Thalassemia is a hereditary cause of microcytic hypochromic anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types and results from a deficiency in either the α or β globin chains, resulting in hemoglobinopathy. The presentation of thalassemia depends on the number of defective chains present and can range from being asymptomatic to rendering the more severely affected patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship to be transfusion dependent. The diagnosis can be confirmed using hemoglobin electrophoresis Electrophoresis An electrochemical process in which macromolecules or colloidal particles with a net electric charge migrate in a solution under the influence of an electric current. Blotting Techniques, which will reveal the presence of abnormal α- or β-globin chains.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
| Number of genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure deleted/ genotype Genotype The genetic constitution of the individual, comprising the alleles present at each genetic locus. Basic Terms of Genetics | Disease | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (αα/α-) |
α-Thalassemia minima | Silent carrier Carrier Vaccination |
| 2 (α-/α-; trans) (αα/–; cis CIS Multiple Sclerosis) |
α-Thalassemia minor |
|
| 3 (α-/–) |
HbH (4 β chains) | Moderate-to-severe anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types |
| 4 (–/–) |
Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange Barts (4 γ chains) | Hydrops Hydrops Cholecystitis fetalis (incompatible with life) |
| Number of genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure deleted/ genotype Genotype The genetic constitution of the individual, comprising the alleles present at each genetic locus. Basic Terms of Genetics | Disease | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| β0/β or β+/β | Thalassemia minor | Asymptomatic (mild) |
| β0/β0 or β+/β+ | Thalassemia major (Cooley’s anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types) | Transfusion dependent |
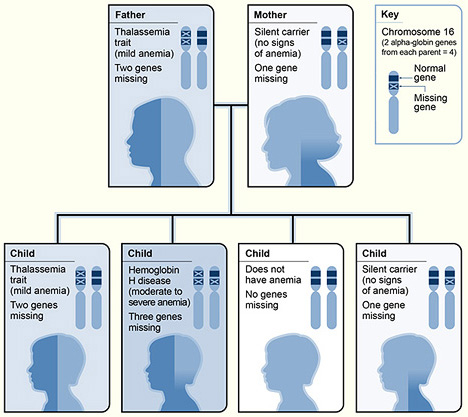
An example of α-thalassemia inheritance
Image: “The picture shows one example of how alpha thalassemia is inherited” by National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NIH). License: Public Domain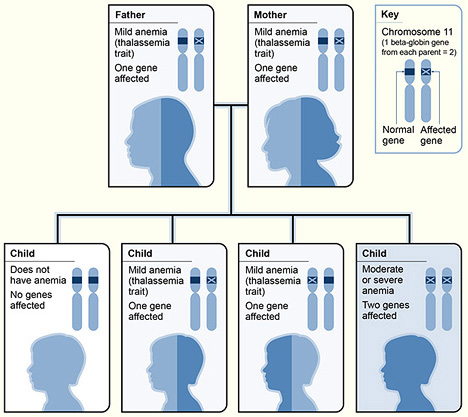
An example of β-thalassemia inheritance
Image: “The picture shows one example of how beta thalassemia is inherited” by National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NIH). License: Public Domain| Disease | Presentation |
|---|---|
| α-Thalassemia minima | Asymptomatic |
| α-Thalassemia minor |
|
| HbH disease |
|
| Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange Barts |
|
| β-Thalassemia minor |
|
| β-Thalassemia major (Cooley’s anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types) |
|
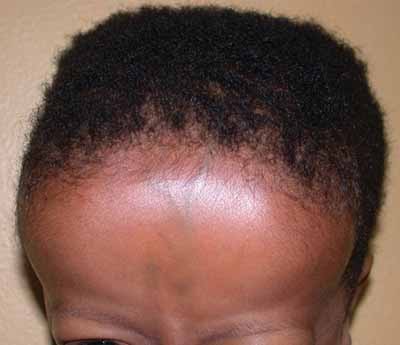
Frontal bossing due to excessive need for hematopoiesis
Image: “Frontal bossing (abnormally enlarged forehead) in a child” by National Human Genome Research Institute (NIH). License: Public Domain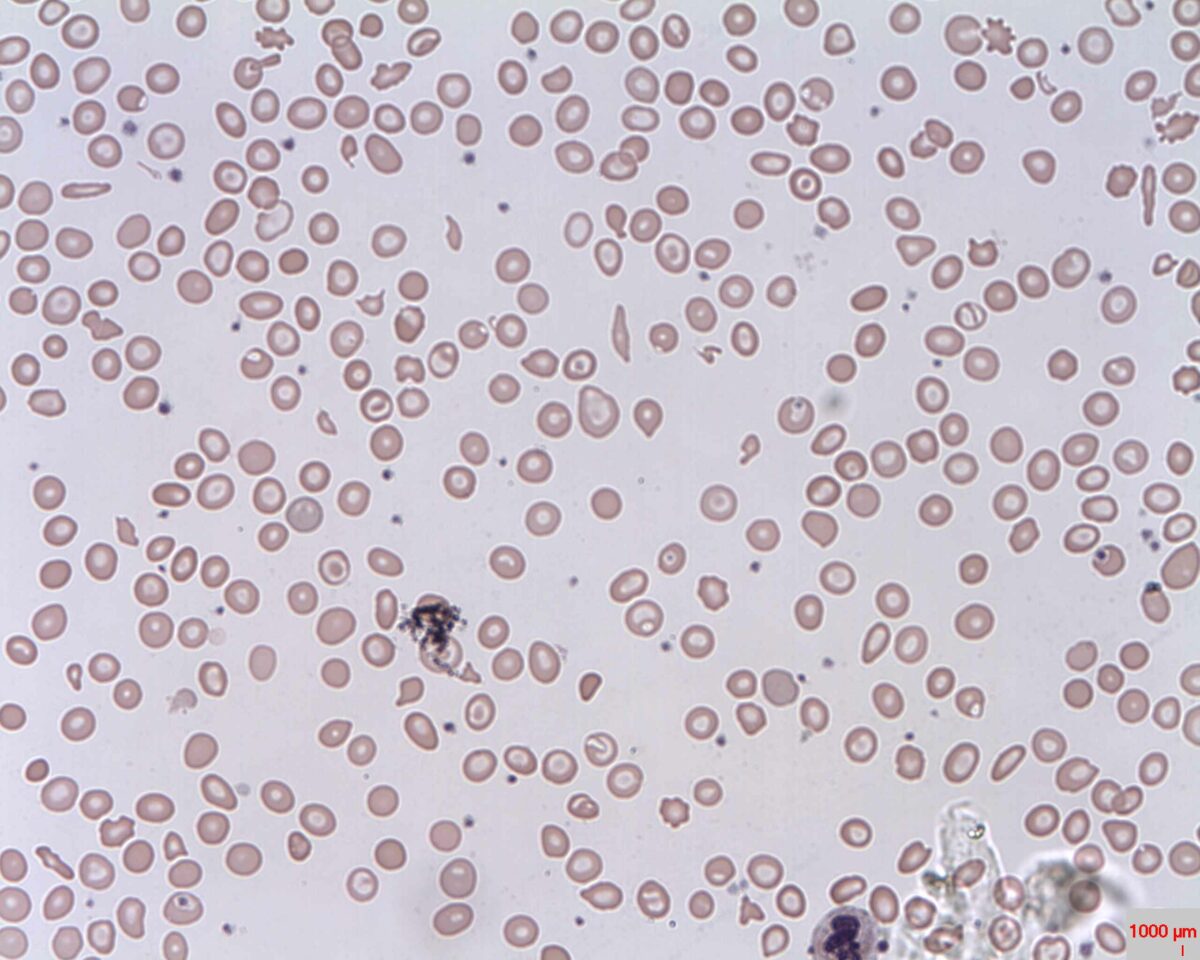
Peripheral Smear: microcytic hypochromic anemia with target cells (bull’s eye); anisocytosis (unequal-sized RBCs) is also seen
Image: “Target cells (Codocytes, Leptocytes or Mexican hat cells)” by Prof. Osaro Erhabor. License: CC0 1.0The differential diagnosis includes other conditions associated with microcytic anemia Microcytic anemia Conditions in which there is a generalized increase in the iron stores of body tissues, particularly of liver and the mononuclear phagocyte system, without demonstrable tissue damage. The name refers to the presence of stainable iron in the tissue in the form of hemosiderin. Anemia: Overview and Types or target cells.