Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus Brachial Plexus The large network of nerve fibers which distributes the innervation of the upper extremity. The brachial plexus extends from the neck into the axilla. In humans, the nerves of the plexus usually originate from the lower cervical and the first thoracic spinal cord segments (c5-c8 and T1), but variations are not uncommon. Peripheral Nerve Injuries in the Cervicothoracic Region, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. The most common etiology involves structural abnormalities. Thoracic outlet syndrome can present as the neurogenic, arterial, or venous type. The neurogenic type is the most common among the 3 variants and mainly involves the inferior trunk of the brachial plexus Brachial Plexus The large network of nerve fibers which distributes the innervation of the upper extremity. The brachial plexus extends from the neck into the axilla. In humans, the nerves of the plexus usually originate from the lower cervical and the first thoracic spinal cord segments (c5-c8 and T1), but variations are not uncommon. Peripheral Nerve Injuries in the Cervicothoracic Region (C8–T1). Signs and symptoms vary based on the structure that is involved. The diagnosis of TOS is clinical and supported by radiography and a number of provocation maneuvers. Untreated TOS can lead to various complications such as a frozen shoulder Frozen Shoulder Chronic Shoulder Pain. Management of TOS is using pharmacological and surgical methods.
Last updated: Jan 15, 2024
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) refers to a spectrum of signs and symptoms that arise from the compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma of the neurovascular bundle by any of the various structures within the confined space of the thoracic outlet, usually within the scalene triangle.
Structural causes:
Other causes:
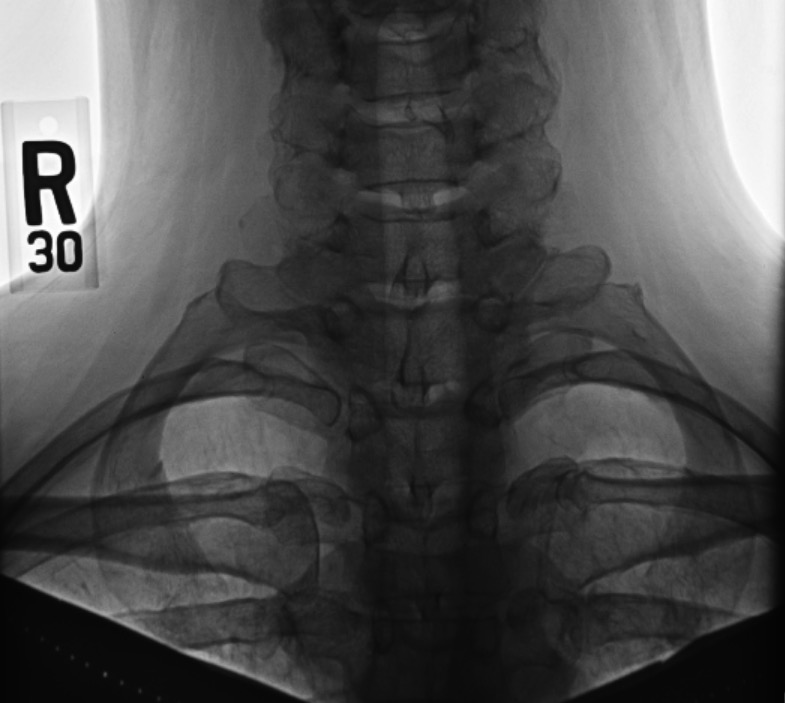
X-ray of the cervical ribs
Image: “Cervical Ribs” by Huntsville Hospital Imaging. License: Public DomainThoracic outlet:
The structures of significance in TOS are:
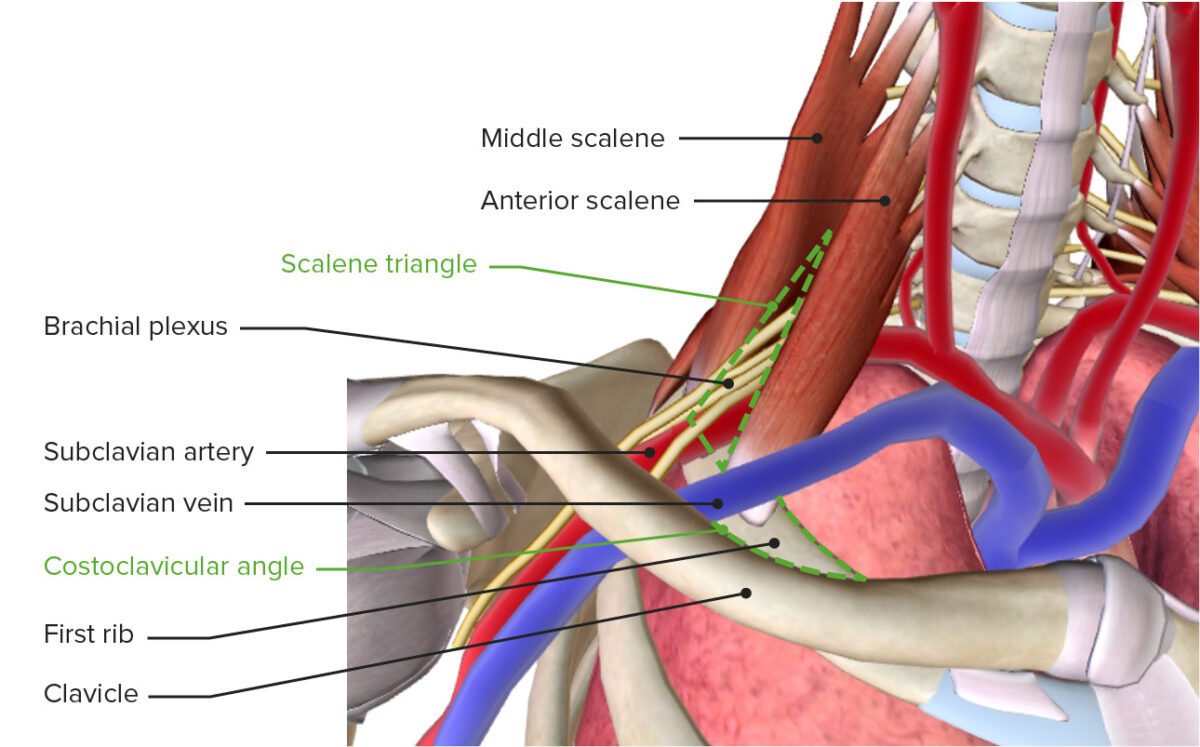
The thoracic outlet featuring the brachial plexus, subclavian vessels, scalene triangle, and costoclavicular angle
Image by BioDigital, edited by LecturioThere are 3 main sites where the compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma of structures occurs in TOS:
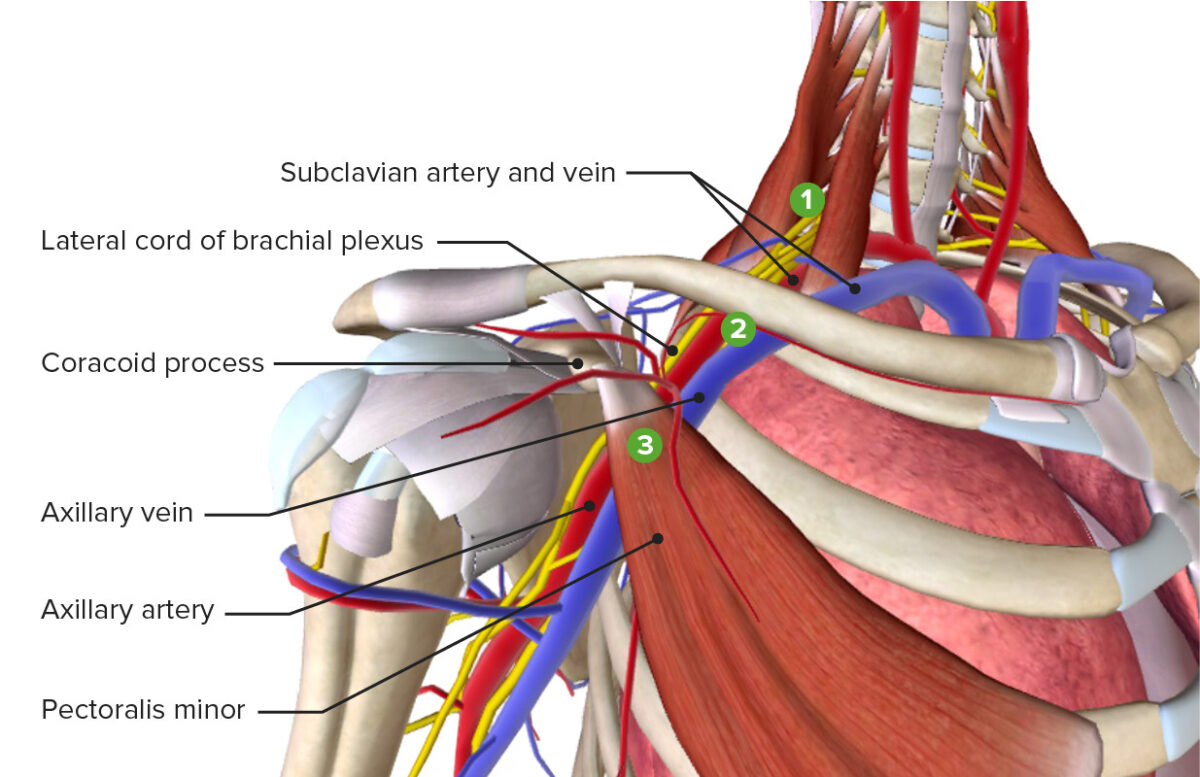
The 3 most common sites of compression leading to thoracic outlet syndrome: scalene triangle, costoclavicular angle, and subcoracoid space
Image by BioDigital, edited by LecturioAdson’s test:
Roos or elevated-arm test:
Wright’s hyperabduction test:
Costoclavicular maneuver:
Lidocaine Lidocaine A local anesthetic and cardiac depressant used as an antiarrhythmic agent. Its actions are more intense and its effects more prolonged than those of procaine but its duration of action is shorter than that of bupivacaine or prilocaine. Local Anesthetics scalene block test:
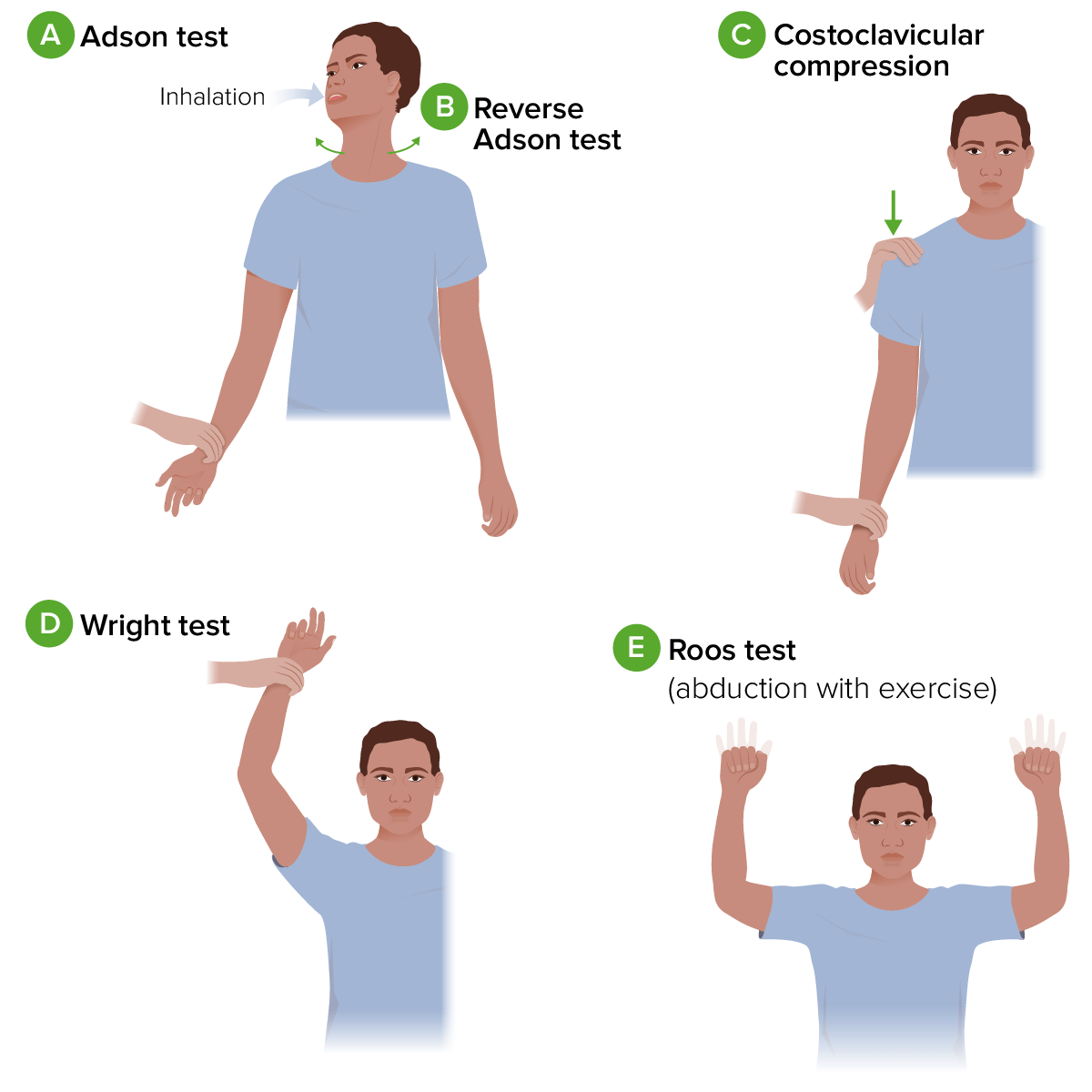
Diagram of provocative tests for thoracic outlet syndrome:
A. Adson test: The individual’s arm is fully extend and abducted. As the examiner palpates the radial pulse, the individual is asked to extend their neck and rotate it towards the affected shoulder. They then take a deep breath and hold this position.
B. Reverse Adson test: similar to the procedure for the Adson test, but the individual is asked to rotate their head to the opposite side.
C. Costoclavicular compression: While palpating the radial pulse, the examiner passively moves the individual’s shoulder down and back while they lift their chest.
D. Wright test: The individual’s arm is passively abducted and externally rotated with a flexed elbow. The position is held for 1 minute while the examiner palpates the radial pulse. The test is then repeated with the patient’s arm in hyperabduction.
E. Roos test: The individual’s arms are held at 90 degrees of abduction and external rotation, with the elbows flexed and in the frontal plane. The position is held while the individual opens and closes their fists for a few minutes.
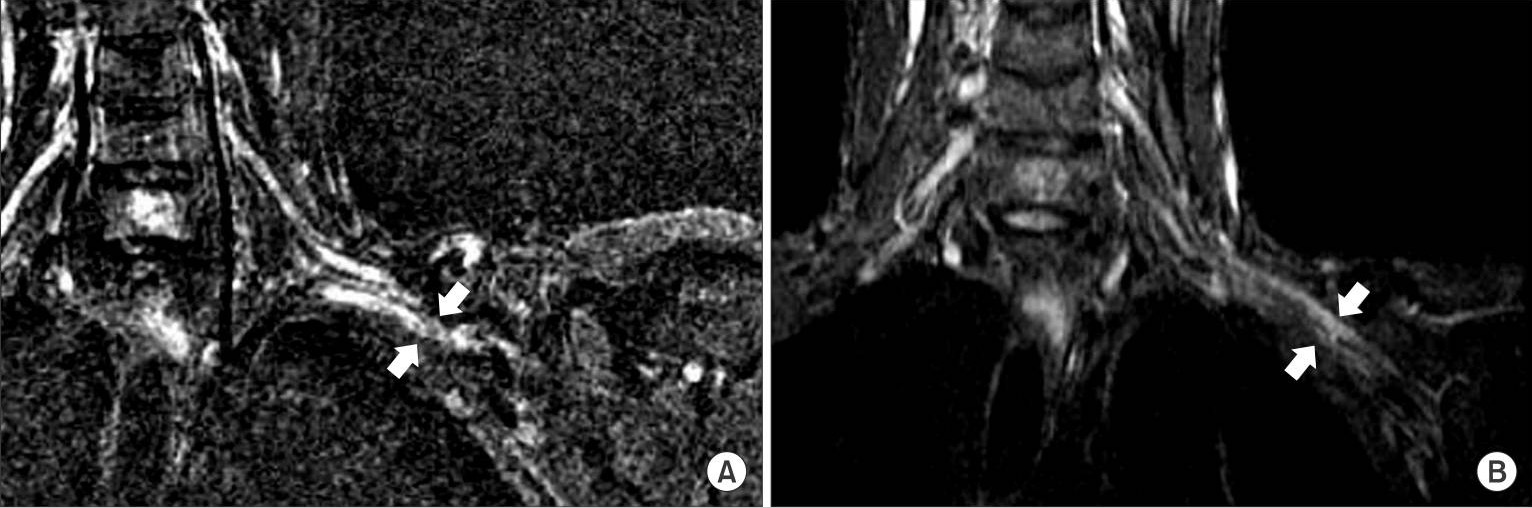
Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome:
MRI shows that the left brachial plexus is compressed by the malunited clavicle in the costoclavicular space (white arrows).
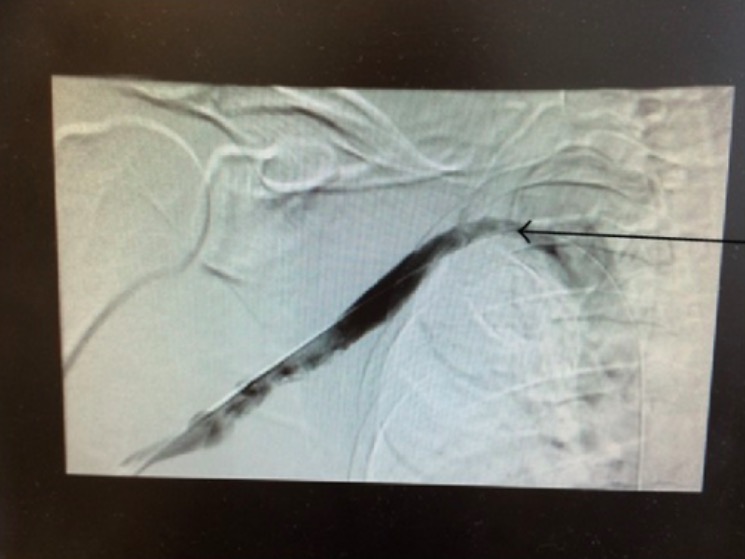
Venogram showing chronic scarring of right subclavian vein associated with thoracic outlet syndrome
Image: “Chronic scarring of the right subclavian vein” by Department of Internal Medicine, Saint Joseph Hospital, Chicago, IL 60657, USA. License: CC BY 3.0The management and care of TOS are approached via 2 different methods: