Swyer syndrome is a disorder of sex Sex The totality of characteristics of reproductive structure, functions, phenotype, and genotype, differentiating the male from the female organism. Gender Dysphoria development caused by a defect in the SRY gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics on chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics Y. The syndrome is characterized by complete testicular dysgenesis in an individual who has a 46,XY karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System and is phenotypically female. The presentation of Swyer syndrome is that of a tall female with a normal childhood and development until puberty Puberty Puberty is a complex series of physical, psychosocial, and cognitive transitions usually experienced by adolescents (11-19 years of age). Puberty is marked by a growth in stature and the development of secondary sexual characteristics, achievement of fertility, and changes in most body systems. Puberty, which is characterized by primary amenorrhea Amenorrhea Absence of menstruation. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System and no development of secondary sexual characteristics Secondary Sexual Characteristics Precocious Puberty. Management includes hormone replacement therapy Hormone Replacement Therapy Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause and in combination to suppress ovulation. Risks and side effects include uterine bleeding, predisposition to cancer, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine headaches, hypertension, bloating, and mood changes. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins and gonadectomy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System of an individual with Swyer syndrome is 46 XY.
Swyer syndrome can be caused by various genetic abnormalities:
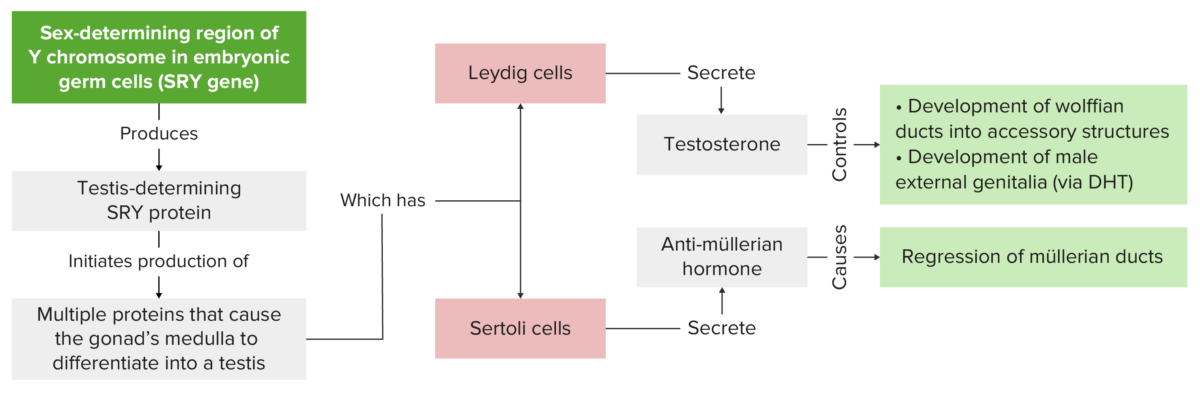
Image displaying the importance of the SRY gene in normal male genital development
DHT: dihydrotestosterone
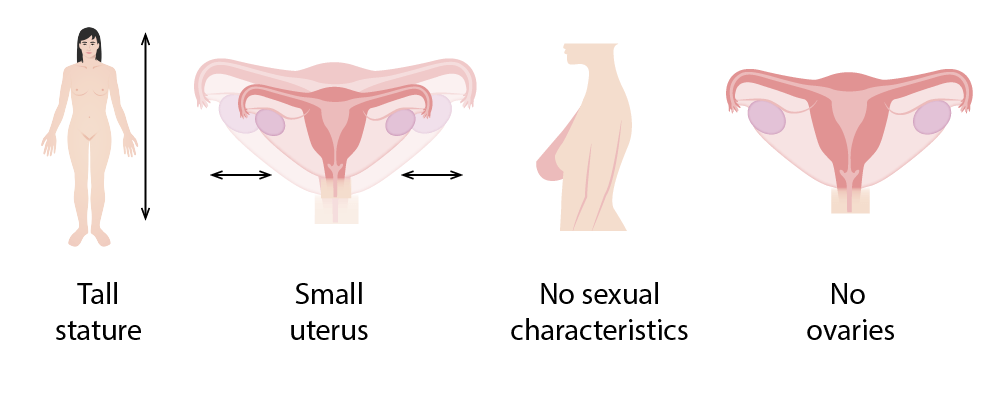
Clinical manifestations of Swyer syndrome:
Tall stature, small uterus, no secondary sexual characteristics, and absent ovaries (will instead have streak gonads)
The following conditions are differential diagnoses for Swyer syndrome: