Takotsubo cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy refers to a group of myocardial diseases associated with structural changes of the heart muscles (myocardium) and impaired systolic and/or diastolic function in the absence of other heart disorders (coronary artery disease, hypertension, valvular disease, and congenital heart disease). Cardiomyopathy: Overview and Types (also known as stress cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy refers to a group of myocardial diseases associated with structural changes of the heart muscles (myocardium) and impaired systolic and/or diastolic function in the absence of other heart disorders (coronary artery disease, hypertension, valvular disease, and congenital heart disease). Cardiomyopathy: Overview and Types, or “broken heart syndrome”) is a type of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy refers to a group of myocardial diseases associated with structural changes of the heart muscles (myocardium) and impaired systolic and/or diastolic function in the absence of other heart disorders (coronary artery disease, hypertension, valvular disease, and congenital heart disease). Cardiomyopathy: Overview and Types in which there is transient regional systolic dysfunction Systolic dysfunction Dilated Cardiomyopathy of the left ventricle. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with symptoms of acute coronary syndrome, including chest pressure and shortness of breath Shortness of breath Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea. Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ( ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)) may show ST-segment elevations. Coronary angiography Angiography Radiography of blood vessels after injection of a contrast medium. Cardiac Surgery can help in differentiating this condition from myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction MI is ischemia and death of an area of myocardial tissue due to insufficient blood flow and oxygenation, usually from thrombus formation on a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque in the epicardial arteries. Clinical presentation is most commonly with chest pain, but women and patients with diabetes may have atypical symptoms. Myocardial Infarction. Echocardiogram Echocardiogram Transposition of the Great Arteries can confirm the diagnosis by demonstrating characteristic apical wall motion abnormalities. Management includes the removal of inciting stressors and beta blockers.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The exact cause for this condition is unknown, but it is associated with the following:
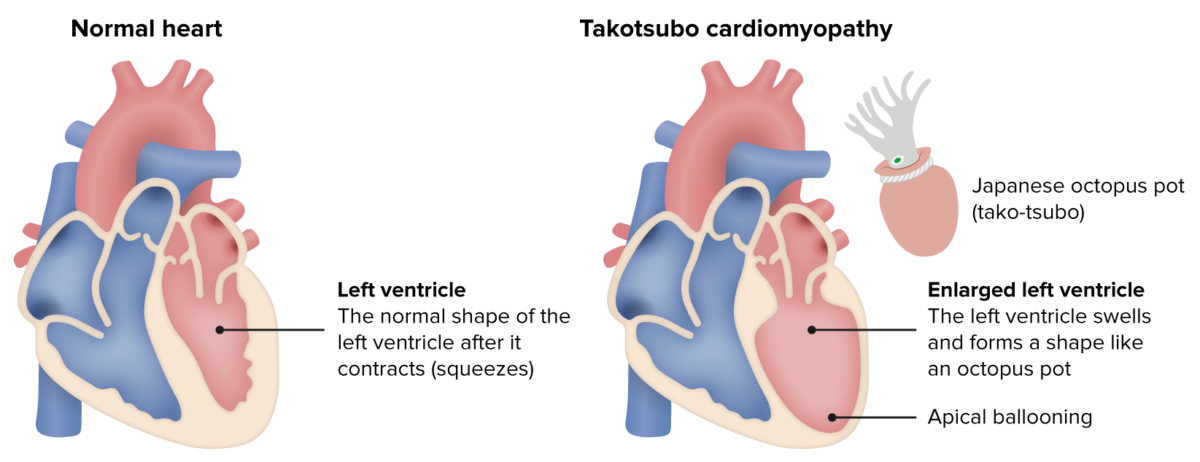
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
Image by Lecturio.Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship will present similar to those with ACS or heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR):
Symptoms
Physical exam
Because patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present similar to ACS, the diagnostic process will be similar.
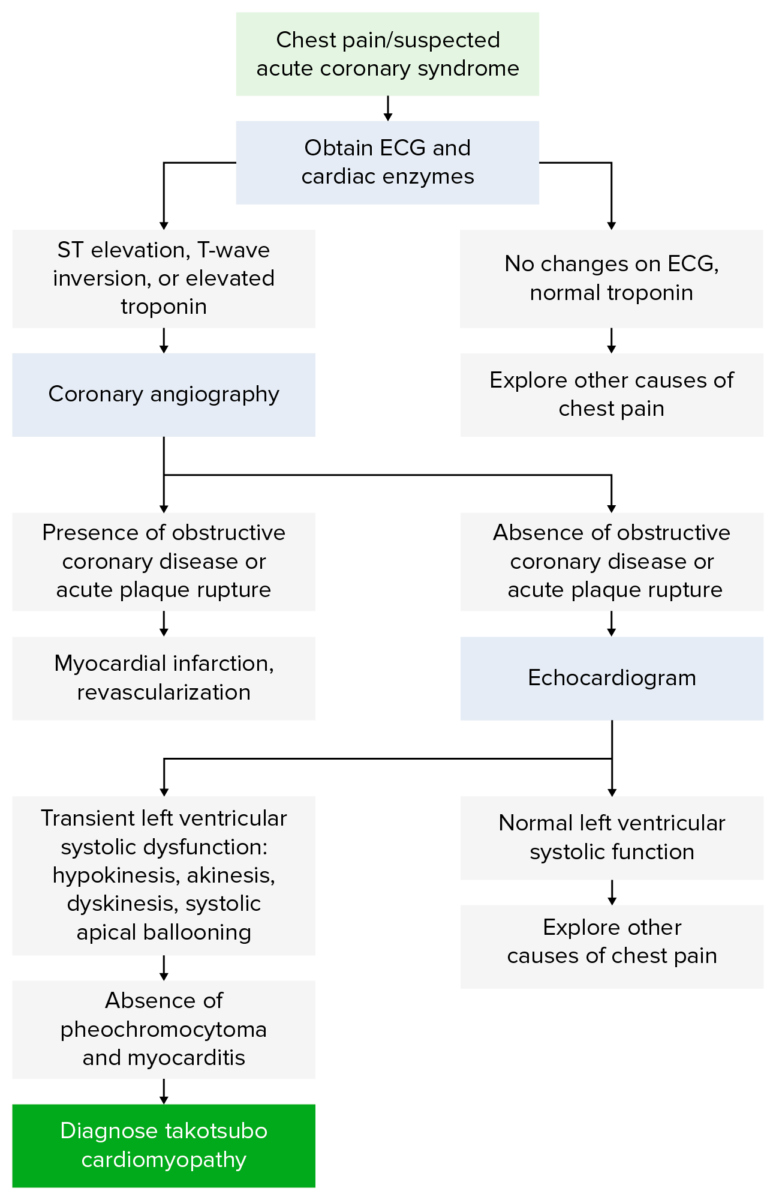
Diagnostic Algorithm for Takosubo cardiomyopathy
Image by Lecturio.Initial testing:
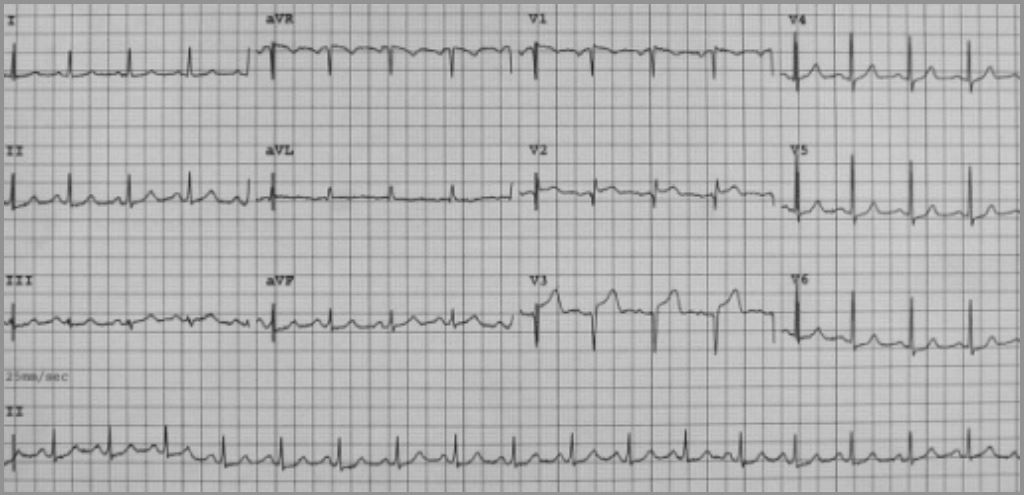
A 12-lead electrocardiogram for a patient presenting with takotsubo cardiomyopathy. The ECG shows sinus tachycardia with 2–3 mm ST-segment elevation in leads V2–V3, and 1 mm ST-segment depression in leads V5–V6. Note how this would be concerning for myocardial infarction.
Image: “Twelve-lead electrocardiogram on admission” by Lisi M, Zacà V, Maffei S, Casucci F, Maggi M, Lunghetti S, Aitiani P, Carrera A, Castellani D, Favilli R, Pierli C, Mondillo S. License: CC BY 2.0Next steps:
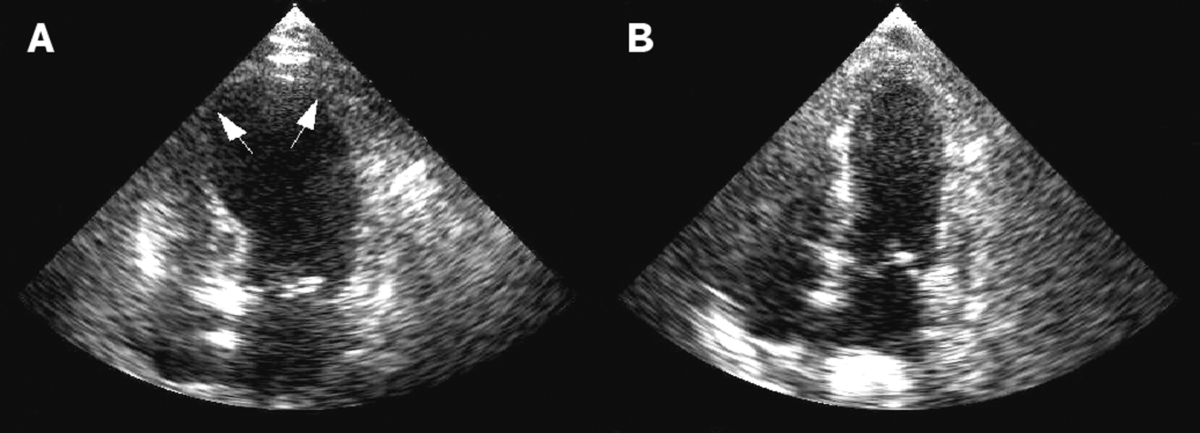
A. Echocardiography showing dilatation (or ballooning) of the left ventricle in the acute phase of takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
B. Resolution of left ventricular function on repeat echocardiogram 6 days later.
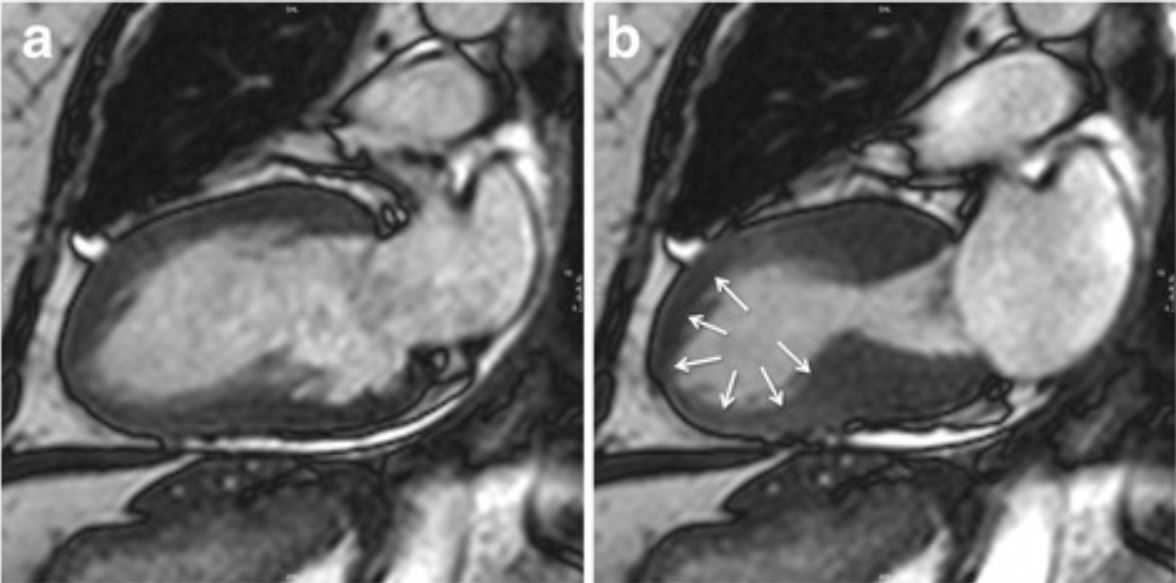
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (cMRI) showing the typical apical ballooning in takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
Image: “Typical apical balloning in takotsubo syndrome” by Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. License: CC BY 4.0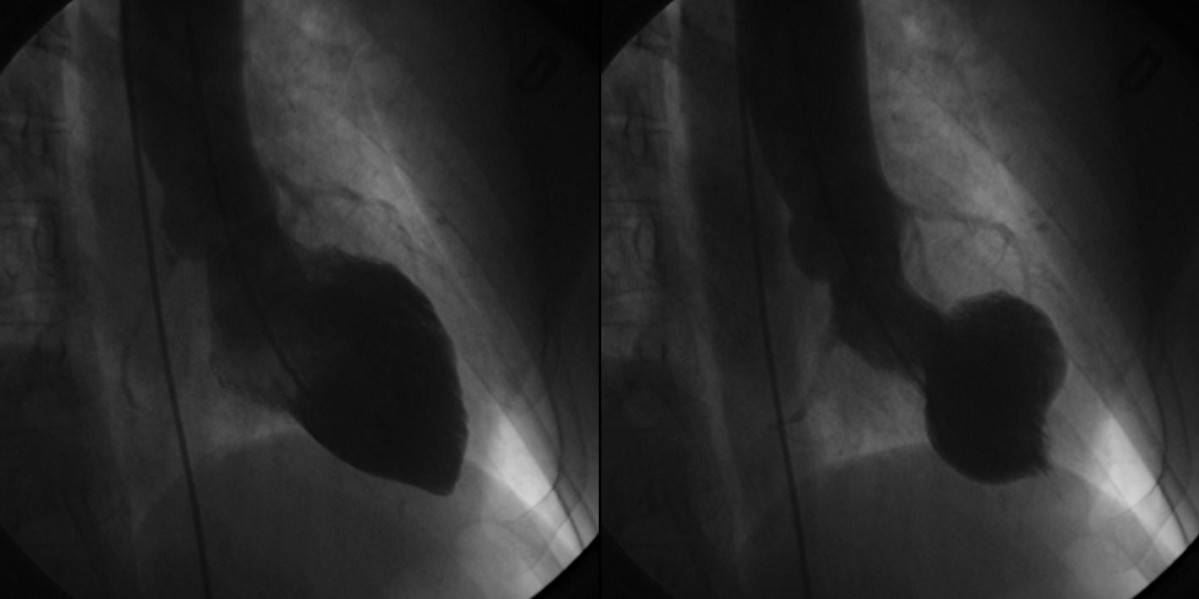
Left ventriculogram during cardiac catheterization showing characteristic findings of takotsubo cardiomyopathy. The left image is during diastole. The image on the right shows apical ballooning and basal hyperkinesis during systole.
Image: “Left ventriculograms” by Lisi M, Zacà V, Maffei S, Casucci F, Maggi M, Lunghetti S, Aitiani P, Carrera A, Castellani D, Favilli R, Pierli C, Mondillo S. License: CC BY 2.0The following 4 criteria are required for diagnosis:
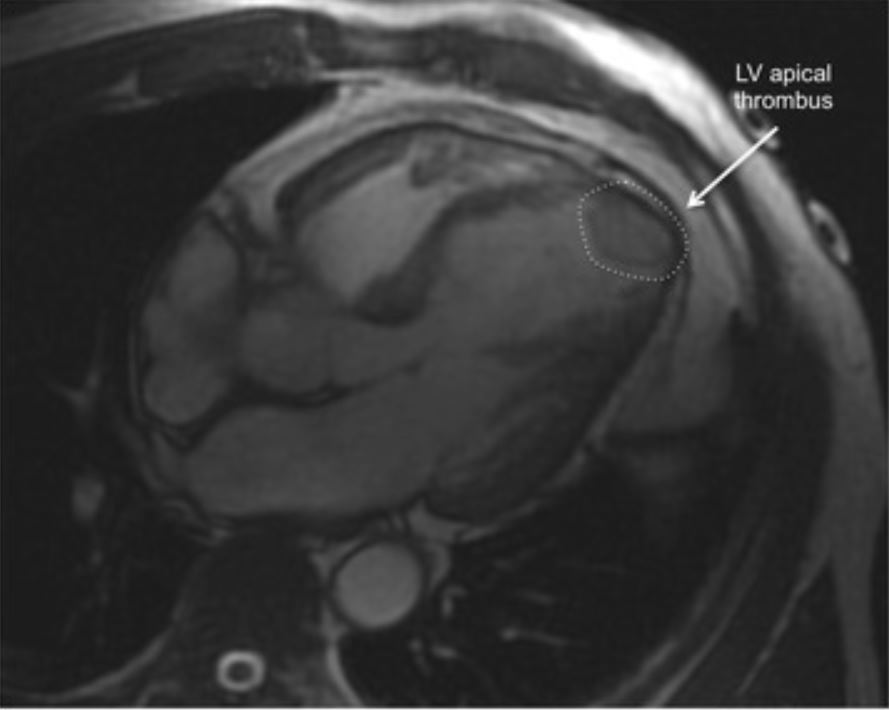
Cardiac MRI image demonstrating an apical thrombus (dashed circle), 1 of the complications of takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
Image: “Apical thrombus” by Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. License: CC BY 4.0