A thyroid nodule is a disordered growth of thyroid cells that produces a mass in the thyroid gland. Most thyroid nodules are benign and detected either by the patient or by the clinician on examination. In other cases, a thyroid nodule is found in radiologic imaging incidentally. Ruling out of malignancy is important. Workup includes thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid ultrasound followed by radioactive iodine (RAI) uptake scan or thyroid scan if initial tests suggest the presence of hyperthyroidism. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) is recommended in patients with suspicious ultrasound findings, "cold" nodules ( iodine Iodine A nonmetallic element of the halogen group that is represented by the atomic symbol I, atomic number 53, and atomic weight of 126. 90. It is a nutritionally essential element, especially important in thyroid hormone synthesis. In solution, it has anti-infective properties and is used topically. Thyroid Hormones uptake < surrounding tissue) on thyroid scan Thyroid Scan Nuclear Imaging, large nodules (generally > 1.5 cm), or risk factors for malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax. Management is dictated by pathology findings and can range from periodic ultrasound monitoring to surgery.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Thyroid nodule: left anterolateral neck mass in a woman
Image: “Concurrent hyperthyroidism and papillary thyroid cancer: a fortuitous and ambiguous case report from a resource-poor setting” by Kadia BM, Dimala CA, Bechem NN, Aroke D. License: CC BY 4.0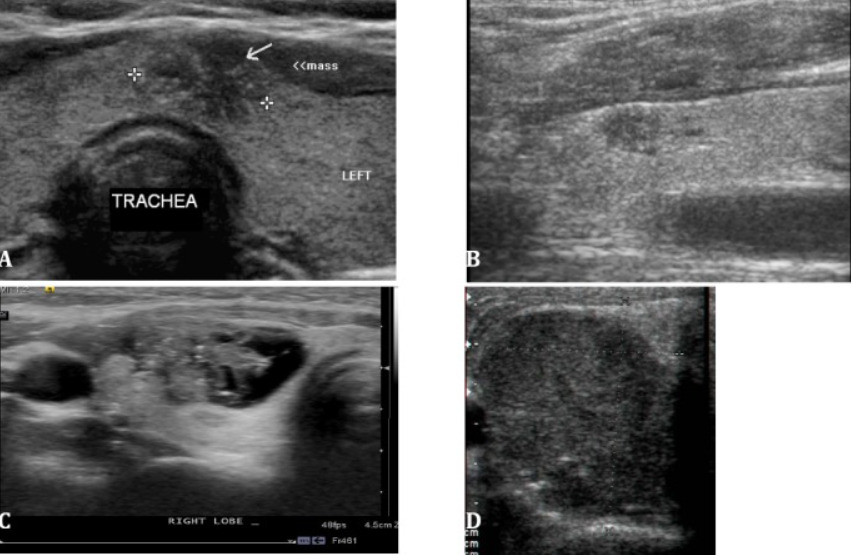
Spectrum of findings in malignant thyroid nodules (all cases of papillary carcinoma):
A: small isthmic mass with an irregular contour, marked hypoechogenicity, and microcalcifications
B: marked hypoechogenicity with pointed margins in the upper pole of the right lobe
C: complex mixed cystic and solid mass with lateral contour irregularity and microcalcifications
D: uniformly solid, markedly hypoechoic, taller-than-wide mass with a few internal microcalcifications
Based on TSH and ultrasound findings:
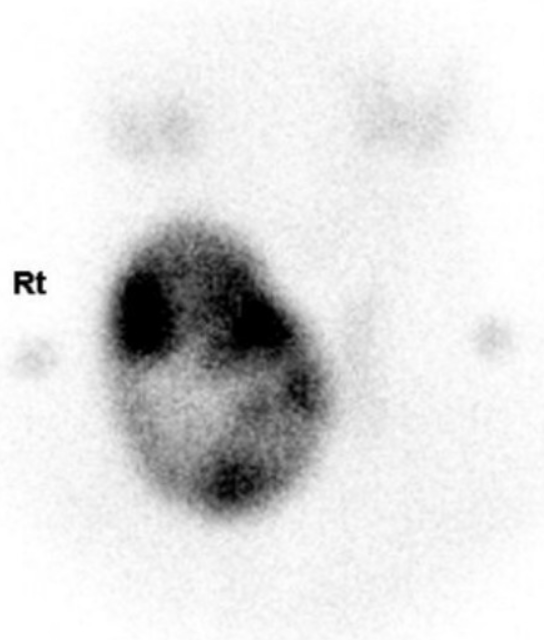
Thyroid scan of a nodule: heterogeneously increased uptake in a large or hot nodule of the thyroid gland with decreased uptake by the remaining tissue
Image: “Thyroid scan. 99 m-Technetium pertechnetate thyroid scan reveals heterogeneously increased uptake in the large nodule of the right thyroid gland with decreased uptake by the remaining thyroid gland, suggesting a functioning nodule” by Eun Ae Cho, Jee Hee Yoon, Hee Kyung Kim & Ho-Cheol Kang. License: CC BY 2.0FNAB indicated in:
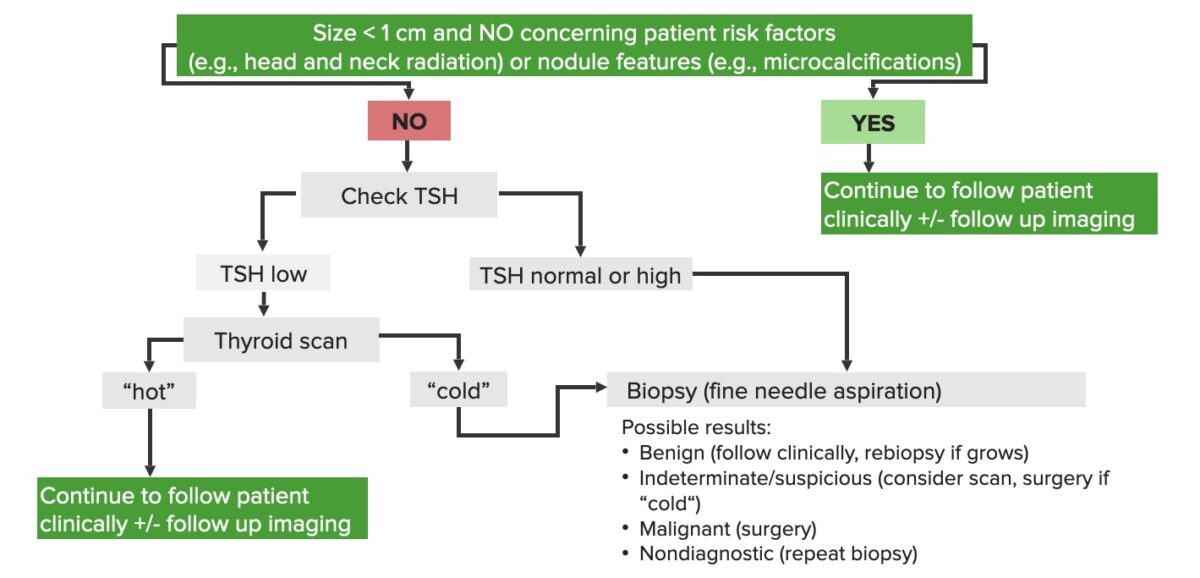
Schematic diagram of the diagnostic approach to thyroid nodules
Image by Lecturio.Based on biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma results ( Bethesda system Bethesda system A standardized reporting of results of PAP test, which includes the specimen adequacy, general categorization of findings, and results Cervical Cancer Screening diagnostic categories for reporting thyroid Thyroid The thyroid gland is one of the largest endocrine glands in the human body. The thyroid gland is a highly vascular, brownish-red gland located in the visceral compartment of the anterior region of the neck. Thyroid Gland: Anatomy cytopathology):