Supracondylar fractures are the most common elbow fractures in the pediatric population. The most common mechanism of injury involves a fall on an outstretched hand Hand The hand constitutes the distal part of the upper limb and provides the fine, precise movements needed in activities of daily living. It consists of 5 metacarpal bones and 14 phalanges, as well as numerous muscles innervated by the median and ulnar nerves. Hand: Anatomy, resulting in a fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures of the distal humerus Humerus Bone in humans and primates extending from the shoulder joint to the elbow joint. Arm: Anatomy. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship frequently present with pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, visible deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs, and limited range of motion Range of motion The distance and direction to which a bone joint can be extended. Range of motion is a function of the condition of the joints, muscles, and connective tissues involved. Joint flexibility can be improved through appropriate muscle strength exercises. Examination of the Upper Limbs of the injured elbow. This fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures often requires immediate orthopedic consultation secondary to the displacement Displacement The process by which an emotional or behavioral response that is appropriate for one situation appears in another situation for which it is inappropriate. Defense Mechanisms of the fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures and the frequency of concomitant neurovascular injury.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A supracondylar fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures affects the distal humerus Humerus Bone in humans and primates extending from the shoulder joint to the elbow joint. Arm: Anatomy, just above the elbow, and is seen frequently in the pediatric population.
The distal humerus Humerus Bone in humans and primates extending from the shoulder joint to the elbow joint. Arm: Anatomy‘s supracondylar area in children is made of thin, structurally weak developing bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types, making it a common fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures site.
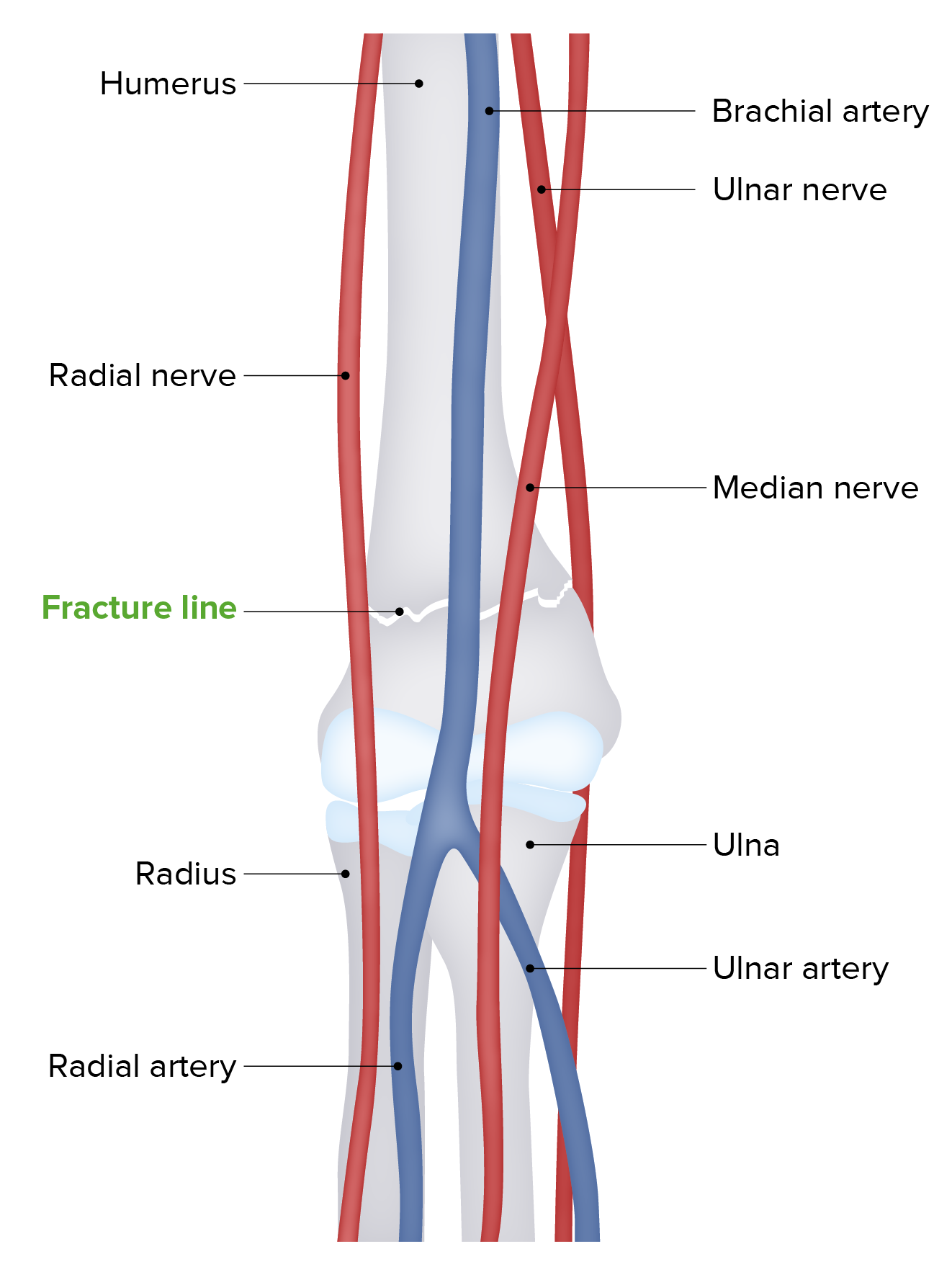
Anatomy of the elbow:
The distal humerus’s supracondylar area in children is made of thin, structurally weak developing bone, making it a common fracture site. Approximately 5%–10% of supracondylar fractures are associated with damage to neurovascular structures. Particularly vulnerable are the brachial artery and the median, radial, and ulnar nerves.
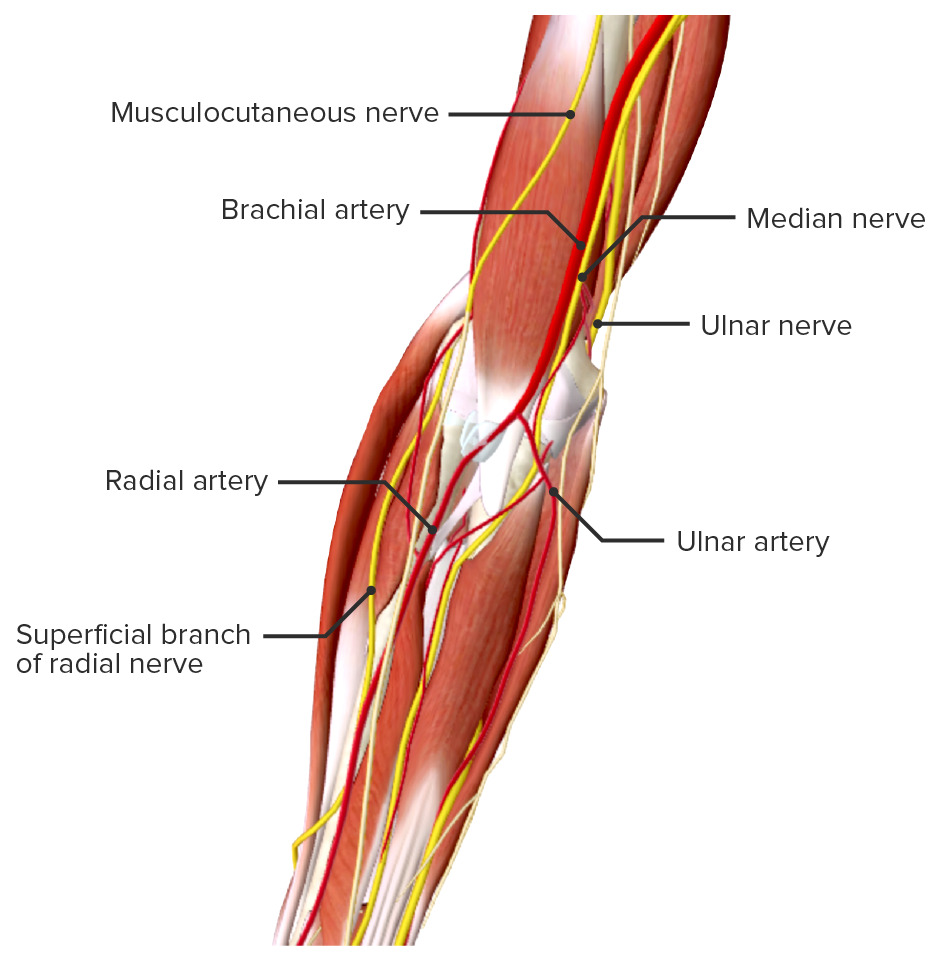
Neurovascular structures around the elbow
Image by BioDigital, edited by LecturioGartland classification is based on the degree of displacement Displacement The process by which an emotional or behavioral response that is appropriate for one situation appears in another situation for which it is inappropriate. Defense Mechanisms:
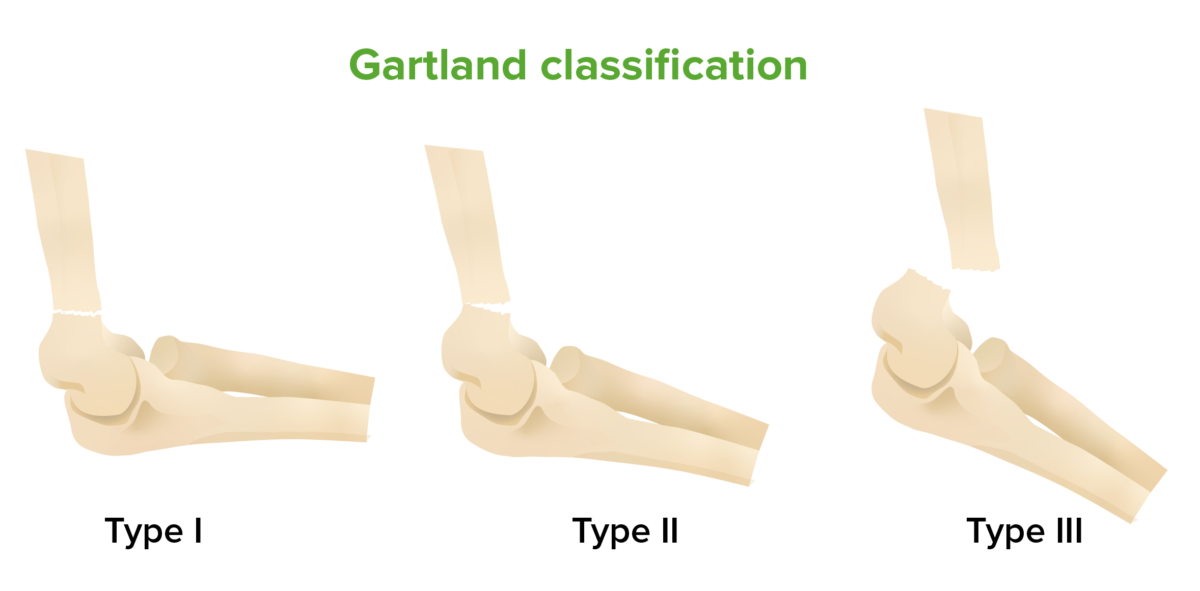
Gartland classification of supracondylar fractures:
The Gartland classification system of supracondylar elbow fractures is based on the degree of displacement of the fractures. Gartland type I is a minimally displaced fracture. Gartland type II features more displacement, but the posterior cortex remains intact. Gartland type III is a completely displaced fracture.
Supracondylar fractures are the most common type of elbow fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures found in children. These fractures often require emergent treatment secondary to associated neurovascular injuries.
Repetitively evaluate motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology and sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology nerve function and assess for vascular insufficiency Vascular insufficiency Anal Fissure.
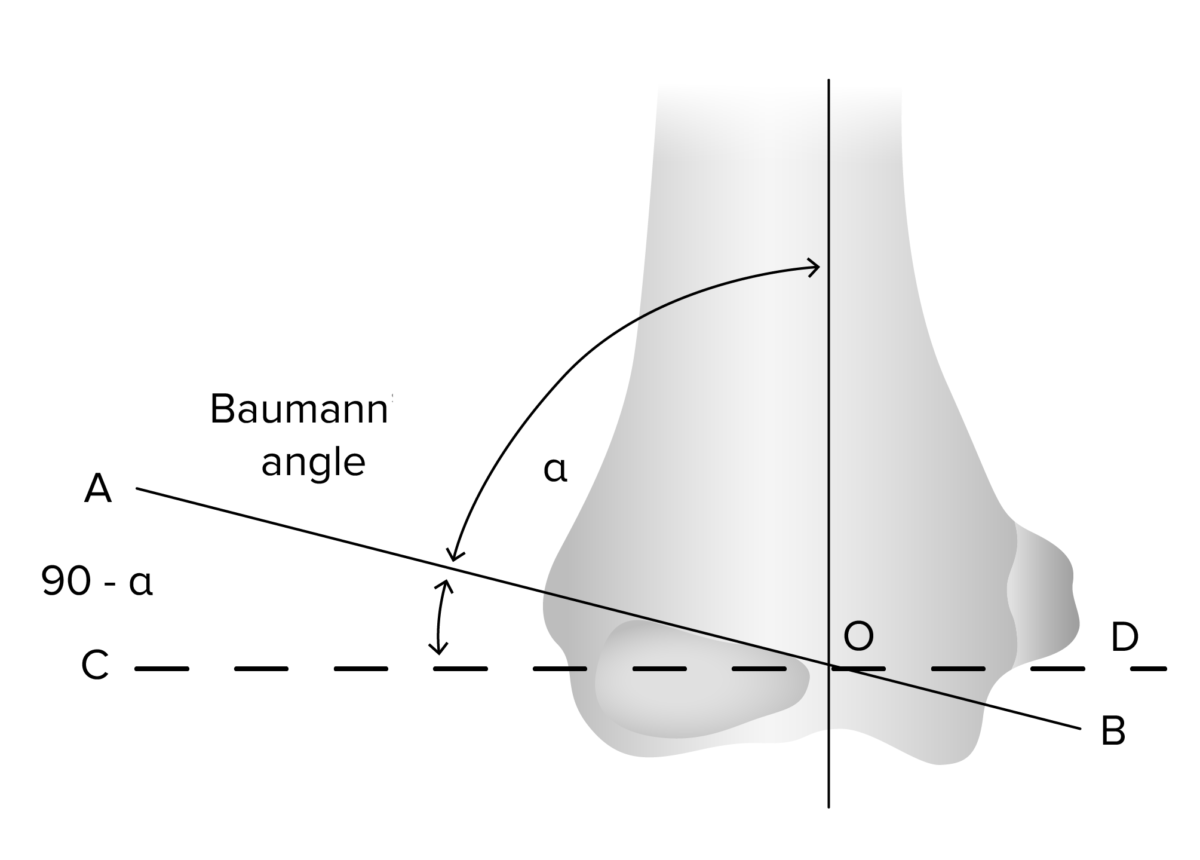
The Baumann angle (measured on AP view) assesses the adequacy of the reduction in the coronal plane and may be compared to the contralateral elbow. The Baumann angle is the angle between the line perpendicular to the long axis of the humerus and the line along the lateral condyle physis.
Image by Lecturio.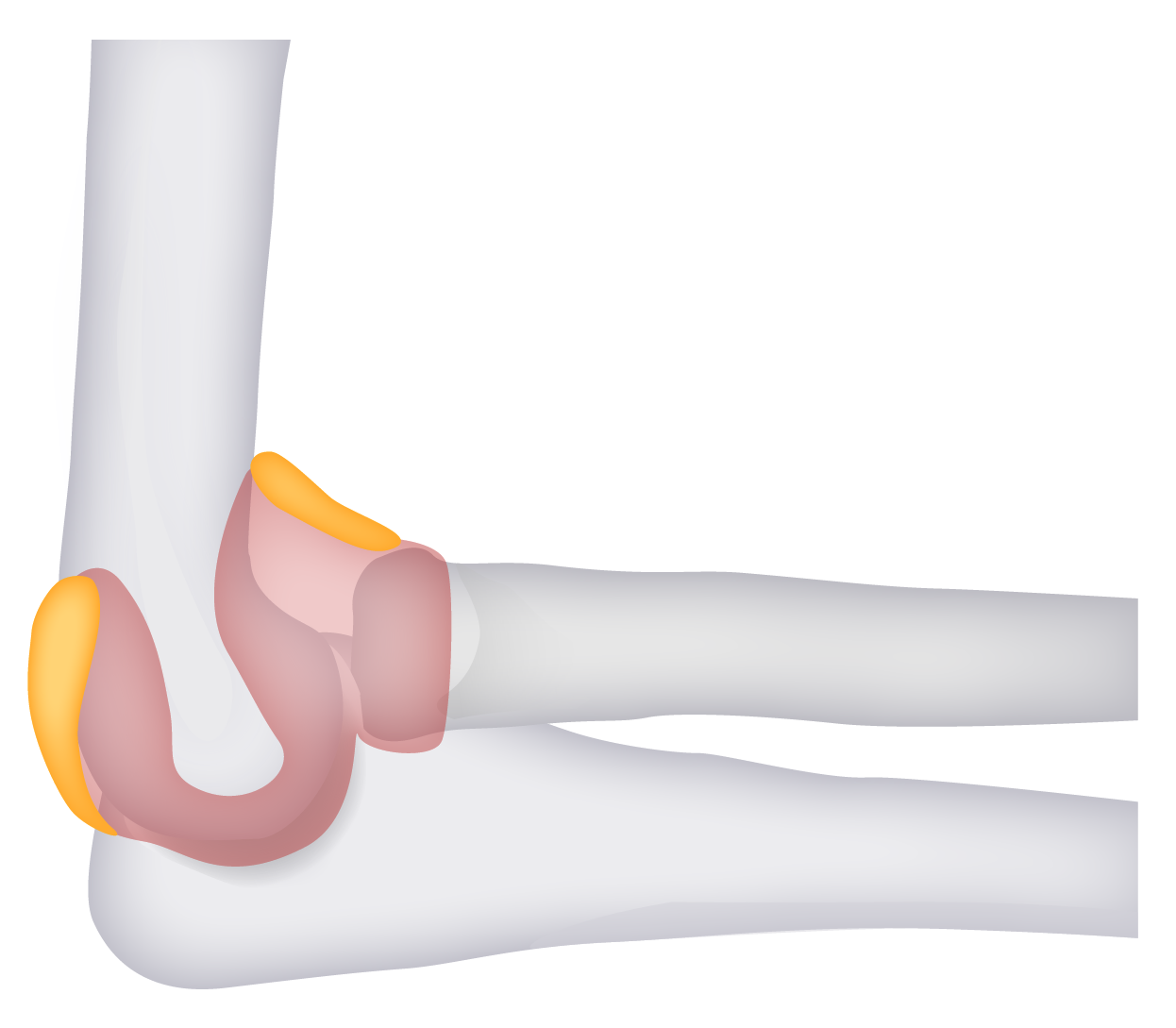
“Fat pad signs”:
Posterior and anterior fat pads (identified in yellow) can be seen in abnormal radiographs. Lucency in these areas is indicative of effusion and suggestive (but not specific) of fractures.
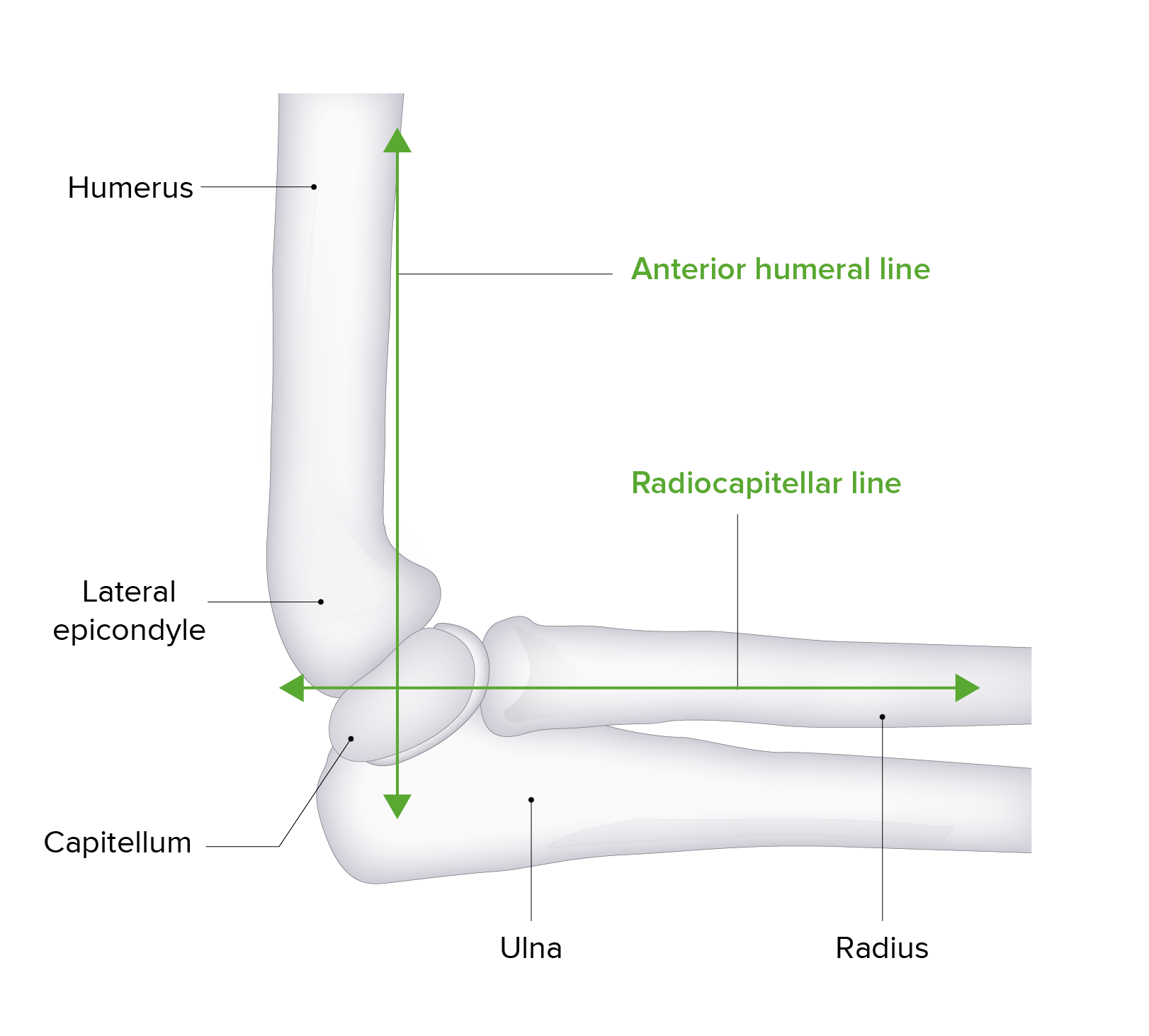
Anterior humeral line:
The anterior humeral line is an imaginary vector used in radiology to evaluate elbow alignment and for the displacement of fractures. The line is drawn down the anterior surface of the humerus. In normal anatomy, this line should intersect the middle 3rd of the capitellum. Anterior or posterior movement of this intersection point is suggestive of a displaced fracture.
Treatment of supracondylar fractures is based on the amount of displacement Displacement The process by which an emotional or behavioral response that is appropriate for one situation appears in another situation for which it is inappropriate. Defense Mechanisms of the fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures.
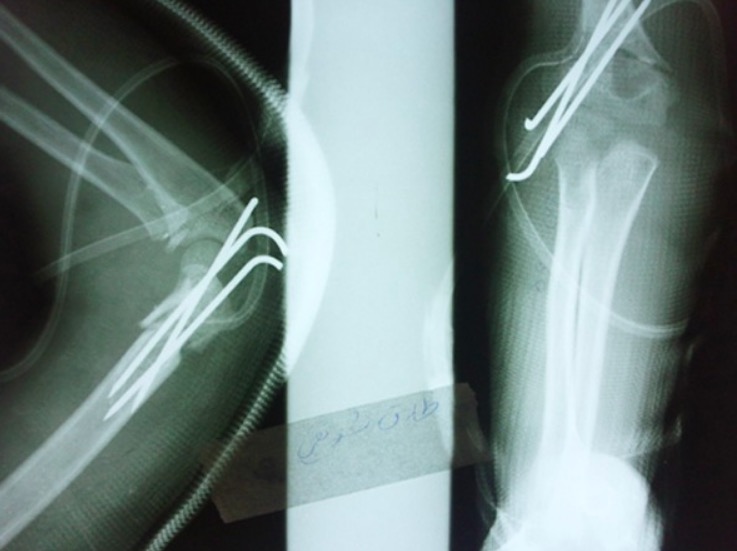
Postoperative elbow radiography
Image: “Fig.1B” by Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences. License: CC BY 3.0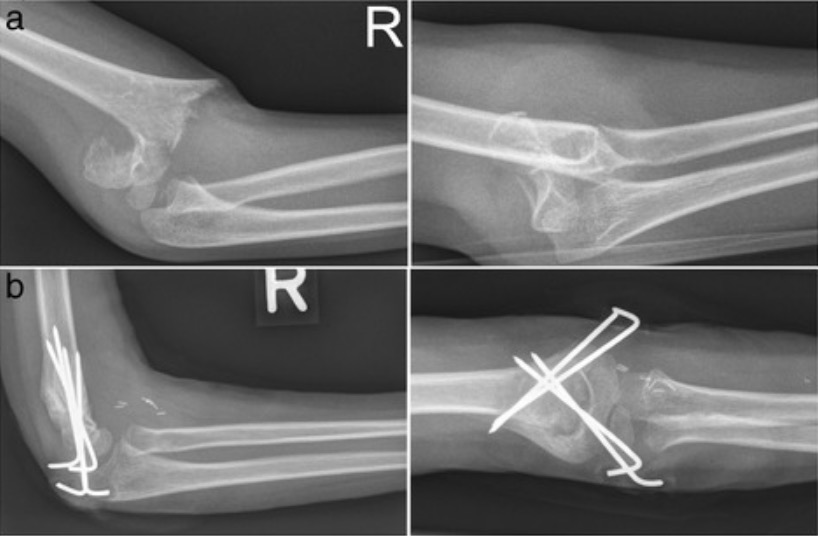
Posterolaterally displaced supracondylar fracture humerus classified as Gartland type III, pre- and postoperative
Image: “Radiographs in two planes” by David Latz et al. License: CC BY 4.0Additional important pediatric skeletal injuries: