated tissue injury in blood vessel wall, vasculitis, which is associated with various conditions.
Image by Lecturio..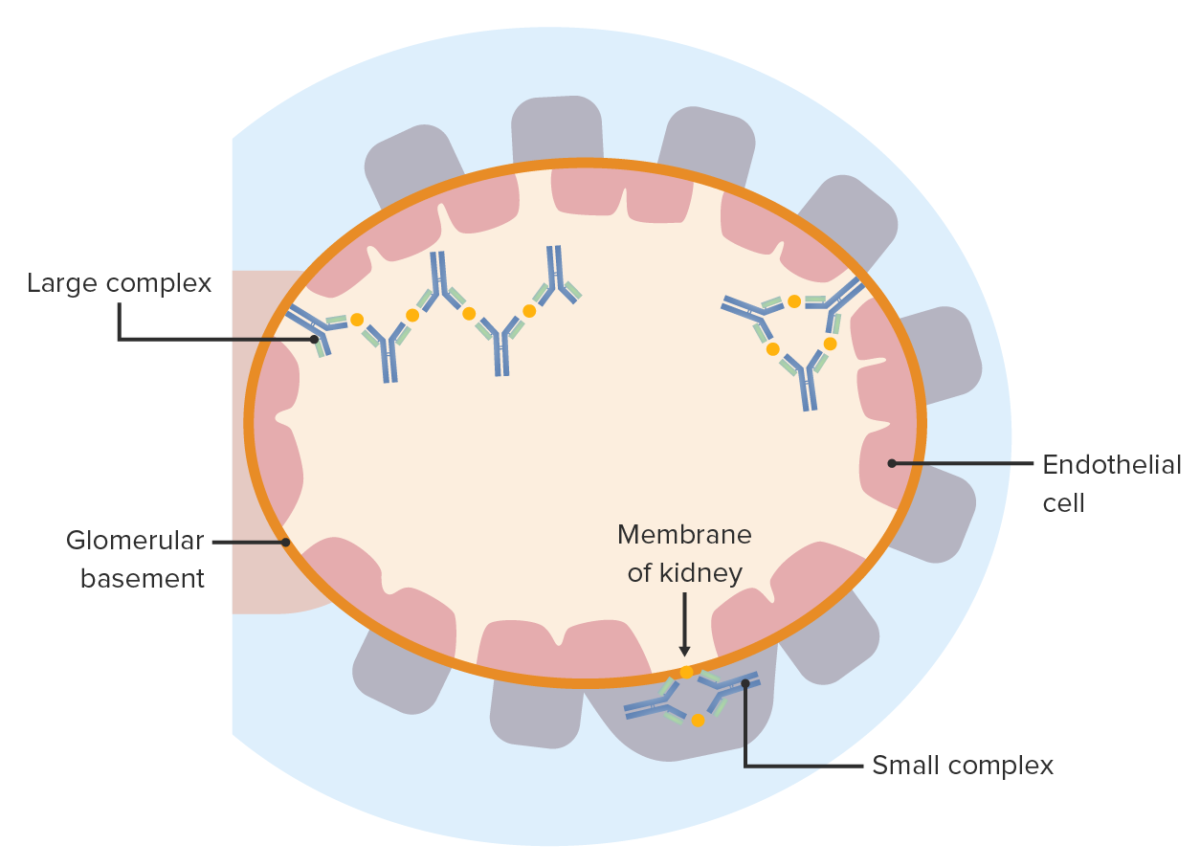
Immune complex disease: Antigen-antibody complexes deposit on either side of the glomerular basement membrane. These elicit an inflammatory reaction and cause glomerular injury.
Image by Lecturio.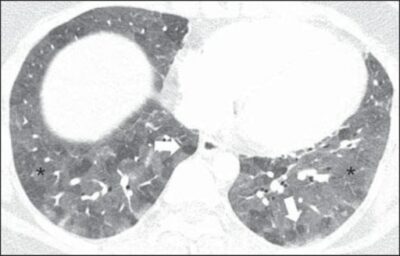
A 27-year-old female patient with a history of exposure to mold. High-resolution CT scans of the chest (lung window) at the level of the lower lobes show extensive ground-glass opacities (asterisks), with overlapping foci of lobular air trapping (arrows).
Image: “Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis” by Torres PP, Moreira MA, Silva DG, da Gama RR, Sugita DM, Moreira MA. License: CC BY 4.0