Thin basement membrane nephropathy (TBMN), also called benign Benign Fibroadenoma familial hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, is a type of nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome is a broad category of glomerular diseases characterized by glomerular hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension. These features are in contrast to those of nephrotic syndrome, which includes glomerular diseases characterized by severe proteinuria, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephritic Syndrome caused by diffuse thinning of the glomerular basement membrane Glomerular basement membrane The layer of extracellular matrix that lies between the endothelium of the glomerular capillaries and the podocytes of the inner or visceral layer of the bowman capsule. It is the product of these two cell types. It acts as a physical barrier and an ion-selective filter. Goodpasture Syndrome (GBM). The syndrome is often familial and due to mutations in the alpha chains of type IV collagen Type IV collagen A non-fibrillar collagen found in the structure of basement membrane. Collagen type IV molecules assemble to form a sheet-like network which is involved in maintaining the structural integrity of basement membranes. The predominant form of the protein is comprised of two alpha1(IV) subunits and one alpha2(IV) subunit, however, at least six different alpha subunits can be incorporated into the heterotrimer. Alport Syndrome. Clinical presentation can range from asymptomatic microscopic hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma to gross hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, flank pain Flank pain Pain emanating from below the ribs and above the ilium. Renal Cell Carcinoma, proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children, and hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension. Diagnosis is by clinical evaluation. Renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis is rarely required but will show diffuse thinning of the GBM on electron microscopy. Most cases are benign Benign Fibroadenoma, but ACE inhibitors ACE inhibitors Truncus Arteriosus and ARBs ARBs Agents that antagonize angiotensin receptors. Many drugs in this class specifically target the angiotensin type 1 receptor. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication may be used in certain cases.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
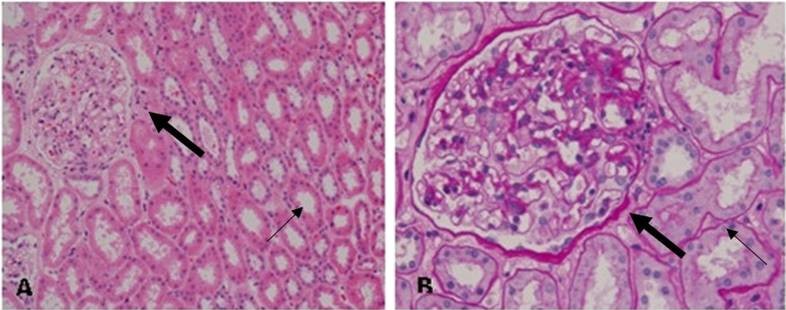
Light microscopy of renal samples in thin basement membrane nephropathy (TBMN) shows almost normal glomerular histology.
(A) Periodic acid–Schiff staining (200×): The large arrow indicates the glomerulus and the thin arrow indicates the kidney tubules.
(B) Periodic acid–Schiff staining (400×): The glomerular basement membrane (GBM) and mesangial matrix were dyed fuchsia. The PAS staining showed almost normal glomerular histology with only occasional mild mesangial cellular proliferation and matrix expansion.
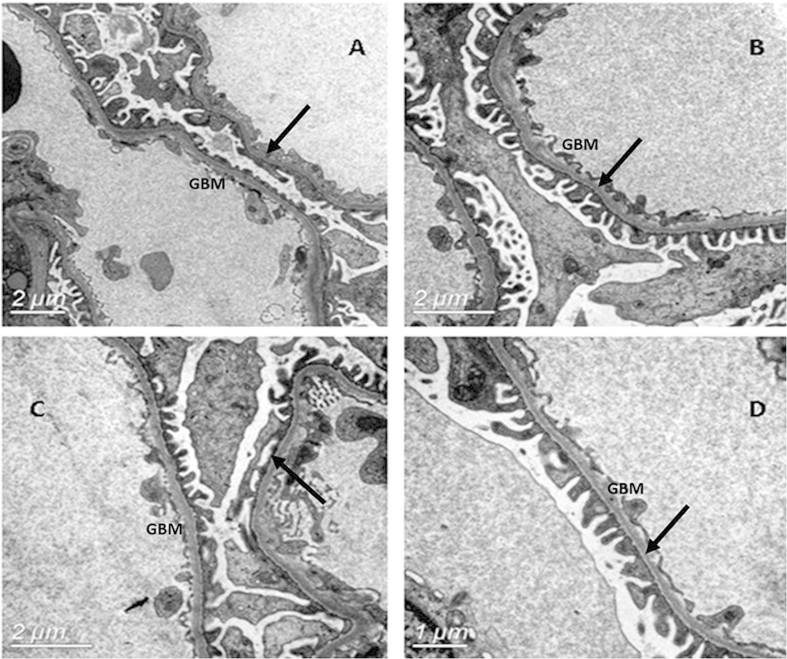
Electron microscopy of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) in thin basement membrane nephropathy (TBMN) showed a uniformly thinned GBM. The GBM is located between the fenestrated endothelial cells and the podocyte foot processes.
The arrows show the characteristically thinned GBM and few podocyte fusions.