Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage without infarction that resolves completely when blood supply is restored. Transient ischemic attack is a neurologic emergency that warrants urgent medical attention Attention Focusing on certain aspects of current experience to the exclusion of others. It is the act of heeding or taking notice or concentrating. Psychiatric Assessment. A “tissue-based” definition is currently used rather than the former time-based limit Limit A value (e.g., pressure or time) that should not be exceeded and which is specified by the operator to protect the lung Invasive Mechanical Ventilation of symptoms lasting less than 24 hours. The causes of TIA may be small clots or thromboemboli imposed on a blood vessel compromised by atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a common form of arterial disease in which lipid deposition forms a plaque in the blood vessel walls. Atherosclerosis is an incurable disease, for which there are clearly defined risk factors that often can be reduced through a change in lifestyle and behavior of the patient. Atherosclerosis, inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation, or amyloid; inadequate cerebral blood flow Inadequate Cerebral Blood Flow Syncope from systemic hypoperfusion Systemic Hypoperfusion Ischemic Stroke; or severe hypotension Hypotension Hypotension is defined as low blood pressure, specifically < 90/60 mm Hg, and is most commonly a physiologic response. Hypotension may be mild, serious, or life threatening, depending on the cause. Hypotension. The clinical presentation includes transient neurologic deficits Neurologic Deficits High-Risk Headaches that resolve spontaneously. Management includes the reduction of risk factors to decrease the risk of a future stroke.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage without infarction that resolves completely when blood supply is restored.
The presentation depends on the pathophysiologic mechanism: embolic, lacunar (small penetrating vessel) TIA, or large artery TIA.
The affected individual may not recall the time of onset of neurological symptoms. Establish a precise account of the event, if possible, from family members or caregivers, and include the time of onset and resolution, if the symptoms have already improved.
Symptoms of TIA relate to the vascular territory that is being compromised:
Since the etiologies for stroke and TIA are very similar, the diagnostic evaluation for TIA resembles that for ischemic stroke Ischemic Stroke An ischemic stroke (also known as cerebrovascular accident) is an acute neurologic injury that occurs as a result of brain ischemia; this condition may be due to cerebral blood vessel occlusion by thrombosis or embolism, or rarely due to systemic hypoperfusion. Ischemic Stroke.
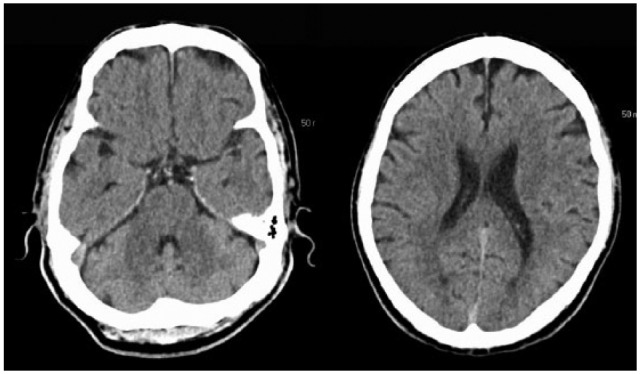
Axial cut of a CT scan of an individual with acute ischemic stroke performed at the time of admission:
Note the lack of discernible changes.