Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) is the abnormal dilation of a segment of the thoracic aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy, usually the ascending aorta Ascending aorta Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy. Most TAAs are due to degenerative aortic disorders, commonly in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship > 65 years of age. Genetic TAAs account for 20% of cases and are frequently found in younger patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship. Most TAAs are asymptomatic (incidentally found in imaging) but could present with symptoms from their effects on surrounding structures. Aortic rupture is a life-threatening emergency. Among diagnostic imaging studies, computed tomography (CT) angiography Angiography Radiography of blood vessels after injection of a contrast medium. Cardiac Surgery is the most widely utilized. In asymptomatic cases, aortic expansion is monitored. Operative repair is recommended for symptomatic TAAs and increasing aortic diameter (criteria varies with location and underlying condition).
Last updated: Mar 15, 2025
Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA)
Types
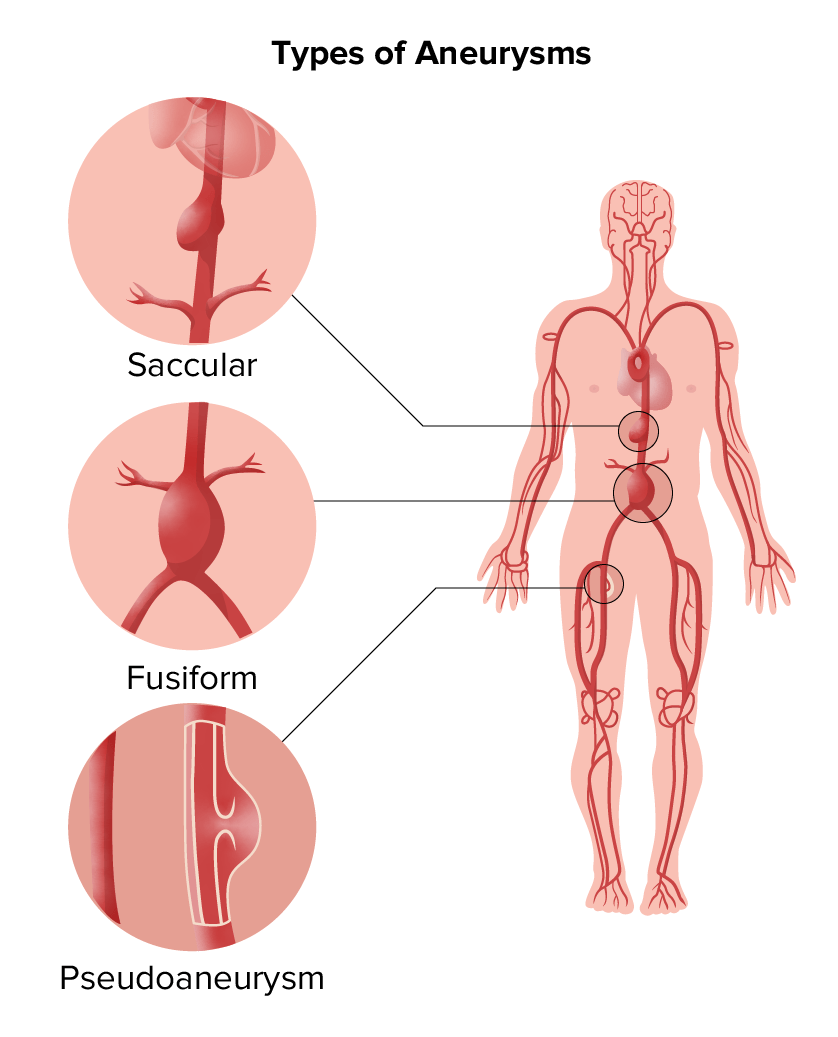
Types of aneurysms:
Saccular and fusiform aneurysms are in the category of true aneurysms; pseudoaneurysm is another type.
Location
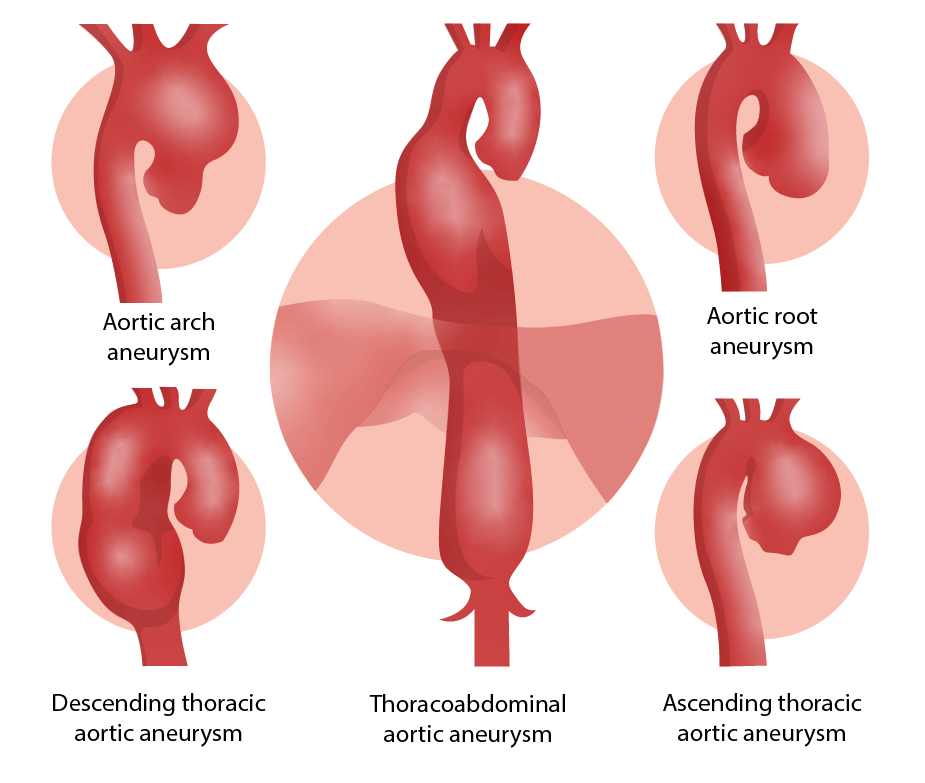
Locations of aortic aneurysms
Image by Lecturio.| Management of asymptomatic patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship | Degenerative ascending or aortic root aneurysm | Descending aortic aneurysm |
|---|---|---|
|
Annual
CTA
CTA
A non-invasive method that uses a ct scanner for capturing images of blood vessels and tissues. A contrast material is injected, which helps produce detailed images that aid in diagnosing vascular diseases.
Pulmonary Function Tests/
MRA
MRA
Imaging of the Heart and Great Vessels
( echocardiography Echocardiography Ultrasonic recording of the size, motion, and composition of the heart and surrounding tissues. The standard approach is transthoracic. Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA) to follow valvular disease if needed) |
3.5–4.4 cm | 4–4.9 cm |
| Biannual (every 6 months)
CTA
CTA
A non-invasive method that uses a ct scanner for capturing images of blood vessels and tissues. A contrast material is injected, which helps produce detailed images that aid in diagnosing vascular diseases.
Pulmonary Function Tests/
MRA
MRA
Imaging of the Heart and Great Vessels
( echocardiography Echocardiography Ultrasonic recording of the size, motion, and composition of the heart and surrounding tissues. The standard approach is transthoracic. Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA) to follow valvular disease if needed) |
4–4.9 cm | 5–6 cm |
| Consider elective repair |
≥ 5.5 cm
Rapid expansion (> 0.5 cm/year) ≥ 4.5 cm if aortic valve Aortic valve The valve between the left ventricle and the ascending aorta which prevents backflow into the left ventricle. Heart: Anatomy surgery or coronary bypass needed |
≥ 5.5 cm, consider thoracic endovascular repair (TEVAR);
≥ 6 cm (TEVAR not technically possible) for open surgery; Rapid expansion (> 0.5 cm/year) |
Indications for operative repair
Operative options
Differential diagnoses of TAA include the following conditions: