Taenia belong to the Cestoda class of helminths Helminths Commonly known as parasitic worms, this group includes the acanthocephala; nematoda; and platyhelminths. Some authors consider certain species of leeches that can become temporarily parasitic as helminths. Anthelmintic Drugs. Humans are infected with these tapeworms by eating undercooked beef (T. saginata) or pork (T. solium and T. asiatica). Taeniasis is often asymptomatic, but the ingestion of larvae Larvae Wormlike or grublike stage, following the egg in the life cycle of insects, worms, and other metamorphosing animals. Ascaris/Ascariasis can cause abdominal discomfort, nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics, and constipation Constipation Constipation is common and may be due to a variety of causes. Constipation is generally defined as bowel movement frequency < 3 times per week. Patients who are constipated often strain to pass hard stools. The condition is classified as primary (also known as idiopathic or functional constipation) or secondary, and as acute or chronic. Constipation or diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea. Passing proglottids in the stool is the most common sign of taeniasis. A patient who ingests T. solium eggs can develop cysticercosis, which may present with muscular and dermatologic cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change, ocular involvement, or neurologic manifestations (neurocysticercosis). The diagnosis is made by identifying proglottids or eggs in the stool. Characteristic findings on CT or MRI will help diagnose neurocysticercosis. Management generally includes anthelmintic therapy Anthelmintic therapy Agents that kill parasitic worms. They are used therapeutically in the treatment of helminthiasis in man and animal. Toxocariasis.
Last updated: Feb 11, 2025
Taenia is a genus of parasitic cestodes (tapeworms).
Eggs:
Adults:
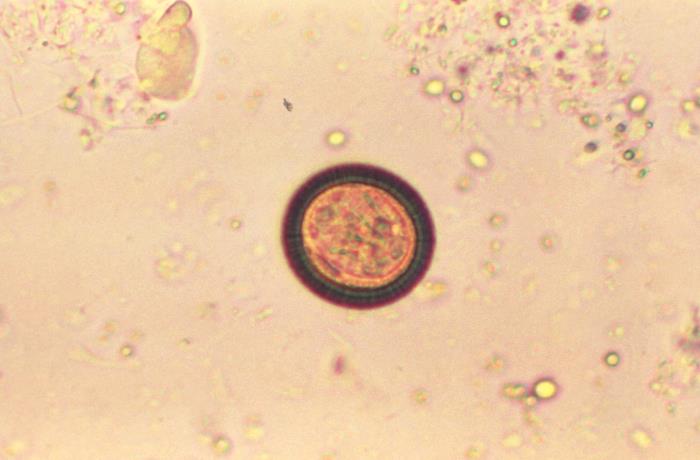
Photomicrograph of a Taenia egg:
These eggs are round and have a thick, striated wall.
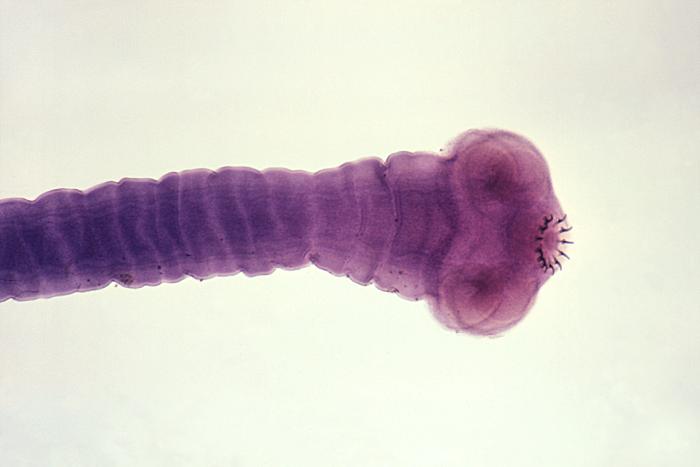
An image of the scolex of an adult Taenia solium tapeworm
Image: “14377” by CDC/Dr. Mae Melvin. License: Public Domain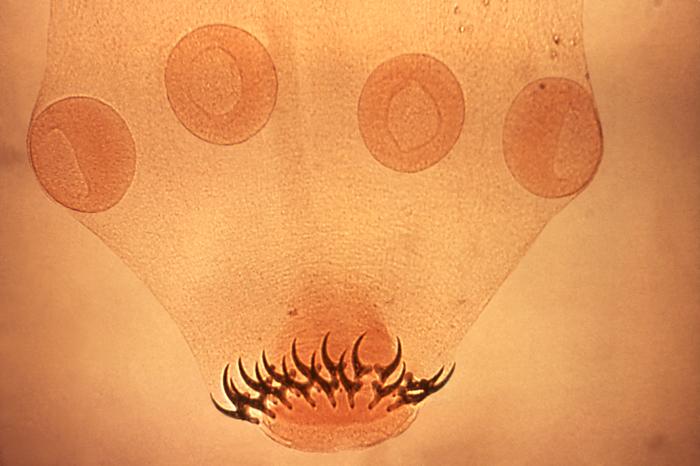
Photomicrograph showing the scolex of a Taenia solium worm:
Note the 4 suckers and 2 rows of hooks.
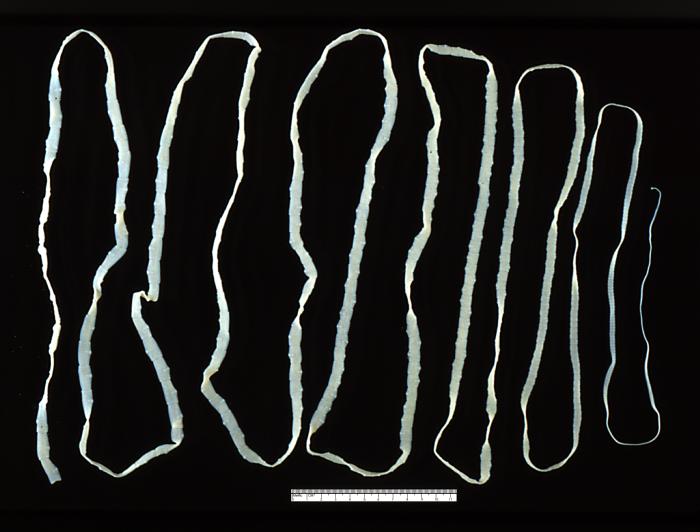
Adult Taenia saginata tapeworm measuring approximately 4 m
Image: “5260” by CDC. License: Public DomainTaenia tapeworms cause the following diseases:
Geographic distribution of species:
Taeniasis:
Cysticercosis:
Taeniasis:
Cysticercosis:
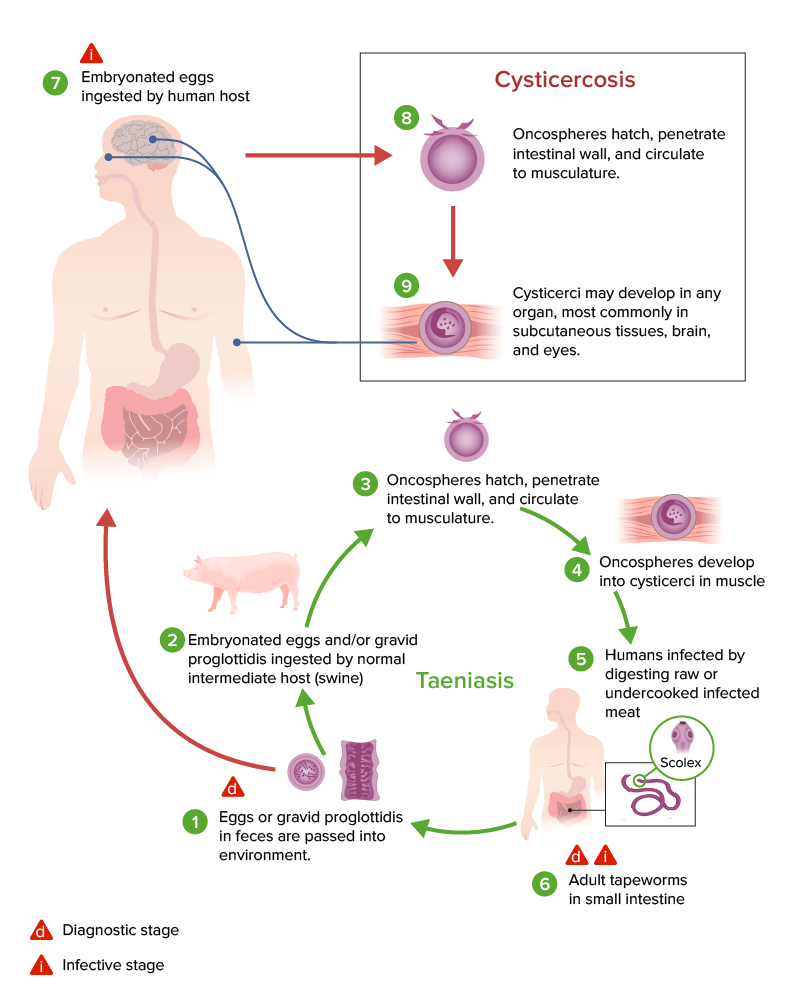
Life cycle of Taenia solium and the development of cysticercosis versus taeniasis.
Most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship (particularly adults) are asymptomatic.
Signs and symptoms depend on the tissues involved.
Muscular and dermatologic cysticercosis:
Ocular cysticercosis:
Neurocysticercosis:
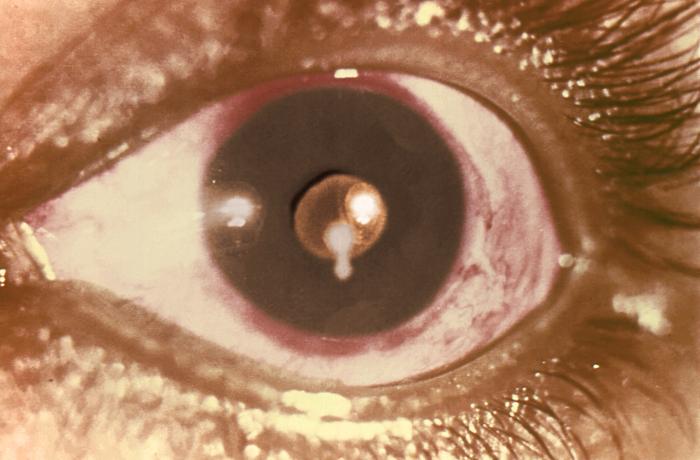
A cysticercus of the Taenia solium pork tapeworm in the pupil of a patient’s eye:
Although rare, cysticerci may float in the eye, causing vision changes.
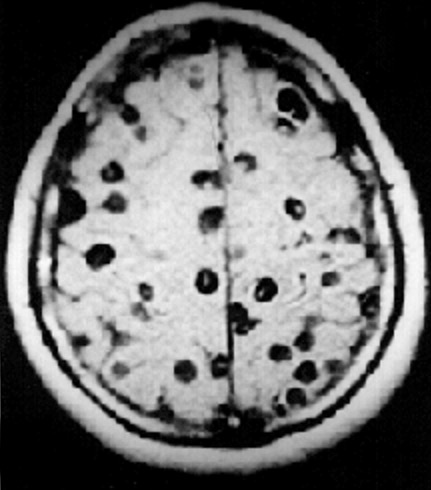
MRI from a patient with neurocysticercosis:
Note the “Swiss cheese” cystic lesions present throughout the brain.
Taeniasis can be treated with anthelmintic therapy Anthelmintic therapy Agents that kill parasitic worms. They are used therapeutically in the treatment of helminthiasis in man and animal. Toxocariasis:
| Organism | Dibothriocephalus latus | Taenia saginata | Echinococcus Echinococcus Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by Echinococcus tapeworms. Infection most often occurs from the ingestion of Echinococcus eggs in food or water contaminated with dog feces. Signs and symptoms are caused by hydatid cyst development in visceral organs and depend on the species. Echinococcus/Echinococcosis granulosus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics |
|
|
|
| Transmission | Eating raw infected fish FISH A type of in situ hybridization in which target sequences are stained with fluorescent dye so their location and size can be determined using fluorescence microscopy. This staining is sufficiently distinct that the hybridization signal can be seen both in metaphase spreads and in interphase nuclei. Chromosome Testing | Eating raw infected beef | Fecal–oral (ingestion of contaminated food or water) |
| Disease | Diphyllobothriasis Diphyllobothriasis Diphyllobothriasis represents an intestinal parasitic infection caused by the cestode Diphyllobothrium. Diphyllobothriasis is acquired by ingestion of late larvae in undercooked or raw fish. The clinical presentation of diphyllobothriasis varies from asymptomatic, nonspecific symptoms to intestinal obstruction, and/or vitamin B12 deficiency. Dibothriocephalus/Diphyllobothriasis | Taeniasis | Cystic echinococcosis Cystic Echinococcosis Echinococcus/Echinococcosis |
| Clinical |
|
|
Depends on location and size of hydatid cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change |
| Diagnosis | Eggs or proglottids in stool | Eggs or proglottids in stool |
|
| Management |
|
|
|
| Prevention |
|
Beef should be cooked thoroughly. |
|
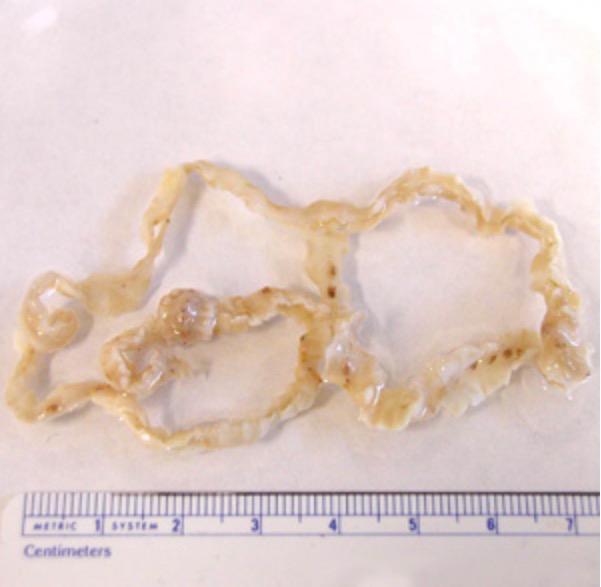
Adult Diphyllobothrium latum tapeworm
Image: “Dibothriocephalus latus with ruler” by CDC. License: CC BY 3.0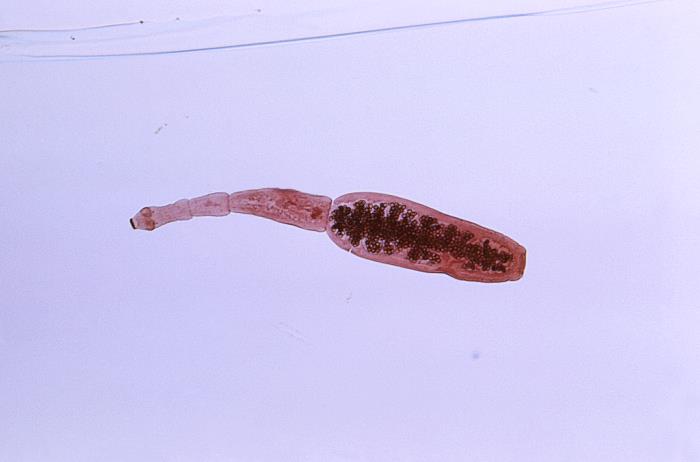
Photomicrograph showing the morphology of the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus:
Note the head on the left and the scolex with hook-rimmed rostellum.