Triptans and ergot alkaloids are agents used mainly for the management of acute migraines. The therapeutic effect is induced by binding to serotonin Serotonin A biochemical messenger and regulator, synthesized from the essential amino acid l-tryptophan. In humans it is found primarily in the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and blood platelets. Serotonin mediates several important physiological functions including neurotransmission, gastrointestinal motility, hemostasis, and cardiovascular integrity. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors, which causes reduced vasoactive neuropeptide release, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways conduction, and intracranial vasoconstriction Vasoconstriction The physiological narrowing of blood vessels by contraction of the vascular smooth muscle. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure. Triptans are the preferred therapy, followed by ergot alkaloids, but both agents have good efficacy. Due to the vasoconstriction Vasoconstriction The physiological narrowing of blood vessels by contraction of the vascular smooth muscle. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure effect, the medications should not be used concurrently or be prescribed to patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with cardiovascular disease.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Triptans and serotonin Serotonin A biochemical messenger and regulator, synthesized from the essential amino acid l-tryptophan. In humans it is found primarily in the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and blood platelets. Serotonin mediates several important physiological functions including neurotransmission, gastrointestinal motility, hemostasis, and cardiovascular integrity. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS share a similar core molecule (tryptamine).
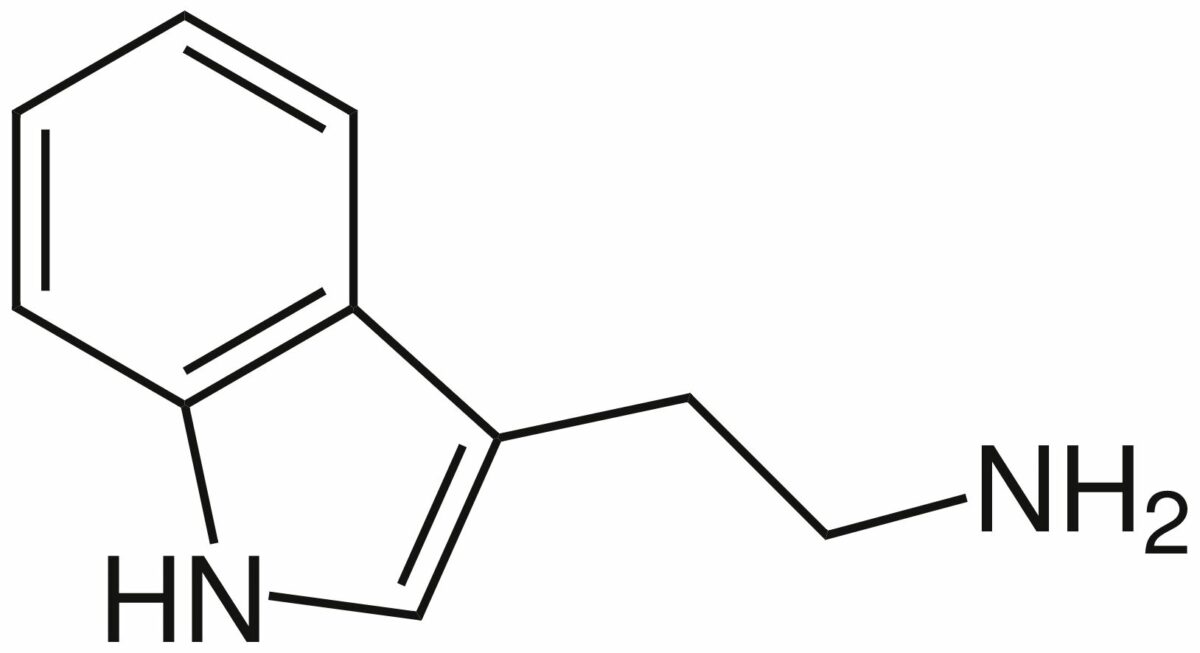
Chemical structure of tryptamine:
the core molecule for both serotonin and triptans
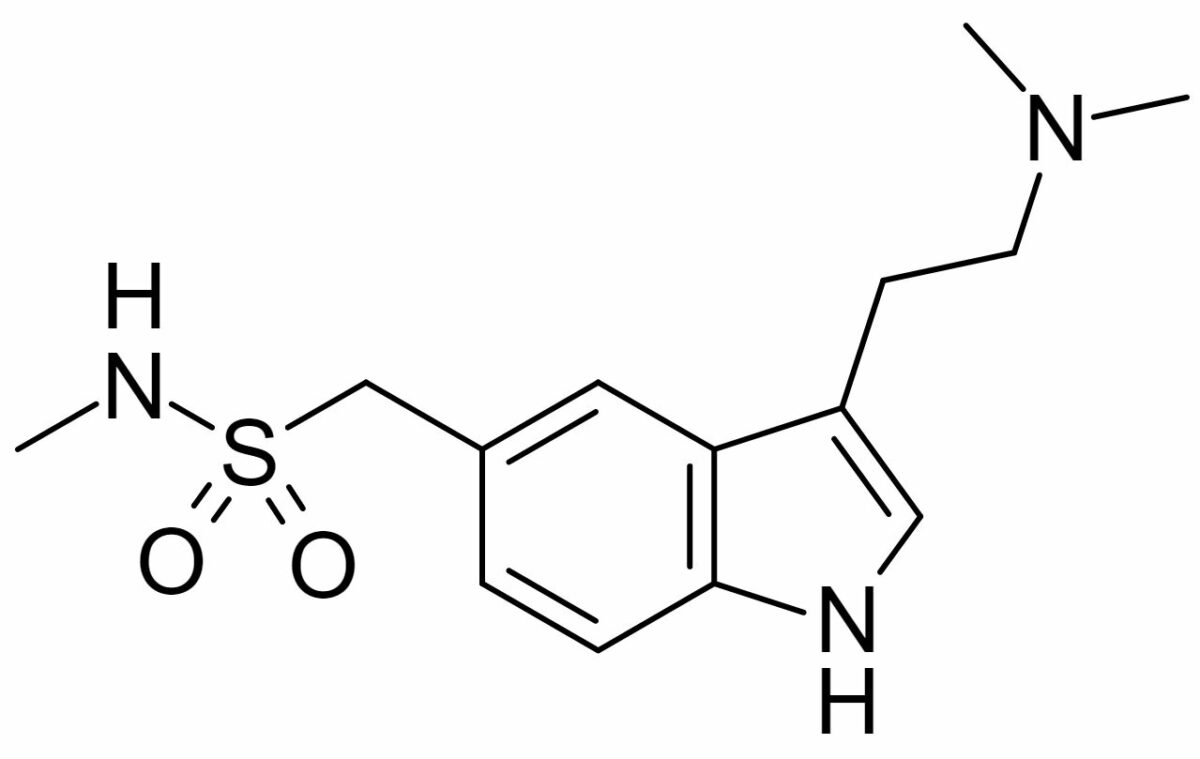
Chemical structure of sumatriptan:
A similar ring structure is shared with serotonin. Other members of the triptan class have variations in the 2 side chains.
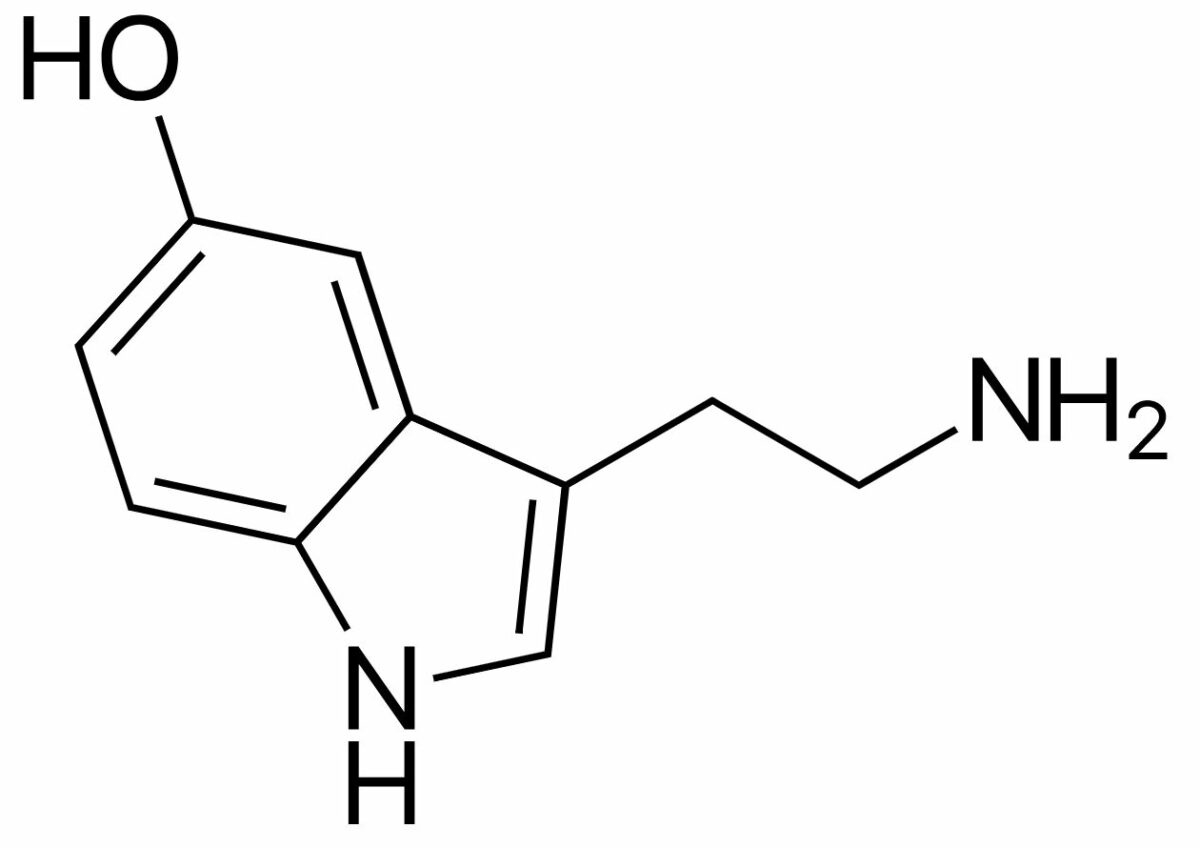
Chemical structure of serotonin:
Notice the similar ring structure to sumatriptan.
Pharmacokinetic variability exists among the triptan medications.
Absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption:
Distribution:
Metabolism:
Excretion:
| Medication | Onset of action and formulation | Elimination Elimination The initial damage and destruction of tumor cells by innate and adaptive immunity. Completion of the phase means no cancer growth. Cancer Immunotherapy half-life Half-Life The time it takes for a substance (drug, radioactive nuclide, or other) to lose half of its pharmacologic, physiologic, or radiologic activity. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics | Metabolism and excretion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sumatriptan |
|
2 hours |
|
| Zolmitriptan |
|
2–3 hours |
|
| Naratriptan | Oral: 1–2 hours | 6 hours |
|
| Rizatriptan | Oral: 30–60 minutes | 2–3 hours |
|
| Almotriptan | Oral: 30–60 minutes | 3–4 hours |
|
| Eletriptan | Oral: 30–60 minutes | 3–4 hours |
|
| Frovatriptan | Oral: 2 hours | Approximately 25 hours |
|
Adverse effects:
Drug interactions:
Contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation:

A tetracyclic ergoline nucleus (common in ergot alkaloids)
Image: “Ergoline Structural Formulae V.1” by Jü. License: CC0 1.0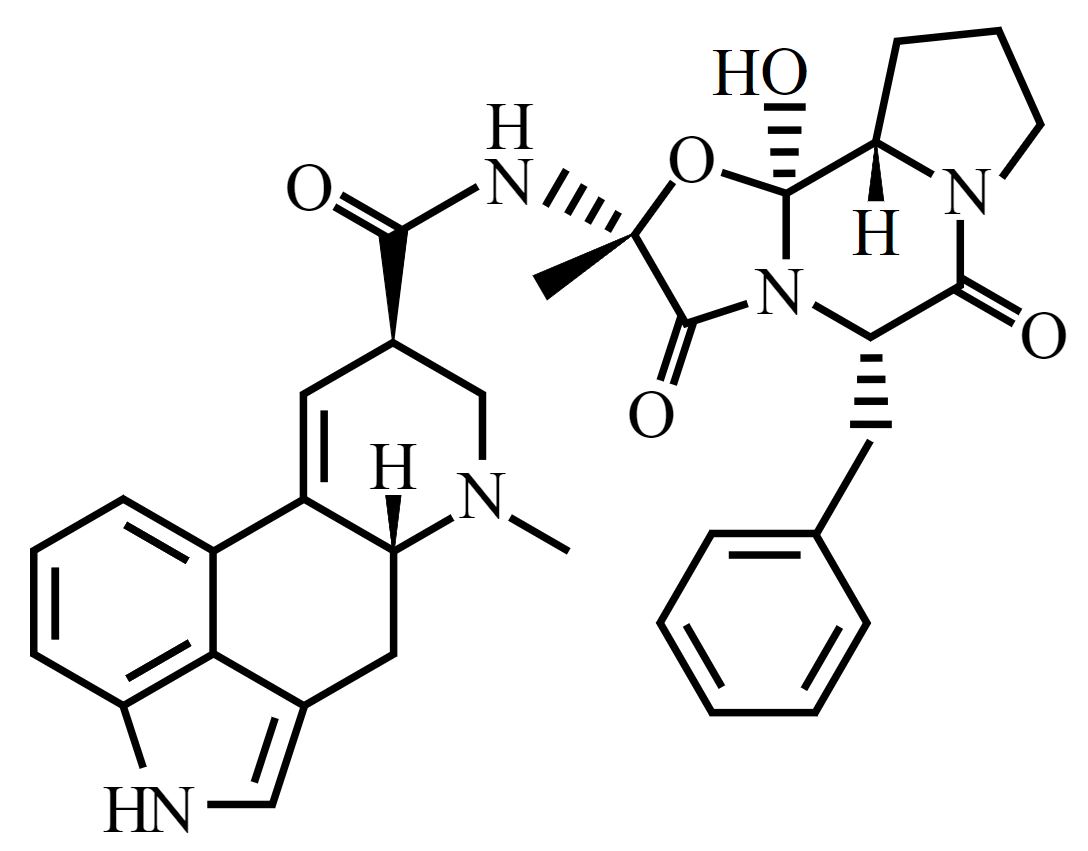
Chemical structure of ergotamine
Image: “Ergotamine-skeletal” by Benrr101. License: Public DomainAbsorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption:
Metabolism:
Excretion:
Adverse effects:
Drug interactions:
Contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation:
Etiology:
Clinical presentation:
Management: