Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is an often chronic and recurring pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways syndrome involving the sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology distribution of the trigeminal nerve Trigeminal nerve The 5th and largest cranial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is a mixed motor and sensory nerve. The larger sensory part forms the ophthalmic, mandibular, and maxillary nerves which carry afferents sensitive to external or internal stimuli from the skin, muscles, and joints of the face and mouth and from the teeth. Most of these fibers originate from cells of the trigeminal ganglion and project to the trigeminal nucleus of the brain stem. The smaller motor part arises from the brain stem trigeminal motor nucleus and innervates the muscles of mastication. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (cranial nerve (CN) V). The pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways is typically unilateral and described as an acute, sharp, electric-shock–like pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways involving the maxillary or mandibular areas and often associated with spasm of facial muscles Facial muscles The facial muscles (also called mimetic muscles) control facial expression and are supplied by the facial nerve. Most of them originate from the skull and attach to the skin around the facial openings, which serve as a method to group or classify them. Facial Muscles: Anatomy. Trigeminal neuralgia occurs in multiple, short-acting episodes. Most cases are usually due to vascular compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma of the trigeminal nerve Trigeminal nerve The 5th and largest cranial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is a mixed motor and sensory nerve. The larger sensory part forms the ophthalmic, mandibular, and maxillary nerves which carry afferents sensitive to external or internal stimuli from the skin, muscles, and joints of the face and mouth and from the teeth. Most of these fibers originate from cells of the trigeminal ganglion and project to the trigeminal nucleus of the brain stem. The smaller motor part arises from the brain stem trigeminal motor nucleus and innervates the muscles of mastication. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions, although secondary causes can be from aneurysms, neuromas, or other neurologic disorders. A detailed history is the hallmark for diagnosis. Neuroimaging Neuroimaging Non-invasive methods of visualizing the central nervous system, especially the brain, by various imaging modalities. Febrile Infant with MRI is useful to determine the exact pathology involving the trigeminal nerve Trigeminal nerve The 5th and largest cranial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is a mixed motor and sensory nerve. The larger sensory part forms the ophthalmic, mandibular, and maxillary nerves which carry afferents sensitive to external or internal stimuli from the skin, muscles, and joints of the face and mouth and from the teeth. Most of these fibers originate from cells of the trigeminal ganglion and project to the trigeminal nucleus of the brain stem. The smaller motor part arises from the brain stem trigeminal motor nucleus and innervates the muscles of mastication. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions root. The 1st line of therapy is pharmacologic ( carbamazepine Carbamazepine A dibenzazepine that acts as a sodium channel blocker. It is used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of grand mal and psychomotor or focal seizures. It may also be used in the management of bipolar disorder, and has analgesic properties. First-Generation Anticonvulsant Drugs). Other treatment options include botulinum toxin Botulinum toxin Toxic proteins produced from the species Clostridium botulinum. The toxins are synthesized as a single peptide chain which is processed into a mature protein consisting of a heavy chain and light chain joined via a disulfide bond. The botulinum toxin light chain is a zinc-dependent protease which is released from the heavy chain upon endocytosis into presynaptic nerve endings. Once inside the cell the botulinum toxin light chain cleaves specific snare proteins which are essential for secretion of acetylcholine by synaptic vesicles. This inhibition of acetylcholine release results in muscular paralysis. Botulism injections or surgical procedures in refractory cases.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a disorder presenting with recurrent, sharp pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways in the distribution of the trigeminal nerve Trigeminal nerve The 5th and largest cranial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is a mixed motor and sensory nerve. The larger sensory part forms the ophthalmic, mandibular, and maxillary nerves which carry afferents sensitive to external or internal stimuli from the skin, muscles, and joints of the face and mouth and from the teeth. Most of these fibers originate from cells of the trigeminal ganglion and project to the trigeminal nucleus of the brain stem. The smaller motor part arises from the brain stem trigeminal motor nucleus and innervates the muscles of mastication. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions.
Trigeminal nerve Trigeminal nerve The 5th and largest cranial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is a mixed motor and sensory nerve. The larger sensory part forms the ophthalmic, mandibular, and maxillary nerves which carry afferents sensitive to external or internal stimuli from the skin, muscles, and joints of the face and mouth and from the teeth. Most of these fibers originate from cells of the trigeminal ganglion and project to the trigeminal nucleus of the brain stem. The smaller motor part arises from the brain stem trigeminal motor nucleus and innervates the muscles of mastication. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (cranial nerve (CN) V):
3 major divisions of CN V:
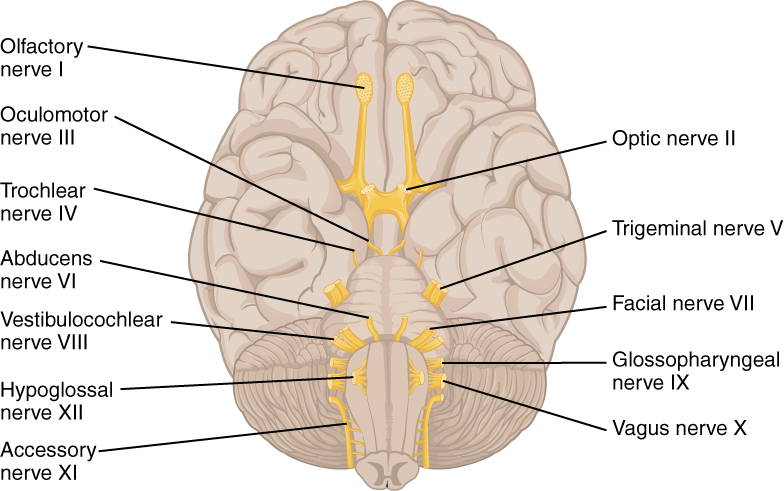
The 12 cranial nerves exiting the brain
Image: “The Cranial Nerves” by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY 4.0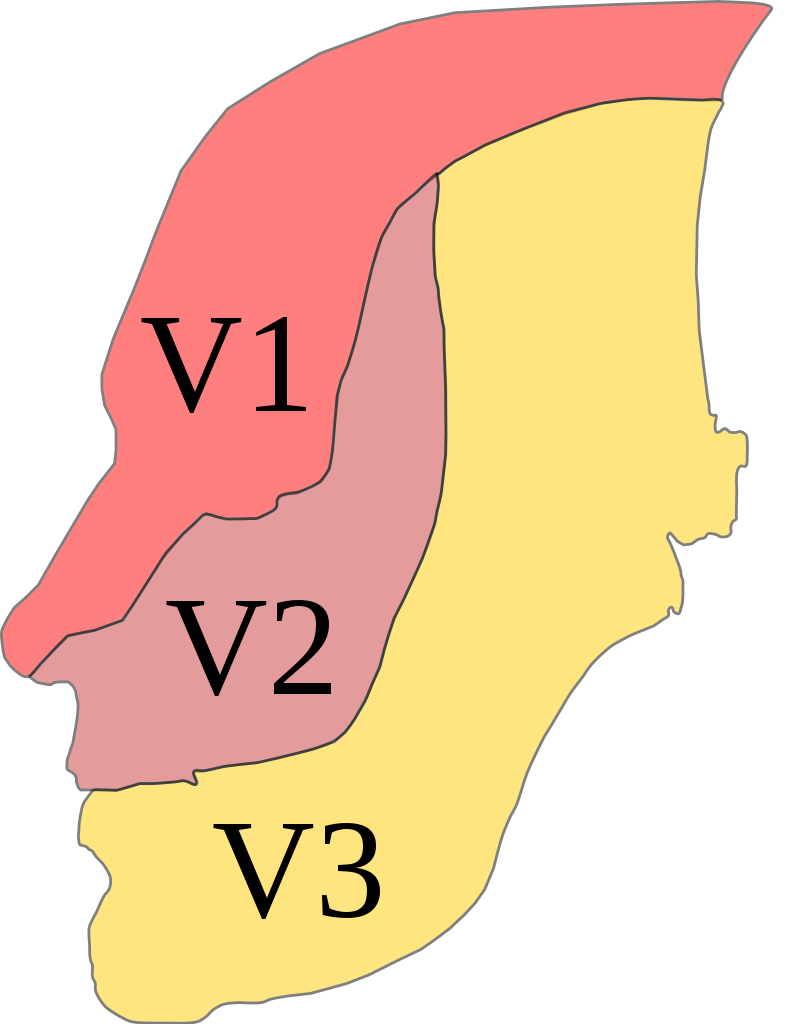
Trigeminal distribution
Image: “Trig innervation” by Madhero88. License: CC BY 3.0, edited by Lecturio.When other neurologic conditions (e.g., multiple sclerosis Sclerosis A pathological process consisting of hardening or fibrosis of an anatomical structure, often a vessel or a nerve. Wilms Tumor or aneurysms) are present, additional symptoms may include:
Diagnosis of TN is clinical with a thorough history and physical. Further workup with imaging or laboratory studies may be required if red-flag symptoms are present.