Congenital malformations or teratogenic birth defects are developmental disorders that arise before birth during the embryonic or fetal period Fetal period Prenatal and Postnatal Physiology of the Neonate. The rate of incidence Incidence The number of new cases of a given disease during a given period in a specified population. It also is used for the rate at which new events occur in a defined population. It is differentiated from prevalence, which refers to all cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency for children born alive is approximately 3%. The cause may be genetic or contingent on external influences or teratogens Teratogens An agent that causes the production of physical defects in the developing embryo. Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate. Teratogens Teratogens An agent that causes the production of physical defects in the developing embryo. Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate are environmental factors that result in permanent structural or functional malformations, or the death of the embryo Embryo The entity of a developing mammal, generally from the cleavage of a zygote to the end of embryonic differentiation of basic structures. For the human embryo, this represents the first two months of intrauterine development preceding the stages of the fetus. Fertilization and First Week or fetus. Teratogens Teratogens An agent that causes the production of physical defects in the developing embryo. Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate include infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, certain medications, drugs, and radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Primary malformations:
Secondary malformations:
Double malformations or “Siamese twins:”
Two fetuses that have grown together due to incomplete intertwining of the embryoblast Embryoblast Embryoblast and Trophoblast Development in the blastocyst Blastocyst A post-morula preimplantation mammalian embryo that develops from a 32-cell stage into a fluid-filled hollow ball of over a hundred cells. A blastocyst has two distinctive tissues. The outer layer of trophoblasts gives rise to extra-embryonic tissues. The inner cell mass gives rise to the embryonic disc and eventual embryo proper. Fertilization and First Week stage (13th day):
The development of malformations varies throughout different stages of embryological/fetal development and is referred to as phase-dependent vulnerability.
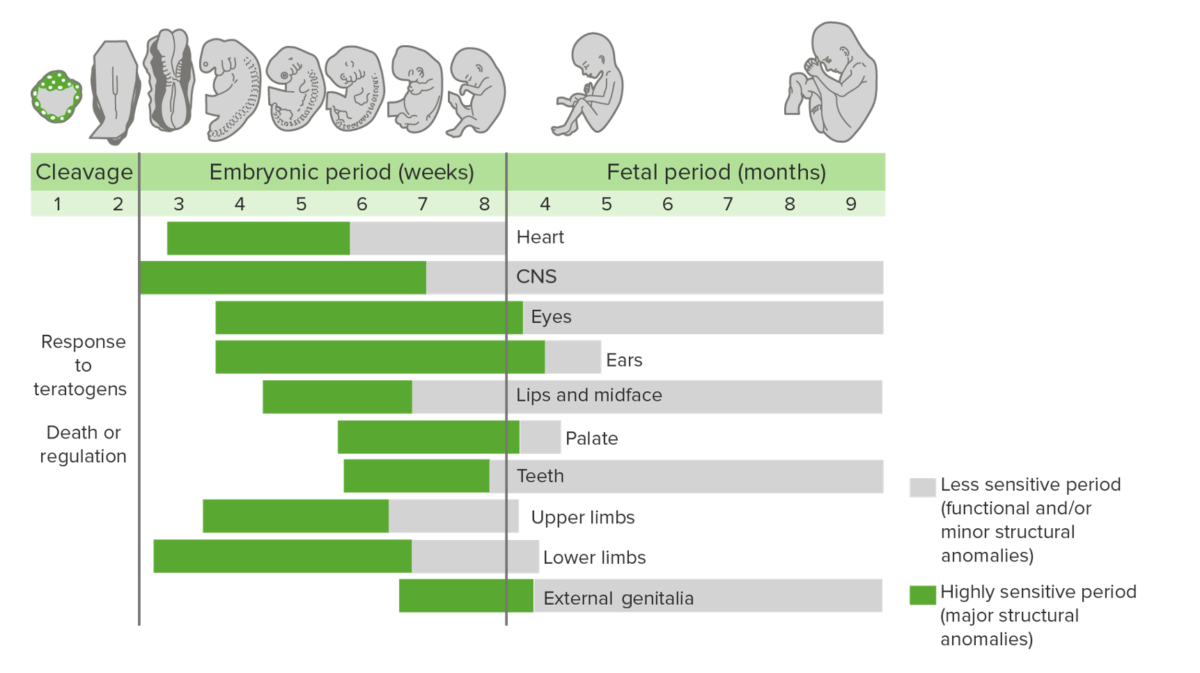
Periods of time within gestation in which organ systems are most susceptible to teratogens:
Gray: less sensitive period (functional and/or minor structural anomalies)
Green: highly sensitive period (major structural anomalies)
Alcohol use disorder Alcohol use disorder Alcohol is one of the most commonly used addictive substances in the world. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is defined as pathologic consumption of alcohol leading to impaired daily functioning. Acute alcohol intoxication presents with impairment in speech and motor functions and can be managed in most cases with supportive care. Alcohol Use Disorder → fetal alcohol spectrum disorder Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) is a group of neonatal pediatric disorders caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy. The term entails a range of physical and neurodevelopmental effects. Classification is based on severity and clinical presentation. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD)/ fetal alcohol syndrome Fetal alcohol syndrome An umbrella term used to describe a pattern of disabilities and abnormalities that result from fetal exposure to ethanol during pregnancy. It encompasses a phenotypic range that can vary greatly between individuals, but reliably includes one or more of the following: characteristic facial dysmorphism, fetal growth retardation, central nervous system abnormalities, cognitive and/or behavioral dysfunction, birth defects. The level of maternal alcohol consumption does not necessarily correlate directly with disease severity. Alcohol Use Disorder (severe end of the spectrum for alcohol-related defects)

Characteristic facial features of an individual with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
Image: “FASkid” by NIH/National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. License: Public DomainMedications that are contraindicated during pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care and the potential complications they are associated with are as follows: