Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium tetani, a gram-positive obligate anaerobic bacterium commonly found in soil that enters the body through a contaminated wound. C. tetani produces a neurotoxin that blocks the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters and causes prolonged tonic muscle contractions. It presents with lockjaw, neck stiffness, opisthotonus, rigid abdomen and severe painful muscle spasms. Diagnosis is made on clinical grounds, as it is rarely possible to isolate the infectious agent from the wound. It is treated with antibiotic therapy and human tetanus immune globulin (HTIG). Untreated tetanus can lead to respiratory failure Respiratory failure Respiratory failure is a syndrome that develops when the respiratory system is unable to maintain oxygenation and/or ventilation. Respiratory failure may be acute or chronic and is classified as hypoxemic, hypercapnic, or a combination of the two. Respiratory Failure and cardiovascular complications and can be fatal. With appropriate treatment, however, most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship will recover.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Tetanus is a nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification disorder characterized by muscle spasms Spasms An involuntary contraction of a muscle or group of muscles. Spasms may involve skeletal muscle or smooth muscle. Ion Channel Myopathy that is caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani.
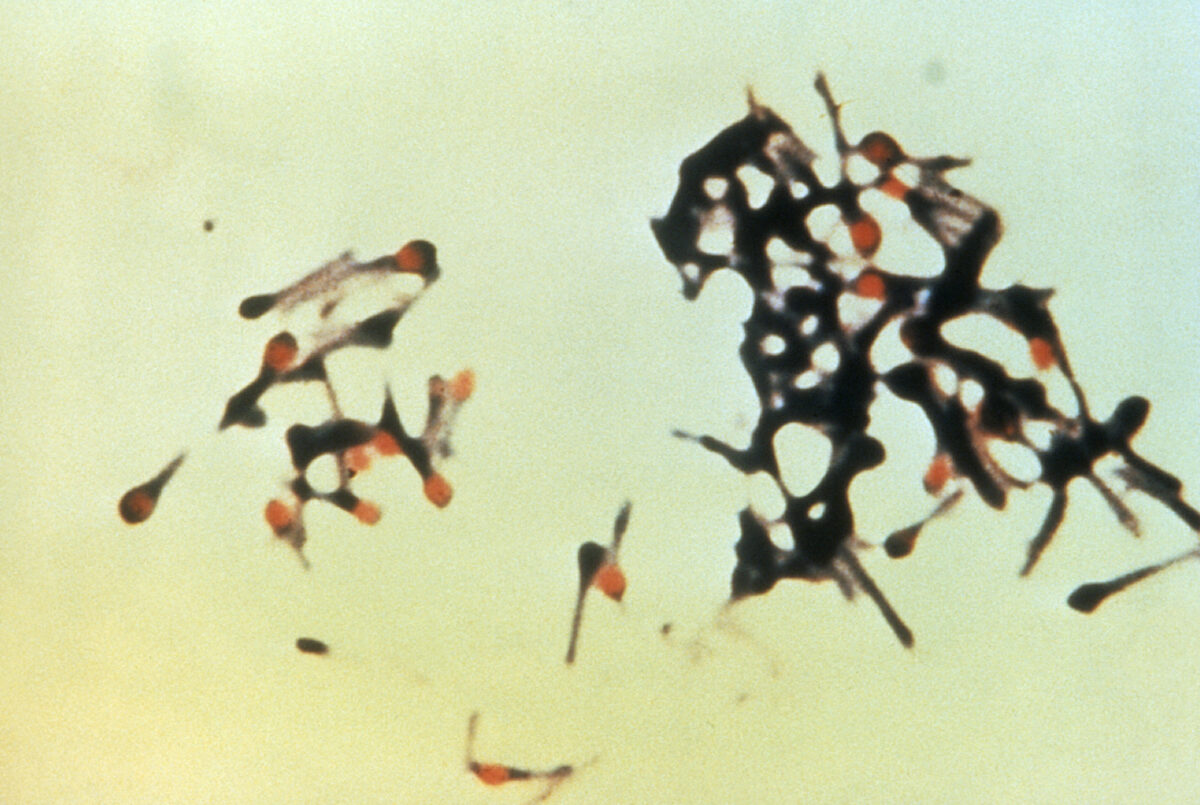
The micrograph depicts a group of Clostridium tetani bacteria, responsible for causing tetanus in humans:
Note the slender bacillus with a characteristic “drumstick”
appearance caused by the spherical terminally located spores.
Inoculation:
Pathogenesis:
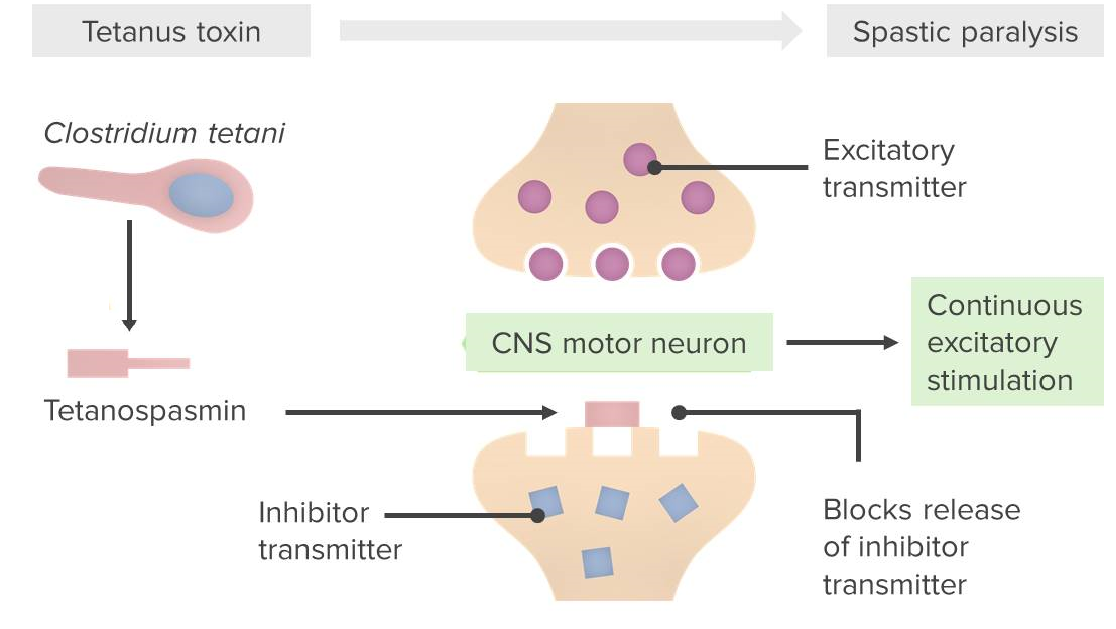
Pathophysiologic mechanism caused by Clostridium tetani:
Tetanospasmin blocks the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters (GABA/glycine) from presynaptic neurons. The end result is that the motor neuron receives only excitatory/stimulatory input, resulting in a spastic paralysis.
Generalized tetanus is the most common and severe clinical form of tetanus.
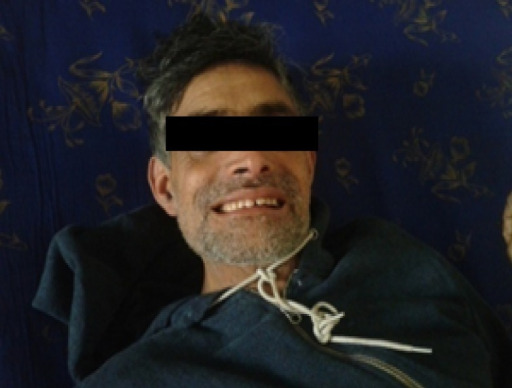
Risus sardonicus in patient with generalized tetanus
Image: “Generalized Tetanus Initially Presenting with Dysmasesis” by Zunga PM, Tarfarosh SF, Farooq O, Dar IH, Rashid S, Yaseen U. License: CC BY 3.0
Opisthotonus: An arched back due to varying degrees of rigidity in the neck and trunk
Image: “Opisthotonus in a patient suffering from tetanus – Painting by Sir Charles Bell – 1809” by Sir Charles Bell/Para. License: Public DomainNeonatal tetanus:
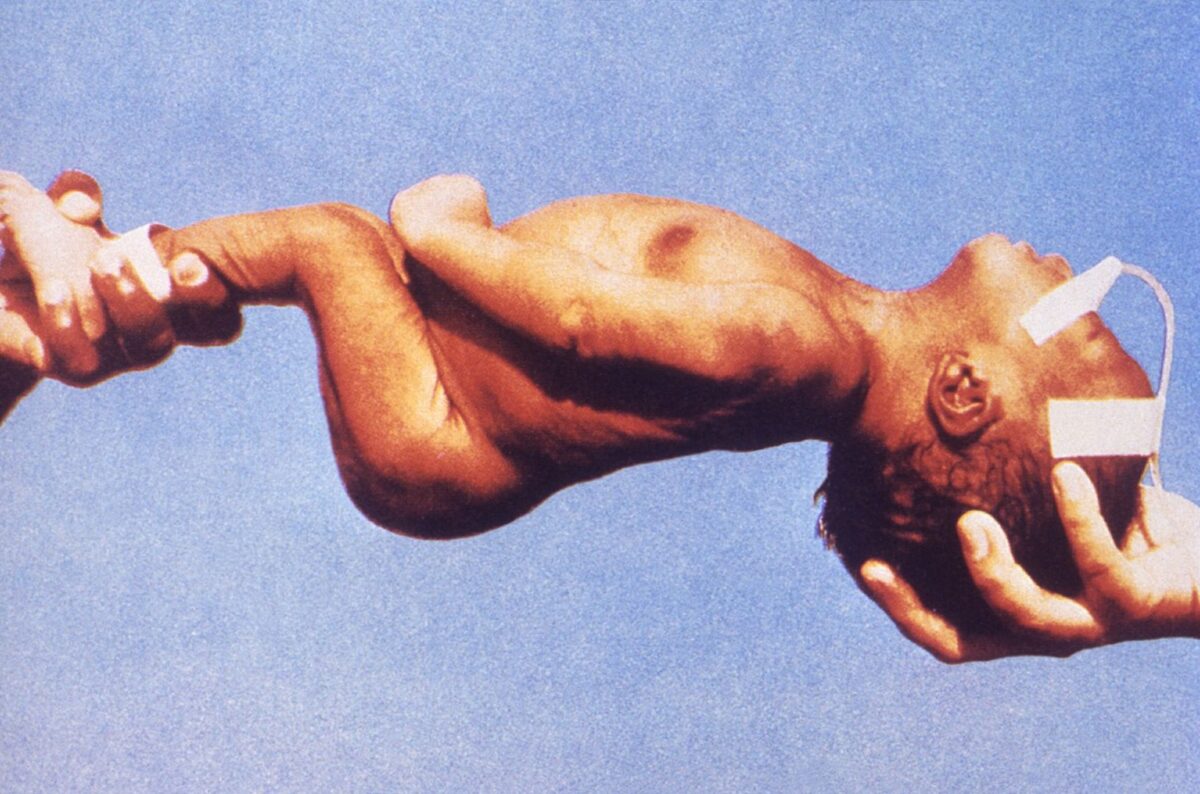

Neonate displaying body rigidity seen in neonatal tetanus
Image: “Neonatal tetanus 6374” by CDC. License: Public DomainLocal tetanus:
Cephalic tetanus:
Halting production of toxin:
Neutralization of unbound toxin:
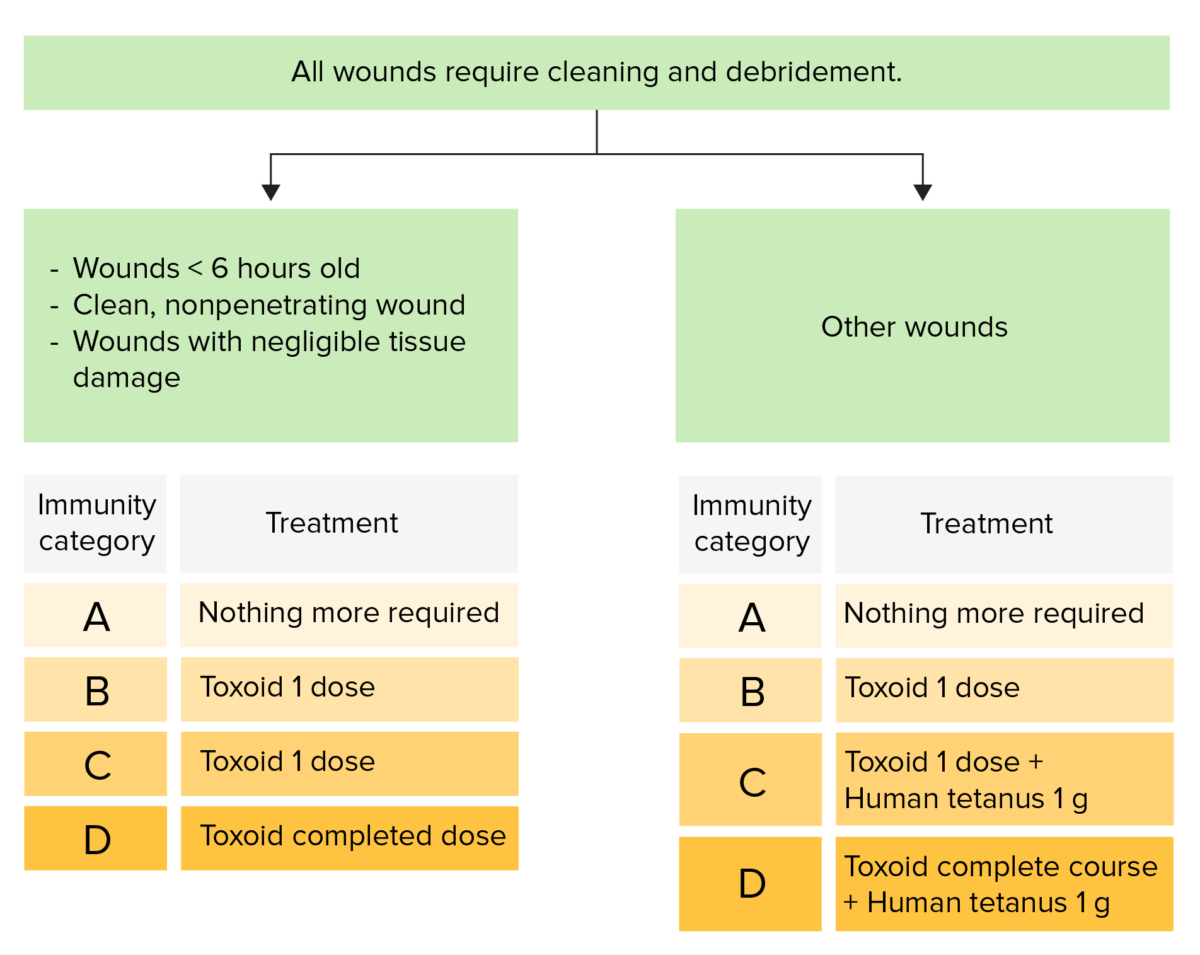
Wound management and prophylaxis of tetanus:
The time from the last dose determines the treatment given to an individual to prevent contracting the disease.
Immunity categories:
A: The patient has had a complete course of toxoid or a booster within the past 5 years.
B: The patient has had a complete course of toxoid or a booster between 5 and 10 years ago.
C: The patient has had a complete course of toxoid or a booster dose > 10 years ago.
D: The patient has not had a complete course of toxoid or immunity status is unknown.